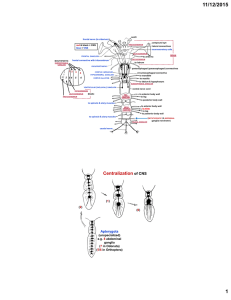
Features of Neuronal Synchrony in Mouse Visual Cortex
... involving a combination of bottom-up and top-down influences (reviewed in Engel et al. 2001). It has been proposed to provide a general mechanism by which activity patterns in spatially separate regions of the brain are temporally coordinated (Gray et al. 1989; Singer and Gray 1995). Dynamic cell as ...
... involving a combination of bottom-up and top-down influences (reviewed in Engel et al. 2001). It has been proposed to provide a general mechanism by which activity patterns in spatially separate regions of the brain are temporally coordinated (Gray et al. 1989; Singer and Gray 1995). Dynamic cell as ...
Brain Function
... Neural Imaging –SPECT/PET SPECT/PET (single photon/positron emission computed tomography) • When radiolabeled compounds are injected in tracer amounts, their photon emissions can be detected much like x-rays in CT. • The images made represent the accumulation of the labeled compound. The compound m ...
... Neural Imaging –SPECT/PET SPECT/PET (single photon/positron emission computed tomography) • When radiolabeled compounds are injected in tracer amounts, their photon emissions can be detected much like x-rays in CT. • The images made represent the accumulation of the labeled compound. The compound m ...
The organisation of the stress response, and its relevance to
... amygdala [28], as well as to the hippocampus, orbitofrontal cortex, cingulate [29] and via the reticular activating system to the sensory cortex [30,31]. The sensory cortex then directs information directly to the amygdala, or via the hippocampus and then to the amygdala. [32]. The hippocampus does ...
... amygdala [28], as well as to the hippocampus, orbitofrontal cortex, cingulate [29] and via the reticular activating system to the sensory cortex [30,31]. The sensory cortex then directs information directly to the amygdala, or via the hippocampus and then to the amygdala. [32]. The hippocampus does ...
Rapid Critical Period Induction by Tonic Inhibition in Visual Cortex
... release with stimulation and do not respond to brief MD (Hensch et al., 1998). Importantly, functional enhancement of GABAergic transmission fully restores OD plasticity to GAD65 KO mice. Rescue is achieved by diazepam, one of the best-characterized benzodiazepine agonists, which selectively bind su ...
... release with stimulation and do not respond to brief MD (Hensch et al., 1998). Importantly, functional enhancement of GABAergic transmission fully restores OD plasticity to GAD65 KO mice. Rescue is achieved by diazepam, one of the best-characterized benzodiazepine agonists, which selectively bind su ...
06-pons + midbrain
... 2-Substantia nigra :a thick lamina of grey matter formed of deeply pigmented nerve cells lying behind crus cerebri. It is an Extrapyramidal motor centre. 3-Tegmentum : the post. part of cerebral peduncle. It contains ascending tract, certain nuclei, decussations & reticular formation of midbrain. ...
... 2-Substantia nigra :a thick lamina of grey matter formed of deeply pigmented nerve cells lying behind crus cerebri. It is an Extrapyramidal motor centre. 3-Tegmentum : the post. part of cerebral peduncle. It contains ascending tract, certain nuclei, decussations & reticular formation of midbrain. ...
Divergent Projections from the Anterior Inferotemporal Area TE to
... of objects. Monkeys with bilateral TE lesions show severe and specific deficits in learning tasks that require these functions (for review, see Gross, 1973; Dean, 1976). Cells in TE respond selectively to particular features of complex objects (for review, see Tanaka, 1996), and cells with similar s ...
... of objects. Monkeys with bilateral TE lesions show severe and specific deficits in learning tasks that require these functions (for review, see Gross, 1973; Dean, 1976). Cells in TE respond selectively to particular features of complex objects (for review, see Tanaka, 1996), and cells with similar s ...
The Adenosine Story Goes Ionic: CaV2.1
... of neurotransmitter will be altered, notably that of adenosine itself. Moreover, loss-of-function of CaV2.1 channels causes major motor disorders19 and compensatory upregulation of other voltage-gated Ca2+ channels.20 Therefore, assessing sleep-wake behavior in animals with dysfunctional channels is ...
... of neurotransmitter will be altered, notably that of adenosine itself. Moreover, loss-of-function of CaV2.1 channels causes major motor disorders19 and compensatory upregulation of other voltage-gated Ca2+ channels.20 Therefore, assessing sleep-wake behavior in animals with dysfunctional channels is ...
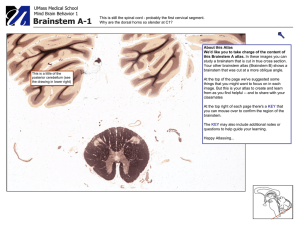
Brainstem A Atlas: Clinical Neuroanatomy Atlas
... What brainstem region? The red arrow points to a lonely white matter structure. Identify it, and its major functions. Several nuclei are circled in green. What function do they serve? Where is the spinothalamic tract located at this level? What's circled in black? You can see it in several different ...
... What brainstem region? The red arrow points to a lonely white matter structure. Identify it, and its major functions. Several nuclei are circled in green. What function do they serve? Where is the spinothalamic tract located at this level? What's circled in black? You can see it in several different ...
