Endelige eksamen 27008 MED svar
... Two individuals have a mutation in gene X but at different sites. The mutation affects the first individual adversely, and the second individual experiences no effect. Explain this observation. Answer: Example of a correct answer: The mutation in gene X in the first individual must have occurred in ...
... Two individuals have a mutation in gene X but at different sites. The mutation affects the first individual adversely, and the second individual experiences no effect. Explain this observation. Answer: Example of a correct answer: The mutation in gene X in the first individual must have occurred in ...
UK_National_Collaborative_Usher_Study
... Changes in the DNA sequence are called variants. Variants can be pathogenic or they could be neutral (this is when they would be called polymorphisms). Q. What is haplotype analysis? Haplotype analysis is a test to identify sections of DNA that are similar to each other. Q. What is a genotype? A gen ...
... Changes in the DNA sequence are called variants. Variants can be pathogenic or they could be neutral (this is when they would be called polymorphisms). Q. What is haplotype analysis? Haplotype analysis is a test to identify sections of DNA that are similar to each other. Q. What is a genotype? A gen ...
uk national collaborative usher study
... Changes in the DNA sequence are called variants. Variants can be pathogenic or they could be neutral (this is when they would be called polymorphisms). Q. What is haplotype analysis? Haplotype analysis is a test to identify sections of DNA that are similar to each other. Q. What is a genotype? A gen ...
... Changes in the DNA sequence are called variants. Variants can be pathogenic or they could be neutral (this is when they would be called polymorphisms). Q. What is haplotype analysis? Haplotype analysis is a test to identify sections of DNA that are similar to each other. Q. What is a genotype? A gen ...
Cross-Product Extensions of the Gene Ontology
... biological quality – these comprise 3 distinct crossproduct sets. The first two are intra-GO; the latter references terms from the PATO ontology of biological qualities7, together with anatomical ontologies. The cross products make use of 3 new relations introduced into GO – regulates, negatively_re ...
... biological quality – these comprise 3 distinct crossproduct sets. The first two are intra-GO; the latter references terms from the PATO ontology of biological qualities7, together with anatomical ontologies. The cross products make use of 3 new relations introduced into GO – regulates, negatively_re ...
Predicting functional linkages from gene fusions with
... are described, of which 117 apply to E. coli. Example KEGG categories are shown in Table 1. Unfortunately, the KEGG functional categories also suffer from certain limitations. Primarily, they are not defined according to objective criteria—some categories represent not pathways, but homologous prote ...
... are described, of which 117 apply to E. coli. Example KEGG categories are shown in Table 1. Unfortunately, the KEGG functional categories also suffer from certain limitations. Primarily, they are not defined according to objective criteria—some categories represent not pathways, but homologous prote ...
A1981LF07700001
... that I received my postdoctoral training. "In the 1960s the emphasis was on the 'mechanism' of phytochrome action, i.e., the biophysical and molecular steps leading from the formation of active phytochrome to the final displays (photoresponses). As a convenient guiding principle in studies about the ...
... that I received my postdoctoral training. "In the 1960s the emphasis was on the 'mechanism' of phytochrome action, i.e., the biophysical and molecular steps leading from the formation of active phytochrome to the final displays (photoresponses). As a convenient guiding principle in studies about the ...
Poster
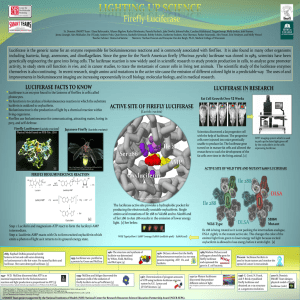
... Luciferase is the generic name for an enzyme responsible for bioluminescence reactions and is commonly associated with fireflies. It is also found in many other organisms including bacteria, fungi, anemones, and dinoflagellates. Since the gene for the North American firefly (Photinus pyralis) lucife ...
... Luciferase is the generic name for an enzyme responsible for bioluminescence reactions and is commonly associated with fireflies. It is also found in many other organisms including bacteria, fungi, anemones, and dinoflagellates. Since the gene for the North American firefly (Photinus pyralis) lucife ...
Genes & Inheritance Series: Set 3 Copyright © 2005 Version: 2.0
... Cells need to control the rate and frequency of protein synthesis. These controls often occur at transcription. Sometimes genes are induced (and therefore transcribed) only when an enzyme product is required to catalyze reactions that may occur infrequently, e.g. use of a particular substrate that i ...
