Visual Awareness - People.csail.mit.edu
... our present knowledge of the visual system. The first is how much we already know—by any standards the amount is enormous… The other surprising thing is that, in spite of all this work, we really have no clear idea how we see anything.” ...
... our present knowledge of the visual system. The first is how much we already know—by any standards the amount is enormous… The other surprising thing is that, in spite of all this work, we really have no clear idea how we see anything.” ...
Unit 01 Biology and the Brain_Part 2
... • Involved in how we process memory. • More involved in volatile emotions like The emotion of anger has anger. not changed much throughout evolution. ...
... • Involved in how we process memory. • More involved in volatile emotions like The emotion of anger has anger. not changed much throughout evolution. ...
Biopsychology - WordPress.com
... • Psychophysiology ~ also studies the neural bases of thought, memory, attention, perception ...
... • Psychophysiology ~ also studies the neural bases of thought, memory, attention, perception ...
Local Cortical Circuits
... 7 Transmission of Information by Coincidence . . 7.1 The Single Neuron as a Coincidence Detector 7.2 Existence of Chains of Neuronal Sets with Appropriate Connections 7.3 Some Properties of Synfire Chains 8 Organization of Generators of the ECoG 8.1 The Generation of the ECoG 8.2 Population Statist ...
... 7 Transmission of Information by Coincidence . . 7.1 The Single Neuron as a Coincidence Detector 7.2 Existence of Chains of Neuronal Sets with Appropriate Connections 7.3 Some Properties of Synfire Chains 8 Organization of Generators of the ECoG 8.1 The Generation of the ECoG 8.2 Population Statist ...
Response to George Johnson`s Review of The Universe in a Single
... insect-eating plants), or in animals (e.g., single cells, insects, human fetuses, or normal human adults). Given that consciousness is invisible to all known means of scientific measurement–unlike all other kinds of physical phenomena–the burden of proof for the physical status of consciousness shou ...
... insect-eating plants), or in animals (e.g., single cells, insects, human fetuses, or normal human adults). Given that consciousness is invisible to all known means of scientific measurement–unlike all other kinds of physical phenomena–the burden of proof for the physical status of consciousness shou ...
Altered States of Consciousness
... Consciousness as a Chord of Subconscious brain events. Neuroscientists believe that consciousness emerges from the interaction of individual subconscious brain events much like a chord that is created from ...
... Consciousness as a Chord of Subconscious brain events. Neuroscientists believe that consciousness emerges from the interaction of individual subconscious brain events much like a chord that is created from ...
A true science of consciousness explains
... when reported, access itself does not seem to be involved in generating the contents of experience, and therefore it has little power to explain phenomenology [10]. Now if it turns out that the neural mechanisms of perception established in our perfect experiment subside when their contents cannot b ...
... when reported, access itself does not seem to be involved in generating the contents of experience, and therefore it has little power to explain phenomenology [10]. Now if it turns out that the neural mechanisms of perception established in our perfect experiment subside when their contents cannot b ...
Ch. 3 Discovering Psy Behaving Brain Video
... 1. In the beginning of the video, Philip Zimbardo compared our brain to a _____________. 2. The human brain houses approximately _____________ number of brain cells. 3. Neurons and glia are designed to do 3 things: a. ___________________________________________________________ b. ___________________ ...
... 1. In the beginning of the video, Philip Zimbardo compared our brain to a _____________. 2. The human brain houses approximately _____________ number of brain cells. 3. Neurons and glia are designed to do 3 things: a. ___________________________________________________________ b. ___________________ ...
3680Lecture29
... Neural Correlates of Rivalry • What Brain areas “experience” rivalry? • Apparently activity in areas in ventral pathway correlates with awareness • But at what stage is rivalry first manifested? • For the answer we need to look to single-cell recording ...
... Neural Correlates of Rivalry • What Brain areas “experience” rivalry? • Apparently activity in areas in ventral pathway correlates with awareness • But at what stage is rivalry first manifested? • For the answer we need to look to single-cell recording ...
Consciousness - www3.telus.net
... enduring change in a living person that is not heralded by genetic inheritance. It may be considered a change in insights, behaviors, perception, motivation, or a combination of these. It always involves a systematic change in behavior or behavioral disposition that occurs as a consequence of one’s ...
... enduring change in a living person that is not heralded by genetic inheritance. It may be considered a change in insights, behaviors, perception, motivation, or a combination of these. It always involves a systematic change in behavior or behavioral disposition that occurs as a consequence of one’s ...
title of video - Discovery Education
... 2. Why are the basal ganglia, limbic system and brain stem referred to as the "old brain"? The basal ganglia, limbic system and brain stem are called the "old brain" because they control the subconscious activities and are thought to have developed in humans before the more conscious brain structure ...
... 2. Why are the basal ganglia, limbic system and brain stem referred to as the "old brain"? The basal ganglia, limbic system and brain stem are called the "old brain" because they control the subconscious activities and are thought to have developed in humans before the more conscious brain structure ...
the brain: anatomical regions
... CEREBRUM is the largest portion of the brain Cerebellum is the second largest portion of the brain. Its function is for balance. ...
... CEREBRUM is the largest portion of the brain Cerebellum is the second largest portion of the brain. Its function is for balance. ...
Quiz Chapter 3 Brain Neural Communication Dr Myer How do
... What are the four lobes in the cortex? What is the frontal lobe responsible for? The parietal lobe? The temporal lobe? The occipital lobe? What is an experience-dependent brain? What is plasticity? What is an experience-expectant brain? What are two types of brain injury? Can your brain ...
... What are the four lobes in the cortex? What is the frontal lobe responsible for? The parietal lobe? The temporal lobe? The occipital lobe? What is an experience-dependent brain? What is plasticity? What is an experience-expectant brain? What are two types of brain injury? Can your brain ...
