PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition) David Myers
... involving as much as half the visual field can nevertheless reach out and touch objects in the "blind" area. This is called blindsight. However, blindsight intrigues investigators because it seems to suggest that visual information can find its way into the brain through some unconscious route. ...
... involving as much as half the visual field can nevertheless reach out and touch objects in the "blind" area. This is called blindsight. However, blindsight intrigues investigators because it seems to suggest that visual information can find its way into the brain through some unconscious route. ...
What is consciousness?
... a. It is a serotonin agonist b. It was developed by Swiss chemist Albert Hoffman in 1938 c. Users develop a tolerance for it d. A low potential exists for physical and psychological dependence 2. Marijuana causes euphoria, relaxation, food craving, time distortion, and an increase in vivid sensation ...
... a. It is a serotonin agonist b. It was developed by Swiss chemist Albert Hoffman in 1938 c. Users develop a tolerance for it d. A low potential exists for physical and psychological dependence 2. Marijuana causes euphoria, relaxation, food craving, time distortion, and an increase in vivid sensation ...
neural spike
... stimulus from being activated, but from the network point of view, it would be indistinguishable from the event when the stimulus is actually present. One can say that the network “thinks” about the stimulus. A sequence of spontaneous activations corresponding to one stimulus, then another, and so o ...
... stimulus from being activated, but from the network point of view, it would be indistinguishable from the event when the stimulus is actually present. One can say that the network “thinks” about the stimulus. A sequence of spontaneous activations corresponding to one stimulus, then another, and so o ...
Neuroscience 5b – Nociception
... sensation of analgesia when pain is rubbed. Because mechanoreceptors have a low-threshold and pain receptors have a high threshold, when the mechanoreceptors fire action potential, they inhibit the pain receptors around them by lateral inhibition. This has an analgesic effect. It takes place at the ...
... sensation of analgesia when pain is rubbed. Because mechanoreceptors have a low-threshold and pain receptors have a high threshold, when the mechanoreceptors fire action potential, they inhibit the pain receptors around them by lateral inhibition. This has an analgesic effect. It takes place at the ...
Stages of Brain Development
... We are born with around 100 billion neurons, and the development of the brain continues long after birth, with dendrites of some neurons in the neocortex continuing to grow well into old age[1]. Pregnancy is a time of great joy and expectation - however, our world and its potential hazards are very ...
... We are born with around 100 billion neurons, and the development of the brain continues long after birth, with dendrites of some neurons in the neocortex continuing to grow well into old age[1]. Pregnancy is a time of great joy and expectation - however, our world and its potential hazards are very ...
Lecture 1
... linked to neural processes – ranging from investigations in animals to humans and from experiments performed in the laboratory to computer simulations ? Neurology is a branch of medical science that deals with the nervous system, both normal and diseased ...
... linked to neural processes – ranging from investigations in animals to humans and from experiments performed in the laboratory to computer simulations ? Neurology is a branch of medical science that deals with the nervous system, both normal and diseased ...
Congenital Malformation & Hydrocephalus
... The volume of brain may be abnormally large (megalencephaly) or small (microencephaly). Microencephaly, by far the more common of the two, is usually associated with a small head as well It can occur in a wide range of clinical settings, including: • chromosome abnormalities • fetal alcohol syndrome ...
... The volume of brain may be abnormally large (megalencephaly) or small (microencephaly). Microencephaly, by far the more common of the two, is usually associated with a small head as well It can occur in a wide range of clinical settings, including: • chromosome abnormalities • fetal alcohol syndrome ...
Personality and Physiology
... – Some drink to seek novelty, some for pleasure boosting, some to relieve stress, some for harm avoidance, some for relief, and some because it is rewarding. ...
... – Some drink to seek novelty, some for pleasure boosting, some to relieve stress, some for harm avoidance, some for relief, and some because it is rewarding. ...
w - Fizyka UMK
... • CAM Brain (ATR Kyoto) – failed attempt to evolve the largescale cellular neural network; based on a bad idea that one can evolve functions without knowing them. It is impossible to repeat evolutionary process (lack of data about initial organisms and environment, almost infinite number of evolutio ...
