Defining the Self: The Orientation Association Area
... inhibitory neurons will look the same on a PET scan as increased activity in excitatory neurons, but the cognitive results could be very different. The attention association area is also divided into various parts. And while we will not discuss the specific function of these various parts, it is imp ...
... inhibitory neurons will look the same on a PET scan as increased activity in excitatory neurons, but the cognitive results could be very different. The attention association area is also divided into various parts. And while we will not discuss the specific function of these various parts, it is imp ...
CH 8-9 BS and CH 10 MT
... of fluid between layers Pia Mater – third layer, located closest to brain and spinal cord, rich in supply of blood vessels Subarachnoid space: below arachnoid membrane, above pia mater – contains cerebrospinal fluid Epidural space: above the duramater – within surrounding bone walls – cushions ...
... of fluid between layers Pia Mater – third layer, located closest to brain and spinal cord, rich in supply of blood vessels Subarachnoid space: below arachnoid membrane, above pia mater – contains cerebrospinal fluid Epidural space: above the duramater – within surrounding bone walls – cushions ...
The Nervous System
... The autonomic nervous system is further subdivided into two parts: –sympathetic nervous system –parasympathetic nervous system which have opposite effects on the same organ system. (Think gas and brake when driving a car.) (Sympathetic nervous system speeds up heart rate; parasympathetic slows it d ...
... The autonomic nervous system is further subdivided into two parts: –sympathetic nervous system –parasympathetic nervous system which have opposite effects on the same organ system. (Think gas and brake when driving a car.) (Sympathetic nervous system speeds up heart rate; parasympathetic slows it d ...
Design Overview - Computer Science & Engineering
... Fun Fact - Longest axons in human body run from base of the spinal cord to the big toe of each foot! ...
... Fun Fact - Longest axons in human body run from base of the spinal cord to the big toe of each foot! ...
You*ve had a concussion! How to return a player to the
... Neurons are basically like on/off switches of a light switch. Neurons are either resting or shooting an electrical impulse down a wire called an axon. Each of the neurons spit out chemicals that trigger other neurons. ...
... Neurons are basically like on/off switches of a light switch. Neurons are either resting or shooting an electrical impulse down a wire called an axon. Each of the neurons spit out chemicals that trigger other neurons. ...
The Nervous System
... • Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease, is caused by motor neurons in the brain and spinal cord dying. This eventually leads to paralysis and patients cannot breath properly. ...
... • Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease, is caused by motor neurons in the brain and spinal cord dying. This eventually leads to paralysis and patients cannot breath properly. ...
The effect of visual experience on the development of the mirror
... is truly engaged by auditory perception. To address this question we investigated brain response to visual and/or auditory perception of different stimuli in sighted and congenitally blind individuals. Using an fMRI (GE Signa 1.5 Tesla scanner) sparse sampling block design we examined neural activit ...
... is truly engaged by auditory perception. To address this question we investigated brain response to visual and/or auditory perception of different stimuli in sighted and congenitally blind individuals. Using an fMRI (GE Signa 1.5 Tesla scanner) sparse sampling block design we examined neural activit ...
nervous system power point
... • Helps regulate body temp, appetite and water balance • Connected to pituitary gland • Thalamus - Relays impulses to cerebrum from sense organs, Relates sensation with emotions ...
... • Helps regulate body temp, appetite and water balance • Connected to pituitary gland • Thalamus - Relays impulses to cerebrum from sense organs, Relates sensation with emotions ...
8 The Most Complex Object in the Known Universe
... A number of different mechanisms have been put forward to describe the manner of neuron interactions at the quantum level – the bottom line being that such effects would work mainly through the existence of chemical exchange processes within the brain involving spread out wave functions; because wav ...
... A number of different mechanisms have been put forward to describe the manner of neuron interactions at the quantum level – the bottom line being that such effects would work mainly through the existence of chemical exchange processes within the brain involving spread out wave functions; because wav ...
The Nervous System and Neurons
... brain, with the nerve fibres forming the white matter Brain and spinal cord are protected by bone and are covered by three membranes called meninges Meningitis is the inflammation of the meninges ...
... brain, with the nerve fibres forming the white matter Brain and spinal cord are protected by bone and are covered by three membranes called meninges Meningitis is the inflammation of the meninges ...
The Nervous System
... • The peripheral nervous system lies outside the central nervous system, and is composed of nerves and ganglia. • Sensory fibers carry information to the CNS, and motor fibers carry information away from the CNS. • Ganglia are swellings associated with nerves that contain collections of cell bodies. ...
