CASE 47
... The motor loop comprises two parallel pathways that travel from the cortex through the basal ganglia and then to the thalamus and back to the cortex (Figure 47-1). Each branch has an opposite effect on thalamic targets. The direct pathway goes through the caudate and putamen (which together form the ...
... The motor loop comprises two parallel pathways that travel from the cortex through the basal ganglia and then to the thalamus and back to the cortex (Figure 47-1). Each branch has an opposite effect on thalamic targets. The direct pathway goes through the caudate and putamen (which together form the ...
Sensory5
... Which receptor types serve DC and AL systems? Note: mechanoceptors have the largest-diameter axons and are the fastest-conducting, covered with thick myelin sheath (what kind of cell provides this sheath?) After DRG cell, axons enter SC at the dorsal root. Dermatome: Area of skin innervated by axons ...
... Which receptor types serve DC and AL systems? Note: mechanoceptors have the largest-diameter axons and are the fastest-conducting, covered with thick myelin sheath (what kind of cell provides this sheath?) After DRG cell, axons enter SC at the dorsal root. Dermatome: Area of skin innervated by axons ...
MR of Neuronal Migration Anomalies
... adjacent gyri are abnormal (small arrow). Ectopic gray matter lines frontal horn (large arrow). This patient was 17 years old when scanned, presenting with mild developmental delay and seizures. ...
... adjacent gyri are abnormal (small arrow). Ectopic gray matter lines frontal horn (large arrow). This patient was 17 years old when scanned, presenting with mild developmental delay and seizures. ...
Nolte – Chapter 3 (Gross Anatomy and General
... o III emerges from the interpeduncular fossa between the cerebral peduncles. This is just below the mammilarry bodies The infundibulum is superior to mammillary bodies. o IV the only to emerge from the dorsal side Just caudal to the inferior colliculi o V emerges from the lateral portion of th ...
... o III emerges from the interpeduncular fossa between the cerebral peduncles. This is just below the mammilarry bodies The infundibulum is superior to mammillary bodies. o IV the only to emerge from the dorsal side Just caudal to the inferior colliculi o V emerges from the lateral portion of th ...
Untitled
... If you choose to work with a complete sheep head (either fresh or preserved) begin by removing any vertebrae that may be attached to the skull and remove the skin and muscle from the top and sides of the head. This can be done with a scalpel (B). Then, using the rongeurs (D) or an autopsy saw (if av ...
... If you choose to work with a complete sheep head (either fresh or preserved) begin by removing any vertebrae that may be attached to the skull and remove the skin and muscle from the top and sides of the head. This can be done with a scalpel (B). Then, using the rongeurs (D) or an autopsy saw (if av ...
Von Economo Neurons in the Elephant Brain
... whether any of the closest relatives of the elephant have VENs, we examined brains from the rock hyrax (Heterohyrax brucei), manatee (Trichechus manatus latirostris), and giant elephant shrew, as well as xenarthrans (one species of sloth, one of armadillo, two species of anteaters, and three species ...
... whether any of the closest relatives of the elephant have VENs, we examined brains from the rock hyrax (Heterohyrax brucei), manatee (Trichechus manatus latirostris), and giant elephant shrew, as well as xenarthrans (one species of sloth, one of armadillo, two species of anteaters, and three species ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Goals and Methods
... • If it refers to 10% of brain tissue, then which ...
... • If it refers to 10% of brain tissue, then which ...
CORTICAL AFFERENT INPUT TO THE PRINCIPALS REGION OF THE RHESUS MONKEY H.
... relative proportion of labeled cells in visual, auditory, somatosensory, premotor and limbic cortical areas projecting to each site. The only site with a significant proportion of projections from visual association areas was the ventral bank of the caudal principalis region (Fig. IB, Z), whereas th ...
... relative proportion of labeled cells in visual, auditory, somatosensory, premotor and limbic cortical areas projecting to each site. The only site with a significant proportion of projections from visual association areas was the ventral bank of the caudal principalis region (Fig. IB, Z), whereas th ...
Nonlinear Changes in Brain Activity During Continuous Word
... RT. Note that random-effects analyses did not reproduce some of the activations seen with our fixed-effects approach. The inverse relationship between the anterior cingulate cortex and individual or group RT was not significant when using random-effects analyses. The right PCC, however, did remain p ...
... RT. Note that random-effects analyses did not reproduce some of the activations seen with our fixed-effects approach. The inverse relationship between the anterior cingulate cortex and individual or group RT was not significant when using random-effects analyses. The right PCC, however, did remain p ...
