(30 MCQ answers). - Blackwell Publishing
... hypothalamus is now thought of as a region that can influence the secretion of insulin and, indirectly, affect body weight, but not as a satiety centre per se. 14) Answer: (c). Taste signals provide one of the most significant rewards for eating. They are processed through different stages in our br ...
... hypothalamus is now thought of as a region that can influence the secretion of insulin and, indirectly, affect body weight, but not as a satiety centre per se. 14) Answer: (c). Taste signals provide one of the most significant rewards for eating. They are processed through different stages in our br ...
CVPR2003TBSM - Department of Statistics
... 1996). Afterwards, a triangular mesh for each cortical surface was generated by deforming a mesh to fit the proper boundary in a segmented volume using a deformable surface algorithm (MacDonald et al., 2000). This algorithm is further used in surface registration and surface template construction (C ...
... 1996). Afterwards, a triangular mesh for each cortical surface was generated by deforming a mesh to fit the proper boundary in a segmented volume using a deformable surface algorithm (MacDonald et al., 2000). This algorithm is further used in surface registration and surface template construction (C ...
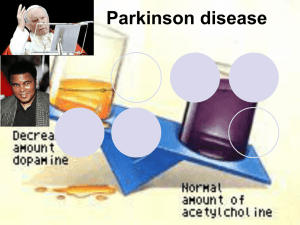
Parkinson disease
... trihexyphenedyl are used. They are less effective than dopaminergic drugs. they are more effective in reducing tremor than the other symptoms. They are useful in treatment of early and advanced parkinson disease, they can reduce parkinsonian symptoms caused by dopamine receptor antagonists eg ...
... trihexyphenedyl are used. They are less effective than dopaminergic drugs. they are more effective in reducing tremor than the other symptoms. They are useful in treatment of early and advanced parkinson disease, they can reduce parkinsonian symptoms caused by dopamine receptor antagonists eg ...
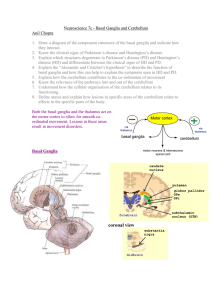
Neuroscience 7c – Basal Ganglia and Cerebellum
... Gait slow, small steps, reduced arm swing. Huntington’s Disease Huntington’s disease is caused by a defective “Huntington Gene” on chromosome 4. This results in the degradation of the spiny GABAergic neurons in the striatum. It is an autosomal dominant disease. Symptoms of Huntington’s Disease C ...
... Gait slow, small steps, reduced arm swing. Huntington’s Disease Huntington’s disease is caused by a defective “Huntington Gene” on chromosome 4. This results in the degradation of the spiny GABAergic neurons in the striatum. It is an autosomal dominant disease. Symptoms of Huntington’s Disease C ...
PPT - UCLA Health
... • Electrophysiological studies in animal model and humans, functional neuro-imaging studies (PET, functional MRI, magneto-encephalographic studies. ...
... • Electrophysiological studies in animal model and humans, functional neuro-imaging studies (PET, functional MRI, magneto-encephalographic studies. ...
Emo7onal decision‐making systems and their role in addic7on
... 1.a. It was also recognized in the late 1980’s and early 1990’s that the abuse potential of drugs of abuse (e.g., opiates, alcohol, nicotine, caffeine, barbiturates, benzodiazepines, cannabis, and phencyclidine) all are linked, one way or another, to this mesolimbic dopamine system. While these ...
... 1.a. It was also recognized in the late 1980’s and early 1990’s that the abuse potential of drugs of abuse (e.g., opiates, alcohol, nicotine, caffeine, barbiturates, benzodiazepines, cannabis, and phencyclidine) all are linked, one way or another, to this mesolimbic dopamine system. While these ...
Dissipation of dark energy by cortex in knowledge retrieval
... and carbon dioxide production. The sensory receptors in the body and on the body surface provide the information by absorbing energy of various types impinging from the internal and external environments (Laughlin et al., 1998). The role of each sensory receptor is selectively to convert a microscop ...
... and carbon dioxide production. The sensory receptors in the body and on the body surface provide the information by absorbing energy of various types impinging from the internal and external environments (Laughlin et al., 1998). The role of each sensory receptor is selectively to convert a microscop ...