... • CAM Brain (ATR Kyoto) – failed attempt to evolve the largescale cellular neural network; based on a bad idea that one can evolve functions without knowing them. It is impossible to repeat evolutionary process (lack of data about initial organisms and environment, almost infinite number of evolutio ...
Document
... • CAM Brain (ATR Kyoto) – failed attempt to evolve the largescale cellular neural network; based on a bad idea that one can evolve functions without knowing them. It is impossible to repeat evolutionary process (lack of data about initial organisms and environment, almost infinite number of evolutio ...
... • CAM Brain (ATR Kyoto) – failed attempt to evolve the largescale cellular neural network; based on a bad idea that one can evolve functions without knowing them. It is impossible to repeat evolutionary process (lack of data about initial organisms and environment, almost infinite number of evolutio ...
Thalamus 1
... neurons, whose axons provide the output of thalamus, and small inhibitory interneurons that use GABA as a neurotransmitter Projection neurons account for 75% or more of the neurons of the most thalamic nuclei, though the relative proportions of projection neurons and interneurons vary in different n ...
... neurons, whose axons provide the output of thalamus, and small inhibitory interneurons that use GABA as a neurotransmitter Projection neurons account for 75% or more of the neurons of the most thalamic nuclei, though the relative proportions of projection neurons and interneurons vary in different n ...
Solution 1
... the information to pass efficiently through the blind spot. These specialized circuits also function as a means of transmitting information about different aspects of the same region in space simultaneously (Nassi & Callaway, 361). Later in the visual system, existence of different parallel processi ...
... the information to pass efficiently through the blind spot. These specialized circuits also function as a means of transmitting information about different aspects of the same region in space simultaneously (Nassi & Callaway, 361). Later in the visual system, existence of different parallel processi ...
Investigating neural correlates of conscious perception by frequency
... Binocular rivalry is a useful experimental paradigm for identifying aspects of neural activity that are correlated with conscious experience (1, 2). If two incongruent visual stimuli are simultaneously presented one through each eye, only one stimulus at a time is consciously perceived, and the two ...
... Binocular rivalry is a useful experimental paradigm for identifying aspects of neural activity that are correlated with conscious experience (1, 2). If two incongruent visual stimuli are simultaneously presented one through each eye, only one stimulus at a time is consciously perceived, and the two ...
Anatomy of the basal ganglia - Gonda Brain Research Center
... • The basal ganglia receive projections from most cortical areas • The basal ganglia project out to cortical areas involved in the generation of behavior • Act in parallel with other output systems of the cortex and thus may not play a primary role in generating ...
... • The basal ganglia receive projections from most cortical areas • The basal ganglia project out to cortical areas involved in the generation of behavior • Act in parallel with other output systems of the cortex and thus may not play a primary role in generating ...
Sensory Systems
... The neurons then emit outgoing signals via the axons. These neurons communicate with each other via chemical secretions called neurotransmitters. • The more the brain engages in problem-solving activities, the more it develops—not through gaining new neurons but through dendritic branching. ...
... The neurons then emit outgoing signals via the axons. These neurons communicate with each other via chemical secretions called neurotransmitters. • The more the brain engages in problem-solving activities, the more it develops—not through gaining new neurons but through dendritic branching. ...
Type A Personality
... – Some drink to seek novelty, some for pleasure boosting, some to relieve stress, some for harm avoidance, some for relief, and some because it is ...
... – Some drink to seek novelty, some for pleasure boosting, some to relieve stress, some for harm avoidance, some for relief, and some because it is ...
introduction and psychophysical methods
... text, submit them using the “Add Attachments” button. Question 1: Describe how the receptive field structure of neurons changes as visual information proceeds from the retina, through the LGN, and on to visual cortex. Describe how cells coding different stimulus features are organized into hypercolu ...
