Slide ()
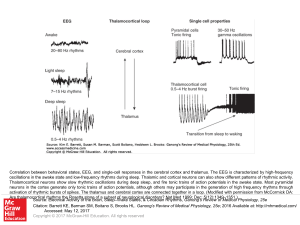
... Correlation between behavioral states, EEG, and single-cell responses in the cerebral cortex and thalamus. The EEG is characterized by high-frequency oscillations in the awake state and low-frequency rhythms during sleep. Thalamic and cortical neurons can also show different patterns of rhythmic act ...
... Correlation between behavioral states, EEG, and single-cell responses in the cerebral cortex and thalamus. The EEG is characterized by high-frequency oscillations in the awake state and low-frequency rhythms during sleep. Thalamic and cortical neurons can also show different patterns of rhythmic act ...
HW CH 5 PSY 2513 Submit your answers on canvas
... gradually stop sucking in response to having his stomach touched. b. learn to suck without having his stomach touched. c. stop eating until Prim touches his stomach and feeds him again. d. increase his level of sucking in response to having his stomach touched. ...
... gradually stop sucking in response to having his stomach touched. b. learn to suck without having his stomach touched. c. stop eating until Prim touches his stomach and feeds him again. d. increase his level of sucking in response to having his stomach touched. ...
Research Synopsis
... Dr. Kelso’s primary research interest is developing novel pharmacological agents for the treatment of traumatic brain injury (TBI). Dr. Kelso’s lab utilizes in vitro and in vivo models of head injury to study the biochemical pathways (secondary injury) that are initiated by the mechanical trauma (pr ...
... Dr. Kelso’s primary research interest is developing novel pharmacological agents for the treatment of traumatic brain injury (TBI). Dr. Kelso’s lab utilizes in vitro and in vivo models of head injury to study the biochemical pathways (secondary injury) that are initiated by the mechanical trauma (pr ...
2320Lecture26
... dorsal pre-motor cortex (also for production) • However, one general observation is that music processes tend to engage more right-hemisphere structures than left – Note this is generally the opposite of language processes, which tend to be strongly left-lateralized ...
... dorsal pre-motor cortex (also for production) • However, one general observation is that music processes tend to engage more right-hemisphere structures than left – Note this is generally the opposite of language processes, which tend to be strongly left-lateralized ...
MIND CONTROLLED ROBOT
... voltage fluctuations resulting within the neurons of the brain. The brain waves measured by EEG falls in the range of 1 – 20 Hz. The waves are subdivided into band widths known as alpha, beta, theta and delta. Each of the bandwidths are emitted during different states of mind. For e.g. Beta is emitt ...
... voltage fluctuations resulting within the neurons of the brain. The brain waves measured by EEG falls in the range of 1 – 20 Hz. The waves are subdivided into band widths known as alpha, beta, theta and delta. Each of the bandwidths are emitted during different states of mind. For e.g. Beta is emitt ...
Brain (Ch 11) keynotes 08--1st
... A ”spinal tap” (Fig. 11A / 11B) is a method used to remove CSF and check for abnormalities in the fluid that may indicate an injury to the CNS. ...
... A ”spinal tap” (Fig. 11A / 11B) is a method used to remove CSF and check for abnormalities in the fluid that may indicate an injury to the CNS. ...
Brain Structure and Function
... Concussion- injury to the head that can cause instant loss of awareness or alertness. The concussion is temporary but may result in permanent damage Skull fracture- a break in the skull bone. Four major types: 1. Linear-break but does not move bone. 2. Depressed-part of skull is sunken in 3. Diastat ...
... Concussion- injury to the head that can cause instant loss of awareness or alertness. The concussion is temporary but may result in permanent damage Skull fracture- a break in the skull bone. Four major types: 1. Linear-break but does not move bone. 2. Depressed-part of skull is sunken in 3. Diastat ...
Introduction to Cognitive Development 2012
... PET/fMRI and DOT are all built on the idea that an active brain site will require more glucose and oxygen to supply energy to the neurons in that site. Therefore, an active brain area will attract more blood and thus it will attract more of the radioactive substance (used in PET), more oxygen (detec ...
... PET/fMRI and DOT are all built on the idea that an active brain site will require more glucose and oxygen to supply energy to the neurons in that site. Therefore, an active brain area will attract more blood and thus it will attract more of the radioactive substance (used in PET), more oxygen (detec ...
Lecture Outline
... In humans, the outermost part of the cerebral cortex forms the neocortex, six parallel layers of neurons arranged tangential to the brain surface. Such a large, highly convoluted neocortex was thought to be required for advanced cognition, the perception and reasoning that form knowledge. Both prima ...
... In humans, the outermost part of the cerebral cortex forms the neocortex, six parallel layers of neurons arranged tangential to the brain surface. Such a large, highly convoluted neocortex was thought to be required for advanced cognition, the perception and reasoning that form knowledge. Both prima ...
Chapter 18: Neurologic Emergencies
... and pain. The diencephalon filters out unneeded information from the cerebral cortex. The midbrain helps to regulate the level of consciousness. The brainstem regulates the blood pressure, pulse rate, and respiratory rate and pattern. The hypothalamus and pituitary control the release of epinephrine ...
... and pain. The diencephalon filters out unneeded information from the cerebral cortex. The midbrain helps to regulate the level of consciousness. The brainstem regulates the blood pressure, pulse rate, and respiratory rate and pattern. The hypothalamus and pituitary control the release of epinephrine ...