Psychology 10th Edition David Myers
... both manifest analytic theory) interpreted in (remembered) content and a latent many different content (hidden meaning). But why do we ways. sometimes Dreams help us sort out the day’s Informationdream about events and consolidate our processing This may be things we have memories. true,not but it R ...
... both manifest analytic theory) interpreted in (remembered) content and a latent many different content (hidden meaning). But why do we ways. sometimes Dreams help us sort out the day’s Informationdream about events and consolidate our processing This may be things we have memories. true,not but it R ...
Midterm questions to know - Doral Academy Preparatory
... 6. You go to a restaurant for dinner & the waiter gives you five choices of salad dressing. When you choose the one you want for you salad you are using ____________ processing. a. Choice b. Decision c. Top-down d. Bottom-up e. Cortical 7. You run into your psychology professor at a baseball game af ...
... 6. You go to a restaurant for dinner & the waiter gives you five choices of salad dressing. When you choose the one you want for you salad you are using ____________ processing. a. Choice b. Decision c. Top-down d. Bottom-up e. Cortical 7. You run into your psychology professor at a baseball game af ...
EN Sokolov`s Neural Model of Stimuli as Neuro
... and react to certain physical impacts of stimuli as signals. Receptors are in turn associated with selective detectors – neurons selectively responding to certain stimuli – and this connection can be either direct or, as shown, mediated by the predetectors. Selective detectors operate by the followi ...
... and react to certain physical impacts of stimuli as signals. Receptors are in turn associated with selective detectors – neurons selectively responding to certain stimuli – and this connection can be either direct or, as shown, mediated by the predetectors. Selective detectors operate by the followi ...
Nervous System - Aurora City Schools
... and bottom of each cerebral hemisphere containing the visual centers of the brain. • Primary visual cortex – processes visual information from the eyes. • Visual association cortex – identifies and makes sense of visual information. • Parietal lobes - sections of the brain located at the top and bac ...
... and bottom of each cerebral hemisphere containing the visual centers of the brain. • Primary visual cortex – processes visual information from the eyes. • Visual association cortex – identifies and makes sense of visual information. • Parietal lobes - sections of the brain located at the top and bac ...
Name: PID: SPRING 2013 COGS 1 Midterm 2 – Form B 1. Which of
... a. Prior probability b. Posterior probability c. Marginal probability d. Likelihood e. Evidence 42. Referring to an object's location as being ""due north"" is an example of a(n): a. Relative frame of reference b. Centric frame of reference c. Absolute frame of reference d. Intrinsic frame of refere ...
... a. Prior probability b. Posterior probability c. Marginal probability d. Likelihood e. Evidence 42. Referring to an object's location as being ""due north"" is an example of a(n): a. Relative frame of reference b. Centric frame of reference c. Absolute frame of reference d. Intrinsic frame of refere ...
Nervous System - Aurora City Schools
... and bottom of each cerebral hemisphere containing the visual centers of the brain. • Primary visual cortex – processes visual information from the eyes. • Visual association cortex – identifies and makes sense of visual information. • Parietal lobes - sections of the brain located at the top and bac ...
... and bottom of each cerebral hemisphere containing the visual centers of the brain. • Primary visual cortex – processes visual information from the eyes. • Visual association cortex – identifies and makes sense of visual information. • Parietal lobes - sections of the brain located at the top and bac ...
Neural correlates of thought suppression
... Additional research is needed to clarify this possibility. The methods of cognitive neuroscience have paved the way towards understanding higher mental operations, such as cognitive control. Considerable evidence has suggested that specific brain regions, notably the anterior cingulate and the insul ...
... Additional research is needed to clarify this possibility. The methods of cognitive neuroscience have paved the way towards understanding higher mental operations, such as cognitive control. Considerable evidence has suggested that specific brain regions, notably the anterior cingulate and the insul ...
Dr.Kaan Yücel yeditepeanatomyfhs122.wordpress.com Pathways in
... The only difference is the different locations where each order of neuron ends. Decussation is the cross-over of the tract from one side to the other. Therefore, there are instances where the left side of the body is controlled by the right brain hemisphere. Decussation occurs at different locations ...
... The only difference is the different locations where each order of neuron ends. Decussation is the cross-over of the tract from one side to the other. Therefore, there are instances where the left side of the body is controlled by the right brain hemisphere. Decussation occurs at different locations ...
LEAP - Life Enrichment Center
... The Learning Enhancement Advanced Program, or LEAP®, has been developed since 1985 in conjunction with clinical psychologists, speech pathologists, neurologists and other health professionals, as a very effective program for the correction of most learning difficulties. LEAP® is based on a new model ...
