The hidden side of the UPR signalling pathway - Reflexions
... The molecular mechanism that controls the choice of the stem cell's differentiative division was still unknown up until now. Why and how does this cell chooses to give birth to a neuron and a stem cell or an intermediate progenitor and a stem cell? The literature still provided no answer to thi ...
... The molecular mechanism that controls the choice of the stem cell's differentiative division was still unknown up until now. Why and how does this cell chooses to give birth to a neuron and a stem cell or an intermediate progenitor and a stem cell? The literature still provided no answer to thi ...
INFORMATION PROCESSING WITH POPULATION CODES
... words, were we to present the same stimulus on many trials, the average estimate over all the trials would equal the true direction of motion of the stimulus, and the variance would be as small as possible12–14. Although ML is often the optimal decoding method13, it requires substantial data, as a p ...
... words, were we to present the same stimulus on many trials, the average estimate over all the trials would equal the true direction of motion of the stimulus, and the variance would be as small as possible12–14. Although ML is often the optimal decoding method13, it requires substantial data, as a p ...
Some Analogies Between Visual Cortical and Genetic Maps
... One of the central ideas of modern genetics is that a particular gene contains the instructions to make a particular protein that has a specific function. One example is the system of genes for photoreceptor proteins. Recently, Nathans et aj30 have mapped the DNA sequences of the genes for the rod a ...
... One of the central ideas of modern genetics is that a particular gene contains the instructions to make a particular protein that has a specific function. One example is the system of genes for photoreceptor proteins. Recently, Nathans et aj30 have mapped the DNA sequences of the genes for the rod a ...
Article Page 08.27.20+
... feedback projections from V1 than it sends (Rockland, 2002). And this seems to be the rule rather than the exception. What is the purpose of this massive feedback system? The answer actually depends on where you are looking. For the early stages of visual processing, like the V1/LGN feedback system ...
... feedback projections from V1 than it sends (Rockland, 2002). And this seems to be the rule rather than the exception. What is the purpose of this massive feedback system? The answer actually depends on where you are looking. For the early stages of visual processing, like the V1/LGN feedback system ...
THALAMUS
... the thalamus, separating it into medial and lateral nuclear masses. The medial mass consists of the medial nuclear group; the lateral mass contains the lateral nuclear group and the ventral nuclear group. In the rostral part of the thalamus the internal medullary lamina splits to form a partial caps ...
... the thalamus, separating it into medial and lateral nuclear masses. The medial mass consists of the medial nuclear group; the lateral mass contains the lateral nuclear group and the ventral nuclear group. In the rostral part of the thalamus the internal medullary lamina splits to form a partial caps ...
Carl L.Faingold, Manish Raisinghani, Prosper N`Gouemo
... FIGURE 26.3 GABA-mediated inhibition defects in GEPR-9s: GABAergic neurotransmission normally plays a critical role in determining the responses of the inferior colliculus (IC) to acoustic stimulation, and defects in specific forms of inhibition are key causative factors in audiogenic seizure initi ...
... FIGURE 26.3 GABA-mediated inhibition defects in GEPR-9s: GABAergic neurotransmission normally plays a critical role in determining the responses of the inferior colliculus (IC) to acoustic stimulation, and defects in specific forms of inhibition are key causative factors in audiogenic seizure initi ...
neuron number decreases in the rat ventral, but not dorsal, medial
... is suggested by our previous work in rats: the neuronal loss in the cortex which takes place relatively late in development (Nunez et al., 2001, 2002). Loss of neurons could contribute to the observed changes in both synaptic density and cortical volume. Prior work from our laboratory has shown that ...
... is suggested by our previous work in rats: the neuronal loss in the cortex which takes place relatively late in development (Nunez et al., 2001, 2002). Loss of neurons could contribute to the observed changes in both synaptic density and cortical volume. Prior work from our laboratory has shown that ...
49 BIOLOGY Nervous Systems CAMPBELL
... To distinguish between genetic and environmental variables, scientists often carry out family studies ...
... To distinguish between genetic and environmental variables, scientists often carry out family studies ...
Schizophrenia is a multi-faceted disorder with highly complex p
... These regions occupy a unique anatomical place within the realm of cortical and sub-cortical connections receiving inputs from the sensory areas in unimodal association cortex and from heteromodal areas such as the dorsal and ventral prefrontal cortex via the entorhinal cortex. This region is theref ...
... These regions occupy a unique anatomical place within the realm of cortical and sub-cortical connections receiving inputs from the sensory areas in unimodal association cortex and from heteromodal areas such as the dorsal and ventral prefrontal cortex via the entorhinal cortex. This region is theref ...