Endocrine System - Brain Mind Forum
... cells to stimulate production of second messengers. Soluble gas neurotransmitters are difficult to study, as they act rapidly and are immediately broken down, existing for only a few seconds. The most prevalent transmitter is glutamate, which is excitatory at well over 90% of the synapses in the hum ...
... cells to stimulate production of second messengers. Soluble gas neurotransmitters are difficult to study, as they act rapidly and are immediately broken down, existing for only a few seconds. The most prevalent transmitter is glutamate, which is excitatory at well over 90% of the synapses in the hum ...
Nature Versus Nurture
... Memory systems start to decline Prefrontal cortex continues to mature New synapses in language and perception centers Myelination continues ...
... Memory systems start to decline Prefrontal cortex continues to mature New synapses in language and perception centers Myelination continues ...
Study Concepts for Exam V - Nervous System
... Divisions of the CNS and PNS, and what parts serve what functions Types of reflex arcs The definitions and differences in location of nuclei vs. ganglia The parts of the brain at the level of detail discussed in lecture. Know at least one major function for each larger and more specific parts, such ...
... Divisions of the CNS and PNS, and what parts serve what functions Types of reflex arcs The definitions and differences in location of nuclei vs. ganglia The parts of the brain at the level of detail discussed in lecture. Know at least one major function for each larger and more specific parts, such ...
The Nervous System
... 1. Control center for all body activities 2. Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
... 1. Control center for all body activities 2. Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
Cerebral Palsy
... Seizures believed to be a result of spontaneous uncontrolled electrical activity of neurons Cause – Uncertain Diagnosed with EEG (electroencephalogram) ...
... Seizures believed to be a result of spontaneous uncontrolled electrical activity of neurons Cause – Uncertain Diagnosed with EEG (electroencephalogram) ...
module 6 The Cerebral Cortex and Our Divided Brain Module
... The cerebral cortex, a thin surface layer of interconnected neural cells, is our body’s ultimate control and information-processing center. Glial cells support, nourish, and protect the nerve cells of the cerebral cortex. The frontal lobes, just behind the forehead, are involved in speaking, muscle ...
... The cerebral cortex, a thin surface layer of interconnected neural cells, is our body’s ultimate control and information-processing center. Glial cells support, nourish, and protect the nerve cells of the cerebral cortex. The frontal lobes, just behind the forehead, are involved in speaking, muscle ...
Test 5 Study Guide
... o The inherited brain disorder Huntington's disease is caused by the destruction of basal nuclei that use different neurotransmitters. One neurotransmitter is acetylcholine and the other is GABA. o Depression is a mental illness is often improved by drugs that block serotonin reuptake? Aging produce ...
... o The inherited brain disorder Huntington's disease is caused by the destruction of basal nuclei that use different neurotransmitters. One neurotransmitter is acetylcholine and the other is GABA. o Depression is a mental illness is often improved by drugs that block serotonin reuptake? Aging produce ...
to-BBB and Lundbeck to join forces on brain delivery of
... to-BBB is a Dutch biotechnology company in the field of enhanced drug delivery across the blood-brain barrier. The company is developing novel treatments for brain disorders by combining existing drugs with its proprietary brain drug delivery platform. The company’s vision is that the treatment of c ...
... to-BBB is a Dutch biotechnology company in the field of enhanced drug delivery across the blood-brain barrier. The company is developing novel treatments for brain disorders by combining existing drugs with its proprietary brain drug delivery platform. The company’s vision is that the treatment of c ...
Intro-biological
... of the cerebrum which regulates higher level functioning such as thought, and the cerebellum which maintains coordination. The brain stem includes the midbrain, pons, and medulla, and controls lower level functioning such as respiration and digestion. The spinal cord connects the brain and the body' ...
... of the cerebrum which regulates higher level functioning such as thought, and the cerebellum which maintains coordination. The brain stem includes the midbrain, pons, and medulla, and controls lower level functioning such as respiration and digestion. The spinal cord connects the brain and the body' ...
Brain
... • External cues – light/dark cycle, magnetic fields, seasonal changes. • Internal cues – “biological clock”; in mammals, the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) -produces specific proteins in response to changing light/dark cycles. -regulates hormone release, hunger, motor activity, etc. ...
... • External cues – light/dark cycle, magnetic fields, seasonal changes. • Internal cues – “biological clock”; in mammals, the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) -produces specific proteins in response to changing light/dark cycles. -regulates hormone release, hunger, motor activity, etc. ...
Essential Questions and Vocabulary
... neurotransmitters, acetylcholine, endorphins, nervous system, central nervous system, peripheral nervous system, nerves, sensory neurons, motor neurons, interneurons, somatic nervous system, autonomic nervous system, sympathetic nervous system, parasympathetic nervous system, reflex, neural networks ...
... neurotransmitters, acetylcholine, endorphins, nervous system, central nervous system, peripheral nervous system, nerves, sensory neurons, motor neurons, interneurons, somatic nervous system, autonomic nervous system, sympathetic nervous system, parasympathetic nervous system, reflex, neural networks ...
PSYB1 Revision sheet Biopsychology JM09
... Genotype: A person’s genetic make-up, as represented by the genes on the 23 pairs of human chromosomes ...
... Genotype: A person’s genetic make-up, as represented by the genes on the 23 pairs of human chromosomes ...