Chapter 3 outline
... 1. Flow of the electrochemical message – the electrochemical message is picked up by the dendrites, organized in the soma, released through the axon and exits through the terminal buttons 2. Resting potential – the tiny electrical charge in place between the inside and the outside of resting neurons ...
... 1. Flow of the electrochemical message – the electrochemical message is picked up by the dendrites, organized in the soma, released through the axon and exits through the terminal buttons 2. Resting potential – the tiny electrical charge in place between the inside and the outside of resting neurons ...
BIOLOGICAL BASES OF BEHAVIOR
... 2. Neurons have a nucleus that contains genes. 3. Neurons contain cytoplasm, mitochondria and other "organelles". However, neurons differ from other cells in the body in some ways such as: 1. Neurons have specialized projections called dendrites and axons. Dendrites bring information to the cell bod ...
... 2. Neurons have a nucleus that contains genes. 3. Neurons contain cytoplasm, mitochondria and other "organelles". However, neurons differ from other cells in the body in some ways such as: 1. Neurons have specialized projections called dendrites and axons. Dendrites bring information to the cell bod ...
Presentation Summary - CAINS Center for Autonomous Intelligent
... prosthetic device for the hippocampus, a region of the brain responsible for the formation of long-term memories, and that frequently is damaged as a result of epilepsy, stroke, and Alzheimer's disease. The hippocampus is typical of most neural systems found in the mammalian brain in that it is comp ...
... prosthetic device for the hippocampus, a region of the brain responsible for the formation of long-term memories, and that frequently is damaged as a result of epilepsy, stroke, and Alzheimer's disease. The hippocampus is typical of most neural systems found in the mammalian brain in that it is comp ...
Lecture 7A
... They think of the brain as if it, too, were a computer doing tons of computations. They attribute human intelligence to our massively parallel connections, all running at the same time and spitting out an answer. They reason that once computers can match the amount of parallel connections in the bra ...
... They think of the brain as if it, too, were a computer doing tons of computations. They attribute human intelligence to our massively parallel connections, all running at the same time and spitting out an answer. They reason that once computers can match the amount of parallel connections in the bra ...
An Examination of the cell densities in Fmr1Ko mice
... multiple subtypes with combinatory expression of different neuronal markers. GABAergic Neurons show a unique easily identifiable multilayering in the posterior piriform cortex. ...
... multiple subtypes with combinatory expression of different neuronal markers. GABAergic Neurons show a unique easily identifiable multilayering in the posterior piriform cortex. ...
A Piece of Your Mind: Brain Anatomy
... a smaller space. (Think about wrinkling a sheet of paper - the 8 1/2” X 11” page fits in a much smaller space after crumpling it.) This makes more neurons available for the complex human nervous system to do its work. The outermost layer of the cerebrum is called the cerebral cortex. The cerebral co ...
... a smaller space. (Think about wrinkling a sheet of paper - the 8 1/2” X 11” page fits in a much smaller space after crumpling it.) This makes more neurons available for the complex human nervous system to do its work. The outermost layer of the cerebrum is called the cerebral cortex. The cerebral co ...
Basic Pattern of the Central Nervous System
... • Involved with ________________________, cognition, recall, and _ • Necessary for judgment, _______________________, persistence, and conscience • Closely linked to the __________________ system (emotional part of the brain) ...
... • Involved with ________________________, cognition, recall, and _ • Necessary for judgment, _______________________, persistence, and conscience • Closely linked to the __________________ system (emotional part of the brain) ...
File
... Primary Name: Nervous Tissue Sub-Primary: Cerebellum Form: The cerebellum is a large mass of tissue located below the occipital lobes of the cerebrum and posterior to the pons and medulla oblongata. It consists of two lateral hemispheres partially separated by a layer of dura mater (falx cerebelli) ...
... Primary Name: Nervous Tissue Sub-Primary: Cerebellum Form: The cerebellum is a large mass of tissue located below the occipital lobes of the cerebrum and posterior to the pons and medulla oblongata. It consists of two lateral hemispheres partially separated by a layer of dura mater (falx cerebelli) ...
Brain Functional Organization
... Newer, more advanced parts of the brain are built around and on the top of the older brain. Cortex or neocortex represents recent development in the human brain and the frontal and parietal lobes are expanded comparing to other primates. Brain is highly interconnected with millions of fibers linking ...
... Newer, more advanced parts of the brain are built around and on the top of the older brain. Cortex or neocortex represents recent development in the human brain and the frontal and parietal lobes are expanded comparing to other primates. Brain is highly interconnected with millions of fibers linking ...