... • The peripheral nervous system lies outside the central nervous system, and is composed of nerves and ganglia. • Sensory fibers carry information to the CNS, and motor fibers carry information away from the CNS. • Ganglia are swellings associated with nerves that contain collections of cell bodies. ...
The Nervous System
... • Each neuron consists of a nucleus situated in the cell body, where outgrowths called processes originate from. The main one of these processes is the axon, which is responsible for carrying outgoing messages from the cell. This axon can originate from the CNS and extend all the way to the body's e ...
... • Each neuron consists of a nucleus situated in the cell body, where outgrowths called processes originate from. The main one of these processes is the axon, which is responsible for carrying outgoing messages from the cell. This axon can originate from the CNS and extend all the way to the body's e ...
The Brain - Midlands State University
... Contralateral control Size of motor area directly related to number and complexity of skeletal muscle movements Contains Sensory Areas Somesthetic, Visual, Auditory, Olfactory ...
... Contralateral control Size of motor area directly related to number and complexity of skeletal muscle movements Contains Sensory Areas Somesthetic, Visual, Auditory, Olfactory ...
The Nervous System
... In the central nervous system the cerebral ganglion is connected to the ventral nerve cord and runs the entire length of the body. Each segmental ganglion branches off of the ventral nerve cord, therefore connecting all of the segments to the brain. ...
... In the central nervous system the cerebral ganglion is connected to the ventral nerve cord and runs the entire length of the body. Each segmental ganglion branches off of the ventral nerve cord, therefore connecting all of the segments to the brain. ...
Quiz
... 15. The giant squid axon is specialized for which of the following? a. Integration of sensory messages regarding the environment b. Planning of feeding-‐related movements c. Rapid contraction of the squid mantle ...
... 15. The giant squid axon is specialized for which of the following? a. Integration of sensory messages regarding the environment b. Planning of feeding-‐related movements c. Rapid contraction of the squid mantle ...
大腦神經解剖與建置
... Through the hypthalamus 下視丘 control of the pituitary gland 腦下垂 體, it regulates hunger and thirst, plays a role in sexual and mating behavior, and controls the fight-or-flight response. It is also the source of posterior pituitary hormones and of releasing hormones that act on the anterior pituitary. ...
... Through the hypthalamus 下視丘 control of the pituitary gland 腦下垂 體, it regulates hunger and thirst, plays a role in sexual and mating behavior, and controls the fight-or-flight response. It is also the source of posterior pituitary hormones and of releasing hormones that act on the anterior pituitary. ...
Document
... Parieto-premotor Pathway Major source areas V6A – located at the boundary of the occipital lobe( known to be devoted to visual information) and the parietal lobe. V6A with both visual and motor cortices. The visual input to V6A derives from area V6, a higher order visual area of the dorsomedia ...
... Parieto-premotor Pathway Major source areas V6A – located at the boundary of the occipital lobe( known to be devoted to visual information) and the parietal lobe. V6A with both visual and motor cortices. The visual input to V6A derives from area V6, a higher order visual area of the dorsomedia ...
Module 10 Guided Notes The Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... 40 Billion – each connected with 10,000 other neurons = 400 Trillion Synapses ...
... 40 Billion – each connected with 10,000 other neurons = 400 Trillion Synapses ...
Chapter 11 The Nervous System
... part of the brain. – The outer layer of each hemisphere is the cortex. – The cerebral cortex consists of many discrete functional regions including motor, sensory, and association areas. – The primary motor cortex controls voluntary movement. – The primary sensory cortex receives sensory information ...
... part of the brain. – The outer layer of each hemisphere is the cortex. – The cerebral cortex consists of many discrete functional regions including motor, sensory, and association areas. – The primary motor cortex controls voluntary movement. – The primary sensory cortex receives sensory information ...
Neuroanatomy Tutorial
... - Ascending : sensory (dorsal in spinal cord) - Descending : motor (ventral in spinal cord) right side of the brain controls left side of body, so fibres must cross (almost all do), at different levels though ...
... - Ascending : sensory (dorsal in spinal cord) - Descending : motor (ventral in spinal cord) right side of the brain controls left side of body, so fibres must cross (almost all do), at different levels though ...
Intelligence Science for Creating a Brain
... Research scientists coming from the above three disciplines work together to explore new concepts, theories, and methodologies. In order to create the brain, more research has to be done on intelligence science, especially the neocortical column, mind model and others. The neocortical column is a gr ...