... Cells need to control the rate and frequency of protein synthesis. These controls often occur at transcription. Sometimes genes are induced (and therefore transcribed) only when an enzyme product is required to catalyze reactions that may occur infrequently, e.g. use of a particular substrate that i ...
Cell Fate Specification in the C. elegans Embryo
... Fig. 1. Partial C. elegans lineage, diagram and images showing stages of embryogenesis. A: The zygote undergoes a set of asymmetric cleavages to generate the six founder cells, AB, MS, E, C, D, and P4 (Sulston et al., 1983). Anterior cells are to the left. B: Diagram of early and midembryogenesis st ...
... Fig. 1. Partial C. elegans lineage, diagram and images showing stages of embryogenesis. A: The zygote undergoes a set of asymmetric cleavages to generate the six founder cells, AB, MS, E, C, D, and P4 (Sulston et al., 1983). Anterior cells are to the left. B: Diagram of early and midembryogenesis st ...
Course details
... • In general, filter based arrays were in vogue about 8-13 years ago in the pre-genomic days. • Typically cDNA libraries were spotted as clones and the arrays were used to perform comparative expression analysis. • Detection was typically performed with radioactive labeling/film or phosphorimaging. ...
... • In general, filter based arrays were in vogue about 8-13 years ago in the pre-genomic days. • Typically cDNA libraries were spotted as clones and the arrays were used to perform comparative expression analysis. • Detection was typically performed with radioactive labeling/film or phosphorimaging. ...
Self-association of the SET domains of human ALL-1 and of
... to self-associate in yeast (Figure 5a). In contrast, mutagenesis of three nonconserved residues located within the SET domain or immediately upstream of it did not aect the interaction. In all cases, the expression level of the mutated polypeptides in yeast was monitored by Western blot analysis (F ...
... to self-associate in yeast (Figure 5a). In contrast, mutagenesis of three nonconserved residues located within the SET domain or immediately upstream of it did not aect the interaction. In all cases, the expression level of the mutated polypeptides in yeast was monitored by Western blot analysis (F ...
Download PDF
... physical characteristics as biomarkers and is a primary bottleneck in the adoption of microfluidic technologies to discriminate cells based on those characteristics. Although this type of bottom-up prediction of physical properties is currently intractable, an alternate top-down approach is to work ...
... physical characteristics as biomarkers and is a primary bottleneck in the adoption of microfluidic technologies to discriminate cells based on those characteristics. Although this type of bottom-up prediction of physical properties is currently intractable, an alternate top-down approach is to work ...
video slide - Morgan Community College
... Apply the cDNA mixture to a microarray, a microscope slide on which copies of singlestranded DNA fragments from the organism’s genes are fixed, a different gene in each spot. The cDNA hybridizes with any complementary DNA on the microarray. Rinse off excess cDNA; scan microarray for fluorescent. Eac ...
... Apply the cDNA mixture to a microarray, a microscope slide on which copies of singlestranded DNA fragments from the organism’s genes are fixed, a different gene in each spot. The cDNA hybridizes with any complementary DNA on the microarray. Rinse off excess cDNA; scan microarray for fluorescent. Eac ...
Activation of hilA expression at low pH requires the signal sensor
... sonnei. The authors examined whether the cpxR–cpxA homologues have some function in the expression of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium invasion genes via the regulation of hilA, an activator for these genes. In a Salmonella cpxA mutant, the hilA expression level was reduced to less than 10 % ...
... sonnei. The authors examined whether the cpxR–cpxA homologues have some function in the expression of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium invasion genes via the regulation of hilA, an activator for these genes. In a Salmonella cpxA mutant, the hilA expression level was reduced to less than 10 % ...
video slide
... Apply the cDNA mixture to a microarray, a microscope slide on which copies of singlestranded DNA fragments from the organism’s genes are fixed, a different gene in each spot. The cDNA hybridizes with any complementary DNA on the microarray. Rinse off excess cDNA; scan microarray for fluorescent. Eac ...
... Apply the cDNA mixture to a microarray, a microscope slide on which copies of singlestranded DNA fragments from the organism’s genes are fixed, a different gene in each spot. The cDNA hybridizes with any complementary DNA on the microarray. Rinse off excess cDNA; scan microarray for fluorescent. Eac ...
Back-translation Using First Order Hidden Markov Models
... backtrack to deduce with perfect accuracy the exact mRNA strand which gave rise to a particular peptide, we can attempt to statistically determine which of the possible mRNA strands acts as the most likely predecessor. In [7], it was shown that "the choice of codons for reverse translation can be re ...