... text, submit them using the “Add Attachments” button. Question 1: Describe how the receptive field structure of neurons changes as visual information proceeds from the retina, through the LGN, and on to visual cortex. Describe how cells coding different stimulus features are organized into hypercolu ...
Structure of the Vertebrate Nervous System
... – responsible for higher functions such as abstract thinking and planning. – responsible for our ability to remember recent events and information (“working memory”). – allows for regulation of impulsive behaviors and the control of more complex behaviors. ...
... – responsible for higher functions such as abstract thinking and planning. – responsible for our ability to remember recent events and information (“working memory”). – allows for regulation of impulsive behaviors and the control of more complex behaviors. ...
Perceiving forms, patterns and objects
... about while remaining asleep - first 2 hours of sleep, in slow-wave sleep - may wake up while walking, may go back to bed without waking up - unknown etiology - possible genetic predisposition - not related to underlying emotional or psychological problems - peaks at age 11 or 12 – usually outgrow i ...
... about while remaining asleep - first 2 hours of sleep, in slow-wave sleep - may wake up while walking, may go back to bed without waking up - unknown etiology - possible genetic predisposition - not related to underlying emotional or psychological problems - peaks at age 11 or 12 – usually outgrow i ...
neurons
... • Read over the sheet, form a PICTURE in your mind for each brain part • Test your partner • With your partner, come up with your own mental images for: – Thalamus – Reticular formation – Occipital lobe ...
... • Read over the sheet, form a PICTURE in your mind for each brain part • Test your partner • With your partner, come up with your own mental images for: – Thalamus – Reticular formation – Occipital lobe ...
Neurobiology of Consciousness Homework 1 Problem 1 Consider a
... What are the two groups of humans that are often compared in the article? What is Ian’s argument against the mutation theory (page 59) What is Ian’s definition of “Symbolic processes” (page 60, bottom left)? For this and the next question concerning definitions, I guess we can paraphrase Theodosius ...
... What are the two groups of humans that are often compared in the article? What is Ian’s argument against the mutation theory (page 59) What is Ian’s definition of “Symbolic processes” (page 60, bottom left)? For this and the next question concerning definitions, I guess we can paraphrase Theodosius ...
PRINCIPLES OF SENSORY TRANSDUCTION
... common type of receptive field is antagonistic for location and for wavelength. Receptive field 1 is excited by turning on red light (R) at its center and is inhibited by turning on green light (G) in its surround. Receptive field 2 is less common and is antagonistic for wavelength (blue vs yellow) ...
... common type of receptive field is antagonistic for location and for wavelength. Receptive field 1 is excited by turning on red light (R) at its center and is inhibited by turning on green light (G) in its surround. Receptive field 2 is less common and is antagonistic for wavelength (blue vs yellow) ...
ch12Boundarygabor
... Striate cortex (primary visual centre) • Neurons are edge detectors fires when an edge of a particular (LGN) orientation is present infrequent output ...
... Striate cortex (primary visual centre) • Neurons are edge detectors fires when an edge of a particular (LGN) orientation is present infrequent output ...
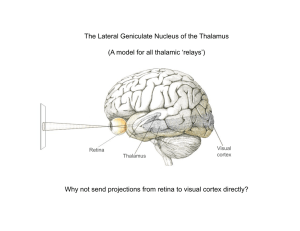
The Lateral Geniculate Nucleus of the Thalamus (A model for all
... Each LGN layer receives input from one eye only, parallel pathways to cortex ...
... Each LGN layer receives input from one eye only, parallel pathways to cortex ...
Neural correlates of consciousness

The neural correlates of consciousness (NCC) constitute the minimal set of neuronal events and mechanisms sufficient for a specific conscious percept. Neuroscientists use empirical approaches to discover neural correlates of subjective phenomena. The set should be minimal because, under the assumption that the brain is sufficient to give rise to any given conscious experience, the question is which of its components is necessary to produce it.