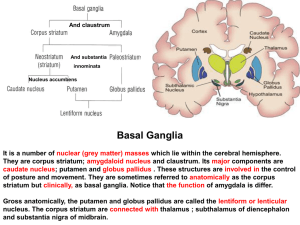
17-Basal ganglion
... They are corpus striatum; amygdaloid nucleus and claustrum. Its major components are caudate nucleus; putamen and globus pallidus . These structures are involved in the control of posture and movement. They are sometimes referred to anatomically as the corpus striatum but clinically, as basal gangli ...
... They are corpus striatum; amygdaloid nucleus and claustrum. Its major components are caudate nucleus; putamen and globus pallidus . These structures are involved in the control of posture and movement. They are sometimes referred to anatomically as the corpus striatum but clinically, as basal gangli ...
Mouth Esophagus Stomach Pyloric Valve Small Intestine
... Decreased response time Get more infections Increased risk for STD’s/HIV ...
... Decreased response time Get more infections Increased risk for STD’s/HIV ...
No Slide Title
... A Key to Distinguishing CF from Linguistic Forms Distinguishing the sign from the affordance or the schema Recall: Two Roles for Imitation in the Evolution of Manual-Based Communication 1. Extending imitation from imitation of hand movements by hand movements to pantomime which uses the degrees of ...
... A Key to Distinguishing CF from Linguistic Forms Distinguishing the sign from the affordance or the schema Recall: Two Roles for Imitation in the Evolution of Manual-Based Communication 1. Extending imitation from imitation of hand movements by hand movements to pantomime which uses the degrees of ...
PDF file
... on Hebbian learning — cofiring of the pre-synaptic activity ṗ and the post-synaptic activity y of the firing neuron. It has been proved that the general-purpose DP can incrementally grows a generative DN to simulate any given finite automaton (FA)on the fly, [28], provided that the Z area of the DN ...
... on Hebbian learning — cofiring of the pre-synaptic activity ṗ and the post-synaptic activity y of the firing neuron. It has been proved that the general-purpose DP can incrementally grows a generative DN to simulate any given finite automaton (FA)on the fly, [28], provided that the Z area of the DN ...
Author`s personal copy
... rats showed opposite patterns of binding in dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in the nucleus accumbens, medial prefrontal cortex, amygdala, ventral tegmental area and substantia nigra. Whereas LD rats showed higher binding than HD rats for D1 receptors, HD rats showed higher binding than LD rats for D2 r ...
... rats showed opposite patterns of binding in dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in the nucleus accumbens, medial prefrontal cortex, amygdala, ventral tegmental area and substantia nigra. Whereas LD rats showed higher binding than HD rats for D1 receptors, HD rats showed higher binding than LD rats for D2 r ...
Epilepsy and Seizure Disorders
... characterized by at least two recurrent seizures that occur without evident cause. Important to note: Seizures that occur with apparent cause are not labelled as epilepsy Seizures are the manifestations/symptoms of epilepsy ...
... characterized by at least two recurrent seizures that occur without evident cause. Important to note: Seizures that occur with apparent cause are not labelled as epilepsy Seizures are the manifestations/symptoms of epilepsy ...
Neural computations that underlie decisions about sensory stimuli
... light, with some values being more likely than others when light is present (see Box 1). How do you use the value from the detector to decide if the light was present? This problem consists of deciding which hypothesis – light is present (h1) or light is absent (h2) – is most likely to be true given ...
... light, with some values being more likely than others when light is present (see Box 1). How do you use the value from the detector to decide if the light was present? This problem consists of deciding which hypothesis – light is present (h1) or light is absent (h2) – is most likely to be true given ...
3-Biological Bases-table - Miami Beach Senior High School
... Cerebral hemispheres- the left and right side of the cerebral cortex Corpus callosum- connects the two hemispheres Split-brain- refers to people who have had their corpus callusum severed/ Roger Sperry found to reduce epileptic seizures Each hemisphere is divided into four lobes. ...
... Cerebral hemispheres- the left and right side of the cerebral cortex Corpus callosum- connects the two hemispheres Split-brain- refers to people who have had their corpus callusum severed/ Roger Sperry found to reduce epileptic seizures Each hemisphere is divided into four lobes. ...
Neuroscience and Behavior Term Explanation
... Cerebral hemispheres- the left and right side of the cerebral cortex Corpus callosum- connects the two hemispheres Split-brain- refers to people who have had their corpus callusum severed/ Roger Sperry found to reduce epileptic seizures Each hemisphere is divided into four lobes. ...