... The Learning Enhancement Advanced Program, or LEAP®, has been developed since 1985 in conjunction with clinical psychologists, speech pathologists, neurologists and other health professionals, as a very effective program for the correction of most learning difficulties. LEAP® is based on a new model ...
Open access
... and sharing a common excitatory input K . Being robust, it serves as foundation for other large scale optimization structures such as the TSP neural solver. The n-flop is the basic building block beyond the concept of programming with neurons [13], the term is derived from flip-flop a computer circuit ...
... and sharing a common excitatory input K . Being robust, it serves as foundation for other large scale optimization structures such as the TSP neural solver. The n-flop is the basic building block beyond the concept of programming with neurons [13], the term is derived from flip-flop a computer circuit ...
14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves
... 2. Supporting the brain. 3. Transporting nutrients, chemical messengers, and waste products. Figure 14-4 The Formation of CSF • The choroid plexus is a combination of specialized ependymal cells and capillaries that produce cerebrospinal fluid. The ependymal cells secrete CSF into the ventricles, re ...
... 2. Supporting the brain. 3. Transporting nutrients, chemical messengers, and waste products. Figure 14-4 The Formation of CSF • The choroid plexus is a combination of specialized ependymal cells and capillaries that produce cerebrospinal fluid. The ependymal cells secrete CSF into the ventricles, re ...
Is neuroimaging measuring information in the brain? | SpringerLink
... modern neuroscience, perhaps because, for the communication systems which he was considering, he merely stated that (p. 2) ‘The receiver ordinarily performs the inverse operation of that done by the transmitter’, and he did not elaborate much further on this point. We will give two examples, a simpl ...
... modern neuroscience, perhaps because, for the communication systems which he was considering, he merely stated that (p. 2) ‘The receiver ordinarily performs the inverse operation of that done by the transmitter’, and he did not elaborate much further on this point. We will give two examples, a simpl ...
phys chapter 51 [3-20
... o When fixation area destroyed bilaterally, animal has difficulty keeping eyes directed toward given fixation point or may become totally unable to do so Involuntary locking fixation results from negative feedback mechanism that prevents object of attention from leaving foveal portion of retina Eyes ...
... o When fixation area destroyed bilaterally, animal has difficulty keeping eyes directed toward given fixation point or may become totally unable to do so Involuntary locking fixation results from negative feedback mechanism that prevents object of attention from leaving foveal portion of retina Eyes ...
Dopamine control of pyramidal neuron activity in the primary motor
... Given the demonstrated role for DA in fine motor skill learning in M1, our results suggest that altered D2 modulation of M1 activity may be involved in the pathophysiology of movement disorders associated with disturbed DA homeostasis. ...
... Given the demonstrated role for DA in fine motor skill learning in M1, our results suggest that altered D2 modulation of M1 activity may be involved in the pathophysiology of movement disorders associated with disturbed DA homeostasis. ...
D.U.C. Assist. Lec. Faculty of Dentistry General Physiology Ihsan
... of the human cerebral cortex, showing that it is divided into about 50 distinct areas called Brodmann’s areas based on histological structural differences. Note in the (figure 1) the large central fissure (also called central sulcus) that extends horizontally across the brain. In general, sensory si ...
... of the human cerebral cortex, showing that it is divided into about 50 distinct areas called Brodmann’s areas based on histological structural differences. Note in the (figure 1) the large central fissure (also called central sulcus) that extends horizontally across the brain. In general, sensory si ...
What Musicians can Learn about Practicing from Current Brain
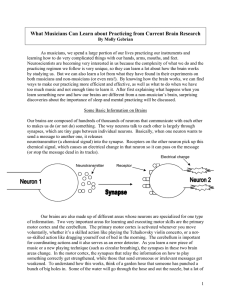
... other simple patterns that are automatic to us that entire brain areas don’t get engaged in a musician’s brain that are very active in a non-musician or amateur’s brain. Two of these areas are the pre-motor cortex and the supplementary motor area. These are involved in planning complex movements and ...
... other simple patterns that are automatic to us that entire brain areas don’t get engaged in a musician’s brain that are very active in a non-musician or amateur’s brain. Two of these areas are the pre-motor cortex and the supplementary motor area. These are involved in planning complex movements and ...
Neural correlates of consciousness

The neural correlates of consciousness (NCC) constitute the minimal set of neuronal events and mechanisms sufficient for a specific conscious percept. Neuroscientists use empirical approaches to discover neural correlates of subjective phenomena. The set should be minimal because, under the assumption that the brain is sufficient to give rise to any given conscious experience, the question is which of its components is necessary to produce it.