The plasticity of human maternal brain: longitudinal changes in brain anatomy during the early postpartum period
... matter volumes in large regions of the prefrontal cortex, parietal lobe, and midbrain were found. Furthermore, a mother’s positive thoughts on her baby at the first month postpartum predicted gray matter volume increase from the first month to 3– 4 months postpartum. This postpartum period marks a c ...
... matter volumes in large regions of the prefrontal cortex, parietal lobe, and midbrain were found. Furthermore, a mother’s positive thoughts on her baby at the first month postpartum predicted gray matter volume increase from the first month to 3– 4 months postpartum. This postpartum period marks a c ...
Inferring functional connections between neurons
... particular importance, since the anatomy of the retina is well known, and the connections in in vitro preparations can potentially be imaged. In both the retina and cultures of neurons there is a strong relationship between the spatial layout of the network and the measured functional connectivity. ...
... particular importance, since the anatomy of the retina is well known, and the connections in in vitro preparations can potentially be imaged. In both the retina and cultures of neurons there is a strong relationship between the spatial layout of the network and the measured functional connectivity. ...
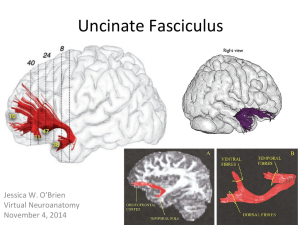
Uncinate Fasciculus
... • During a go/no-‐go task, neurons had differenOal responses to whether a sOmulus indicated reward • Reversing the sOmuli indicated that some neurons were linked to sensory features of sOmuli, some to th ...
... • During a go/no-‐go task, neurons had differenOal responses to whether a sOmulus indicated reward • Reversing the sOmuli indicated that some neurons were linked to sensory features of sOmuli, some to th ...
Lecoq J, Savall J, Vucinic D, Grewe BF, Kim H, Li
... Moreover, microendoscopy is already well established as a means of imaging deep brain areas5–7. To illustrate that our dual-axis approach also enables studies in which one or both of the brain areas lie below the neocortex, we imaged TdTomato-expressing parvalbumin interneurons simultaneously in the ...
... Moreover, microendoscopy is already well established as a means of imaging deep brain areas5–7. To illustrate that our dual-axis approach also enables studies in which one or both of the brain areas lie below the neocortex, we imaged TdTomato-expressing parvalbumin interneurons simultaneously in the ...
motor systems
... cord, they enter the spinal gray matter, where they ramify and synapse. A small fraction of these axons synapse directly on motor neurons in Rexed’s lamina IX. Most of the corticospinal neurons that make such monosynaptic connections to motor neurons have their somata in the anterior bank of the cen ...
... cord, they enter the spinal gray matter, where they ramify and synapse. A small fraction of these axons synapse directly on motor neurons in Rexed’s lamina IX. Most of the corticospinal neurons that make such monosynaptic connections to motor neurons have their somata in the anterior bank of the cen ...
Neuroimaging of cognitive functions in human parietal cortex Jody C
... tools for mapping the human brain. Neuroimaging has been particularly successful in mapping cortical visual areas in the human occipital [1] and temporal [2] lobes. The human parietal lobes (excluding somatosensory regions, which are not discussed here), which traditionally fall into the category of ...
... tools for mapping the human brain. Neuroimaging has been particularly successful in mapping cortical visual areas in the human occipital [1] and temporal [2] lobes. The human parietal lobes (excluding somatosensory regions, which are not discussed here), which traditionally fall into the category of ...
Neuroembryology of Neural Tube Defects
... Development of the Neural Tube Lateral walls of neural tube thicken, gradually reduce the size of the neural canal until only a small central canal remains. Differential thickening of the lateral walls produces a shallow longitudinal groove on each side = sulcus limitans. Dorsal part = alar plate ( ...
... Development of the Neural Tube Lateral walls of neural tube thicken, gradually reduce the size of the neural canal until only a small central canal remains. Differential thickening of the lateral walls produces a shallow longitudinal groove on each side = sulcus limitans. Dorsal part = alar plate ( ...
Pioneers of cortical plasticity: six classic papers by Wiesel and Hubel
... competition from the nondeprived eye in a small region of cortex and experimentally support the hypothesis that the atrophy in the LGN arose from competition between the eye-specific inputs in the cortex. On the basis of long-term dark rearing from birth in a variety of mammals, a number of early in ...
... competition from the nondeprived eye in a small region of cortex and experimentally support the hypothesis that the atrophy in the LGN arose from competition between the eye-specific inputs in the cortex. On the basis of long-term dark rearing from birth in a variety of mammals, a number of early in ...