... Research scientists coming from the above three disciplines work together to explore new concepts, theories, and methodologies. In order to create the brain, more research has to be done on intelligence science, especially the neocortical column, mind model and others. The neocortical column is a gr ...
Everson Nervous system I. Functional/ Anatomical Divisions A
... 3. integrates sensory info for cerebrum interpretation v. Cerebrum (Cerebral hemispheres) 1. Right and left cerebral hemispheres a. Separated by longitudinal fissure b. Connected by Corpus callosum c. Sulci and gyri (grooves and bumps) d. Each contain a lateral ventricle (CSF) 2. Three main points a ...
... 3. integrates sensory info for cerebrum interpretation v. Cerebrum (Cerebral hemispheres) 1. Right and left cerebral hemispheres a. Separated by longitudinal fissure b. Connected by Corpus callosum c. Sulci and gyri (grooves and bumps) d. Each contain a lateral ventricle (CSF) 2. Three main points a ...
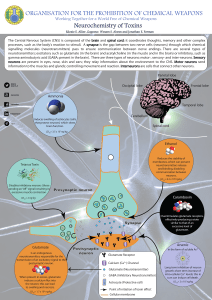
Working Together for a World Free of Chemical Weapons
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) is composed of the brain and spinal cord; it coordinates thoughts, memory and other complex processes, such as the body’s reaction to stimuli. A synapse is the gap between two nerve cells (neurons) through which chemical signalling molecules (neurotransmitters) pass ...
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) is composed of the brain and spinal cord; it coordinates thoughts, memory and other complex processes, such as the body’s reaction to stimuli. A synapse is the gap between two nerve cells (neurons) through which chemical signalling molecules (neurotransmitters) pass ...
Human brain
The human brain is the main organ of the human nervous system. It is located in the head, protected by the skull. It has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but with a more developed cerebral cortex. Large animals such as whales and elephants have larger brains in absolute terms, but when measured using a measure of relative brain size, which compensates for body size, the quotient for the human brain is almost twice as large as that of a bottlenose dolphin, and three times as large as that of a chimpanzee. Much of the size of the human brain comes from the cerebral cortex, especially the frontal lobes, which are associated with executive functions such as self-control, planning, reasoning, and abstract thought. The area of the cerebral cortex devoted to vision, the visual cortex, is also greatly enlarged in humans compared to other animals.The human cerebral cortex is a thick layer of neural tissue that covers most of the brain. This layer is folded in a way that increases the amount of surface that can fit into the volume available. The pattern of folds is similar across individuals, although there are many small variations. The cortex is divided into four lobes – the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and occipital lobe. (Some classification systems also include a limbic lobe and treat the insular cortex as a lobe.) Within each lobe are numerous cortical areas, each associated with a particular function, including vision, motor control, and language. The left and right sides of the cortex are broadly similar in shape, and most cortical areas are replicated on both sides. Some areas, though, show strong lateralization, particularly areas that are involved in language. In most people, the left hemisphere is dominant for language, with the right hemisphere playing only a minor role. There are other functions, such as visual-spatial ability, for which the right hemisphere is usually dominant.Despite being protected by the thick bones of the skull, suspended in cerebrospinal fluid, and isolated from the bloodstream by the blood–brain barrier, the human brain is susceptible to damage and disease. The most common forms of physical damage are closed head injuries such as a blow to the head, a stroke, or poisoning by a variety of chemicals which can act as neurotoxins, such as ethanol alcohol. Infection of the brain, though serious, is rare because of the biological barriers which protect it. The human brain is also susceptible to degenerative disorders, such as Parkinson's disease, and Alzheimer's disease, (mostly as the result of aging) and multiple sclerosis. A number of psychiatric conditions, such as schizophrenia and clinical depression, are thought to be associated with brain dysfunctions, although the nature of these is not well understood. The brain can also be the site of brain tumors and these can be benign or malignant.There are some techniques for studying the brain that are used in other animals that are just not suitable for use in humans and vice versa. It is easier to obtain individual brain cells taken from other animals, for study. It is also possible to use invasive techniques in other animals such as inserting electrodes into the brain or disabling certains parts of the brain in order to examine the effects on behaviour – techniques that are not possible to be used in humans. However, only humans can respond to complex verbal instructions or be of use in the study of important brain functions such as language and other complex cognitive tasks, but studies from humans and from other animals, can be of mutual help. Medical imaging technologies such as functional neuroimaging and EEG recordings are important techniques in studying the brain. The complete functional understanding of the human brain is an ongoing challenge for neuroscience.