Temporal Profiles of Axon Terminals, Synapses and Spines in the
... penumbra of the cerebral cortex is obscure, we studied the temporal profile of these structures up to 12 weeks after the ischemic insult, using a gerbil model. Methods—Stroke-positive animals were selected according to their stroke index score during the first 10-minute left carotid occlusion done t ...
... penumbra of the cerebral cortex is obscure, we studied the temporal profile of these structures up to 12 weeks after the ischemic insult, using a gerbil model. Methods—Stroke-positive animals were selected according to their stroke index score during the first 10-minute left carotid occlusion done t ...
PowerPoint
... spinal cord with the brain and links parts of the brain with one another by way of tracts (Figures 14.1, 14.5). – relays nerve impulses related to voluntary skeletal movements from the cerebral cortex to the cerebellum. – contains the pneumotaxic and apneustic areas, which help control respiration a ...
... spinal cord with the brain and links parts of the brain with one another by way of tracts (Figures 14.1, 14.5). – relays nerve impulses related to voluntary skeletal movements from the cerebral cortex to the cerebellum. – contains the pneumotaxic and apneustic areas, which help control respiration a ...
Sensing Limb Movements in the Motor Cortex: How Humans Sense
... excites the muscle spindle afferents of the vibrated muscles and elicits an illusory limb movement. If we measure the brain activity while totally relaxed subjects experience illusory limb movements, we may detect brain areas that receive and process the kinesthetic afferent inputs. By taking advant ...
... excites the muscle spindle afferents of the vibrated muscles and elicits an illusory limb movement. If we measure the brain activity while totally relaxed subjects experience illusory limb movements, we may detect brain areas that receive and process the kinesthetic afferent inputs. By taking advant ...
Integrated model of visual processing
... 2 1 / 2 D sketch that encodes the position and orientation in depth of small surface elements in 3D and the final stage is the 3D representation that corresponds to the representation of objects in three dimensions. Thus, it is a model based on a cascade of filters, that starts from a local analysis ...
... 2 1 / 2 D sketch that encodes the position and orientation in depth of small surface elements in 3D and the final stage is the 3D representation that corresponds to the representation of objects in three dimensions. Thus, it is a model based on a cascade of filters, that starts from a local analysis ...
Role of the basal ganglia in conditional associative learning
... The arbitrary mapping of sensory information onto action forms an important element of the intelligent behavior of primates (also called conditional associative learning). The cortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical loops are thought to play a key role in such behavior. The present research was under ...
... The arbitrary mapping of sensory information onto action forms an important element of the intelligent behavior of primates (also called conditional associative learning). The cortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical loops are thought to play a key role in such behavior. The present research was under ...
Brain Research, 178 (1979) 363-380 363 © Elsevier/North
... the distribution of receptive field size was not random. There was a greater incidence of very large receptive fields in two regions. The first region was the most anterior part of IT (see Fig. 1C and D). Within this area 67 ~ of the 56 receptive fields were larger than 60 ° × 60 °. The second regio ...
... the distribution of receptive field size was not random. There was a greater incidence of very large receptive fields in two regions. The first region was the most anterior part of IT (see Fig. 1C and D). Within this area 67 ~ of the 56 receptive fields were larger than 60 ° × 60 °. The second regio ...
Task-dependent plasticity of spectrotemporal receptive fields in
... occurs in very diVerent tasks, and learning situations, suggests that “it is a general process of information storage and representation”. Each of these earlier studies measured changes in receptive Weld properties of A1 neurons that arose from behavior – we highlight two speciWc results from the ea ...
... occurs in very diVerent tasks, and learning situations, suggests that “it is a general process of information storage and representation”. Each of these earlier studies measured changes in receptive Weld properties of A1 neurons that arose from behavior – we highlight two speciWc results from the ea ...
International Encyclopedia of Rehabilitation - Cirrie
... memories (episodic memory), and rarely general knowledge and automatic learning (procedural learning). The interview with patients, assisted by a significant other, allows ...
... memories (episodic memory), and rarely general knowledge and automatic learning (procedural learning). The interview with patients, assisted by a significant other, allows ...
Chapter 12 PowerPoint Slided PDF - CM
... Primary motor cortex – plans and executes movement Primary sensory cortices – first regions to receive and process sensory input Association areas integrate different types of information: ...
... Primary motor cortex – plans and executes movement Primary sensory cortices – first regions to receive and process sensory input Association areas integrate different types of information: ...
Large-Scale Functional Connectivity in Associative Learning
... unique extraauditory anatomic relation of these regions. Ascending and descending influences from the IC, particularly the extralemniscal component, were stronger for group TL 0 . Altered converging effects on auditory cortex (AC) from the two parallel paths were noted from the ventral division of m ...
... unique extraauditory anatomic relation of these regions. Ascending and descending influences from the IC, particularly the extralemniscal component, were stronger for group TL 0 . Altered converging effects on auditory cortex (AC) from the two parallel paths were noted from the ventral division of m ...
Huffman PowerPoint Slides
... • The synapse is the junction between an axon terminal and an adjacent dendrite • Neurotransmitters are released from the axon terminal in response to an action potential into the synapse – The molecules diffuse across the synapse – NT molecules interact with receptors to alter the potential of the ...
... • The synapse is the junction between an axon terminal and an adjacent dendrite • Neurotransmitters are released from the axon terminal in response to an action potential into the synapse – The molecules diffuse across the synapse – NT molecules interact with receptors to alter the potential of the ...