17 Human Single Unit Activity for Reach and Grasp Motor Prostheses
... So far we have described a static view of the neuronal encoding of reach and grasp parameters such as end-point position, grasp aperture, and force. Reach and grasp movements, however, occur not just in 3-D space, but also in time. Thus, improved understanding of how neurons code for trajectories of ...
... So far we have described a static view of the neuronal encoding of reach and grasp parameters such as end-point position, grasp aperture, and force. Reach and grasp movements, however, occur not just in 3-D space, but also in time. Thus, improved understanding of how neurons code for trajectories of ...
The Constructive Nature of Visual Processing
... The number of functionally discrete areas of visual cortex varies between species. Macaque monkeys have more than 30 areas. Although not all visual areas in humans have yet been identified, the number is likely to be at least as great as in the macaque. If one includes oculomotor areas and prefronta ...
... The number of functionally discrete areas of visual cortex varies between species. Macaque monkeys have more than 30 areas. Although not all visual areas in humans have yet been identified, the number is likely to be at least as great as in the macaque. If one includes oculomotor areas and prefronta ...
the neurobiology of emotion
... basal nucleus and the accessory basal nucleus. All sensory inputs terminate in the lateral nucleus, which then projects to each of the other three nuclei; the basal and accessory basal both feed into the central nucleus. The central nucleus (CeA) contains the output cells of the amygdala and connect ...
... basal nucleus and the accessory basal nucleus. All sensory inputs terminate in the lateral nucleus, which then projects to each of the other three nuclei; the basal and accessory basal both feed into the central nucleus. The central nucleus (CeA) contains the output cells of the amygdala and connect ...
hypothalamic neuroanatomy and limbic inputs
... processes. These include homeostatic control of temperature, metabolism, and body weight, aspects of cardiovascular function, physiologic adaptation to stress, regulation of growth, reproduction (including sexual behavior), and lactation. Although the regulation of these complex processes depends on ...
... processes. These include homeostatic control of temperature, metabolism, and body weight, aspects of cardiovascular function, physiologic adaptation to stress, regulation of growth, reproduction (including sexual behavior), and lactation. Although the regulation of these complex processes depends on ...
Mirror neurons in monkey area F5 do not adapt to the observation of
... results in a decrease of the responses of single neurons in a variety of areas in monkey visual cortex. They include area V1 (ref. 1), extrastriate visual areas1–4, as well as areas in the inferior5–15 and the medial temporal lobe16–18. This response decrease has been varyingly called ‘adaptation’18 ...
... results in a decrease of the responses of single neurons in a variety of areas in monkey visual cortex. They include area V1 (ref. 1), extrastriate visual areas1–4, as well as areas in the inferior5–15 and the medial temporal lobe16–18. This response decrease has been varyingly called ‘adaptation’18 ...
Basal Ganglia Subcircuits Distinctively Encode the
... Animals were first trained to acquire a regular sequence task under fixed-ratio 4 schedule as described before 9. Training started with a 30 minute magazine training session in which the reinforcer was delivered on a random time schedule, on average every 60 seconds (30 reinforcers). The following d ...
... Animals were first trained to acquire a regular sequence task under fixed-ratio 4 schedule as described before 9. Training started with a 30 minute magazine training session in which the reinforcer was delivered on a random time schedule, on average every 60 seconds (30 reinforcers). The following d ...
Auditory Cortex (1)
... In this chapter and elsewhere, we have stressed the diversity of the neural coding properties of the units in the auditory cortex. This diversity makes the cortex a difficult region to study and makes it especially unattractive to those who like their science in neat packages. Let us hope that new ...
... In this chapter and elsewhere, we have stressed the diversity of the neural coding properties of the units in the auditory cortex. This diversity makes the cortex a difficult region to study and makes it especially unattractive to those who like their science in neat packages. Let us hope that new ...
Advanced biomaterial strategies to transplant preformed micro
... In recent work, we have demonstrated initial efforts to create micro-TENNs using multiple neuronal subtypes, the ability to stereotactically deliver preformed micro-TENNs into the rodent brain, as well as transplant neuronal survival, maintenance of axonal architecture, and synaptic integration with ...
... In recent work, we have demonstrated initial efforts to create micro-TENNs using multiple neuronal subtypes, the ability to stereotactically deliver preformed micro-TENNs into the rodent brain, as well as transplant neuronal survival, maintenance of axonal architecture, and synaptic integration with ...
Neural correlates of consciousness

The neural correlates of consciousness (NCC) constitute the minimal set of neuronal events and mechanisms sufficient for a specific conscious percept. Neuroscientists use empirical approaches to discover neural correlates of subjective phenomena. The set should be minimal because, under the assumption that the brain is sufficient to give rise to any given conscious experience, the question is which of its components is necessary to produce it.