... Cerebral hemispheres- the left and right side of the cerebral cortex Corpus callosum- connects the two hemispheres Split-brain- refers to people who have had their corpus callusum severed/ Roger Sperry found to reduce epileptic seizures Each hemisphere is divided into four lobes. ...
Bill Greenough`s research career
... of brain information storage in later development and adulthood. Combining the “environmental enrichment” procedure pioneered by Donald Hebb and Mark Rosenzweig with quantitative optical and electron microscopic morphological methods drawn from Scheibel, Sholl and others, Greenough’s early studies e ...
... of brain information storage in later development and adulthood. Combining the “environmental enrichment” procedure pioneered by Donald Hebb and Mark Rosenzweig with quantitative optical and electron microscopic morphological methods drawn from Scheibel, Sholl and others, Greenough’s early studies e ...
The Basics of Brain Development | SpringerLink
... Figure 4b orients the embryo within the context of the embryonic placenta, and Fig. 4c shows how the embryonic spatial axes relate to the major spatial dimensions of the infant (see figure caption for details). Each of the two layers contains a different, very primitive cell type (Fig. 5b). The uppe ...
... Figure 4b orients the embryo within the context of the embryonic placenta, and Fig. 4c shows how the embryonic spatial axes relate to the major spatial dimensions of the infant (see figure caption for details). Each of the two layers contains a different, very primitive cell type (Fig. 5b). The uppe ...
Basile, 1999
... • As the data in the study correlates to the CHO cell study findings perhaps the functional differences may contribute to the TD phenotype, although it is difficult to speculate further on the precise mechanism involved. • It could be suggested that the higher affinity of the glycine allele may be ...
... • As the data in the study correlates to the CHO cell study findings perhaps the functional differences may contribute to the TD phenotype, although it is difficult to speculate further on the precise mechanism involved. • It could be suggested that the higher affinity of the glycine allele may be ...
Alterations of the Giant Pyramidal Neurons (Betz Cells) in
... offspring born from gestational diabetics dams: a morphometric study. Int. J. Morphol., 33(3):1120-1125, 2015. SUMMARY: A few studies reported the adverse effects of gestational diabetes on hippocampus and spinal cord of rat offspring. Giant pyramidal neurons are giant pyramidal neurons located in f ...
... offspring born from gestational diabetics dams: a morphometric study. Int. J. Morphol., 33(3):1120-1125, 2015. SUMMARY: A few studies reported the adverse effects of gestational diabetes on hippocampus and spinal cord of rat offspring. Giant pyramidal neurons are giant pyramidal neurons located in f ...
Posterior cingulate cortex: adapting behavior to a
... full range of phenomena shown to modulate activity in CGp. Taking a broader view based on both electrophysiological and functional imaging evidence (summarized below), we conjecture that many of these observed modulations reflect the contribution of CGp to signaling environmental change and, when ne ...
... full range of phenomena shown to modulate activity in CGp. Taking a broader view based on both electrophysiological and functional imaging evidence (summarized below), we conjecture that many of these observed modulations reflect the contribution of CGp to signaling environmental change and, when ne ...
Beyond Spikes: Neural Codes and the Chemical Vocabulary of
... have to correspond to anything an actual cell has to deal with. Even in these cases, though, some of the biological language is preserved. So, if a neuron is considered to be inhibitory, its connection weight to postsynaptic cells will generally be negative; it will be positive in the excitatory cas ...
... have to correspond to anything an actual cell has to deal with. Even in these cases, though, some of the biological language is preserved. So, if a neuron is considered to be inhibitory, its connection weight to postsynaptic cells will generally be negative; it will be positive in the excitatory cas ...
Ch.11
... • Slowed responses and reflexes • Changes increase risk of falling • Sleep problems common ...
... • Slowed responses and reflexes • Changes increase risk of falling • Sleep problems common ...
- Wiley Online Library
... man insular cortex, which fits with considerable evidence (e.g., Ref. 22), and that subjective feelings are based directly on homeostatic sensory integration, which is consistent with the James-Lange theory of emotion and the “somatic marker” hypothesis.23,24 To my mind, this pattern also suggests t ...
... man insular cortex, which fits with considerable evidence (e.g., Ref. 22), and that subjective feelings are based directly on homeostatic sensory integration, which is consistent with the James-Lange theory of emotion and the “somatic marker” hypothesis.23,24 To my mind, this pattern also suggests t ...