The Scientific Method - Northwest ISD Moodle
... The Brain: The three general region are the Brainstem, the Limbic System and the Cerebral Cortex. o The brainstem includes the medulla (heartbeat and breathing), the reticular formation (arousal center), the cerebellum (balance) and the thalamus (the “sensory switchboard”) o The limbic system includ ...
... The Brain: The three general region are the Brainstem, the Limbic System and the Cerebral Cortex. o The brainstem includes the medulla (heartbeat and breathing), the reticular formation (arousal center), the cerebellum (balance) and the thalamus (the “sensory switchboard”) o The limbic system includ ...
Review Sheet 1 scientific method and neurobiology
... The Brain: The three general region are the Brainstem, the Limbic System and the Cerebral Cortex. o The brainstem includes the medulla (heartbeat and breathing), the reticular formation (arousal center), the cerebellum (balance) and the thalamus (the “sensory switchboard”) o The limbic system includ ...
... The Brain: The three general region are the Brainstem, the Limbic System and the Cerebral Cortex. o The brainstem includes the medulla (heartbeat and breathing), the reticular formation (arousal center), the cerebellum (balance) and the thalamus (the “sensory switchboard”) o The limbic system includ ...
The Cerebral Cortex
... 12-1 What are the functions of the various cerebral cortex regions? • The people who first dissected brains used Latin & Greek to names parts….. Cortex means “bark” • Cerebral cortex = brain bark (If you don’t think that’s awesome, there’s NO hope for you!) • While the older brain networks sustain ...
... 12-1 What are the functions of the various cerebral cortex regions? • The people who first dissected brains used Latin & Greek to names parts….. Cortex means “bark” • Cerebral cortex = brain bark (If you don’t think that’s awesome, there’s NO hope for you!) • While the older brain networks sustain ...
Folie 1
... large communities for long periods of time creates culture and tradition. All our "selves" are formed in this framework during critical developmental periods. Cultures adopt characteristic properties, that may continue far beyond several generations. ...
... large communities for long periods of time creates culture and tradition. All our "selves" are formed in this framework during critical developmental periods. Cultures adopt characteristic properties, that may continue far beyond several generations. ...
7-9_BrainDev_ValaczkaiR
... neural tube is created. Some parts of the neural crest remain behind developing into the sensory dorsal root ganglia in the spinal cord. At one end of the neural tube cells divide more rapidly and this part becomes the brain later. Neurons cannot divide freely in contrast to glia cells, therefore pr ...
... neural tube is created. Some parts of the neural crest remain behind developing into the sensory dorsal root ganglia in the spinal cord. At one end of the neural tube cells divide more rapidly and this part becomes the brain later. Neurons cannot divide freely in contrast to glia cells, therefore pr ...
Neurons
... A neuron functions by generating an electric charge in the cell body that propagates down the axon. This is called an action potential. When a neuron generates an action potential, we say that that neuron fires. Action potentials are always the same magnitude. Neurons communicate with each other via ...
... A neuron functions by generating an electric charge in the cell body that propagates down the axon. This is called an action potential. When a neuron generates an action potential, we say that that neuron fires. Action potentials are always the same magnitude. Neurons communicate with each other via ...
Phenomenology without conscious access is a form of
... empirical evidence to the contrary (such as Anton’s blindness, also known as hysterical blindness; Sackeim et al. 1979), if the subject denies any phenomenal experience, this should be accepted as a brute fact. If we take the existence of mere recurrent, strong neuronal activation as evidence for co ...
... empirical evidence to the contrary (such as Anton’s blindness, also known as hysterical blindness; Sackeim et al. 1979), if the subject denies any phenomenal experience, this should be accepted as a brute fact. If we take the existence of mere recurrent, strong neuronal activation as evidence for co ...
Chapter 1
... Reflex – an automatic, stereotyped movement that is produced as the direct result of a stimulus Model – a mathematical or physical analogy for a physiological process ...
... Reflex – an automatic, stereotyped movement that is produced as the direct result of a stimulus Model – a mathematical or physical analogy for a physiological process ...
The human brain
... Defined the cerebral cortex into 52 distinct regions on the basis of their cytoarchitectonic characteristics. ...
... Defined the cerebral cortex into 52 distinct regions on the basis of their cytoarchitectonic characteristics. ...
10-5 Infant Biosocial Development
... Germinal, embryonic, and fetal periods Teratogens: critical period, threshold, interaction Birth process ...
... Germinal, embryonic, and fetal periods Teratogens: critical period, threshold, interaction Birth process ...
Slide ()
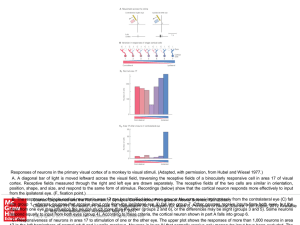
... Responses of neurons in the primary visual cortex of a monkey to visual stimuli. (Adapted, with permission, from Hubel and Wiesel 1977.) A. A diagonal bar of light is moved leftward across the visual field, traversing the receptive fields of a binocularly responsive cell in area 17 of visual cortex. ...
... Responses of neurons in the primary visual cortex of a monkey to visual stimuli. (Adapted, with permission, from Hubel and Wiesel 1977.) A. A diagonal bar of light is moved leftward across the visual field, traversing the receptive fields of a binocularly responsive cell in area 17 of visual cortex. ...
Neural correlates of consciousness

The neural correlates of consciousness (NCC) constitute the minimal set of neuronal events and mechanisms sufficient for a specific conscious percept. Neuroscientists use empirical approaches to discover neural correlates of subjective phenomena. The set should be minimal because, under the assumption that the brain is sufficient to give rise to any given conscious experience, the question is which of its components is necessary to produce it.