Nervous System This week, you will examine the major structures in
... Tomberg, & Noel, 2010). Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) studies revealed reductions in brain volume in chronic alcoholism: reduced gray and white matter volumes, losses in the frontal lobes as well as in medial temporal and parietal cortices, in subcortical structures ( ...
... Tomberg, & Noel, 2010). Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) studies revealed reductions in brain volume in chronic alcoholism: reduced gray and white matter volumes, losses in the frontal lobes as well as in medial temporal and parietal cortices, in subcortical structures ( ...
central_nervous_system_overview_211
... State the functions of the peripheral nervous system, the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system, and distinguish the differences between each. Explain the delicate balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous ...
... State the functions of the peripheral nervous system, the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system, and distinguish the differences between each. Explain the delicate balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous ...
Neuronal Loss in the Brainstem and Cerebellum
... shown that different parts of the human brain are affected differently by aging (1,2) and that phylogenetically younger parts of the brain such as the cerebral and cerebellar cortex are more likely to undergo morphological changes (3) than do the phylogenetically older subcortical structures. It has ...
... shown that different parts of the human brain are affected differently by aging (1,2) and that phylogenetically younger parts of the brain such as the cerebral and cerebellar cortex are more likely to undergo morphological changes (3) than do the phylogenetically older subcortical structures. It has ...
Quiz: The Brain and Addiction
... 5. B: At first, drug use may cause floods of dopamine. But prolonged drug abuse causes the brain’s dopamine levels to decrease. That means the brain might need more of the drug just to get the dopamine levels back to normal and even more to produce the high that it craves. 6. B: The limbic system is ...
... 5. B: At first, drug use may cause floods of dopamine. But prolonged drug abuse causes the brain’s dopamine levels to decrease. That means the brain might need more of the drug just to get the dopamine levels back to normal and even more to produce the high that it craves. 6. B: The limbic system is ...
Quiz: The Brain and Addiction
... 4. A: The brain is wired to remember feelings of pleasure, including those produced by drugs unnaturally. The brain then strives to repeat those feelings, which the drug user experiences as a craving for the drug. 5. B: At first, drug use may cause floods of dopamine. But prolonged drug abuse causes ...
... 4. A: The brain is wired to remember feelings of pleasure, including those produced by drugs unnaturally. The brain then strives to repeat those feelings, which the drug user experiences as a craving for the drug. 5. B: At first, drug use may cause floods of dopamine. But prolonged drug abuse causes ...
D. Eisenhower Polio Myelitis: A Virus which caused Nerve cell
... and destroys motor neurons that connect the brain with the skeletal muscles. Patients become paralyzed and often require ventilation. Loss of respiratory function is ultimately the cause of death. ...
... and destroys motor neurons that connect the brain with the skeletal muscles. Patients become paralyzed and often require ventilation. Loss of respiratory function is ultimately the cause of death. ...
Synthetic neurons
... A scientist examines this tissue under a microscope. Which statement best identifies a function of this tissue? A. It breaks down and processes food. B. It conducts information through the body. C. It moves oxygen and carbon dioxide. D. It provides structure and support. ...
... A scientist examines this tissue under a microscope. Which statement best identifies a function of this tissue? A. It breaks down and processes food. B. It conducts information through the body. C. It moves oxygen and carbon dioxide. D. It provides structure and support. ...
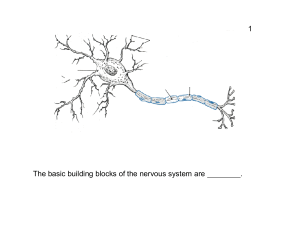
The basic building blocks of the nervous system are . 1
... areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, & speaking ...
... areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, & speaking ...
Document
... • Primary motor cortex, motor association area, behavioral state system, diffuse modulatory systems, and reticular activating system • Circadian rhythms, sleep, motivation, and ...
... • Primary motor cortex, motor association area, behavioral state system, diffuse modulatory systems, and reticular activating system • Circadian rhythms, sleep, motivation, and ...
Overview of the Brain
... • The brain is a complex organ that is organized and functions on several levels that can be broken down into both a micro and macroscopic regions. • At the microscopic level we have the basic nerve cell, the neuron, which is interconnected into a network of neurons that transects, crisscrosses, and ...
... • The brain is a complex organ that is organized and functions on several levels that can be broken down into both a micro and macroscopic regions. • At the microscopic level we have the basic nerve cell, the neuron, which is interconnected into a network of neurons that transects, crisscrosses, and ...