... backtrack to deduce with perfect accuracy the exact mRNA strand which gave rise to a particular peptide, we can attempt to statistically determine which of the possible mRNA strands acts as the most likely predecessor. In [7], it was shown that "the choice of codons for reverse translation can be re ...
pathological effect of endothelial-to
... Sookmyung Women's University, Yongsan-gu, Seoul, Korea Objectives: We research on pathological effects of endothelial to mesenchymal transition (EndMT) on cystic kidney. Furthermore, we try to find novel genes inducing endMT on it. Background: EndMT is a phenomenon that an endothelial cell loses its ...
... Sookmyung Women's University, Yongsan-gu, Seoul, Korea Objectives: We research on pathological effects of endothelial to mesenchymal transition (EndMT) on cystic kidney. Furthermore, we try to find novel genes inducing endMT on it. Background: EndMT is a phenomenon that an endothelial cell loses its ...
Cdiff_expression_supmat_BiolInv.
... encodes a a novel transcriptional repressor harboring two double-stranded RNAbinding domains and a region homologous to the catalytic domain of RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain phosphatases found in yeast and in animals that regulate gene transcription. Protein exhibits innate phosphatase activit ...
... encodes a a novel transcriptional repressor harboring two double-stranded RNAbinding domains and a region homologous to the catalytic domain of RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain phosphatases found in yeast and in animals that regulate gene transcription. Protein exhibits innate phosphatase activit ...
E NEWS -
... boonei: the Reysenbach Lab at Portland State. With their aid, he was able to purify A. boonei’s GH25-muramidase domain, a step that was needed to determine the enzyme’s function. ...
... boonei: the Reysenbach Lab at Portland State. With their aid, he was able to purify A. boonei’s GH25-muramidase domain, a step that was needed to determine the enzyme’s function. ...
Control of notochord gene expression by Brachyury
... -In Ciona, Brachyury controls its direct transcriptional targets through two mechanisms: small clusters of cooperative binding sites or individual binding sites -cooperative and individual binding sites control earlyonset and middle-onset targets, respectively ...
... -In Ciona, Brachyury controls its direct transcriptional targets through two mechanisms: small clusters of cooperative binding sites or individual binding sites -cooperative and individual binding sites control earlyonset and middle-onset targets, respectively ...
File
... Methods: Control and breast tumor (~5-6 mm3) bearing female rats were treated with vehicle, SFN (40 mg/kg oral; 5 days/week), DOX (total of 20 mg/kg, i.p. for 4 weeks) and SFN+DOX. At the end of the regimens cardiac function, tumor growth, Nrf2 activation, transcription level of antioxidant/anti-ele ...
... Methods: Control and breast tumor (~5-6 mm3) bearing female rats were treated with vehicle, SFN (40 mg/kg oral; 5 days/week), DOX (total of 20 mg/kg, i.p. for 4 weeks) and SFN+DOX. At the end of the regimens cardiac function, tumor growth, Nrf2 activation, transcription level of antioxidant/anti-ele ...
Relationship between codon biased genes, microarray expression
... of highly expressed genes had a codon usage bias and w values below 0?1 (10-fold less than the preferred isocodon), only one codon in the data for the whole genome set had a w value less than 0?1 (Table 1). The CAI algorithm was applied to 1802 non-RP full-length gene sequences from the TIGR4 strain ...
... of highly expressed genes had a codon usage bias and w values below 0?1 (10-fold less than the preferred isocodon), only one codon in the data for the whole genome set had a w value less than 0?1 (Table 1). The CAI algorithm was applied to 1802 non-RP full-length gene sequences from the TIGR4 strain ...
IB Image Review Key
... contact proteins at the promoter, initiating transcription. • Coordinate regulation: Enhancer for liver-specific genes ...
... contact proteins at the promoter, initiating transcription. • Coordinate regulation: Enhancer for liver-specific genes ...
Gene regulatory network

A gene regulatory network or genetic regulatory network (GRN) is a collection of regulators thatinteract with each other and with other substances in the cell to govern the gene expression levels of mRNA and proteins.The regulator can be DNA, RNA, protein and their complex. The interaction can be direct or indirect (through their transcribed RNA or translated protein).In general, each mRNA molecule goes on to make a specific protein (or set of proteins). In some cases this protein will be structural, and will accumulate at the cell membrane or within the cell to give it particular structural properties. In other cases the protein will be an enzyme, i.e., a micro-machine that catalyses a certain reaction, such as the breakdown of a food source or toxin. Some proteins though serve only to activate other genes, and these are the transcription factors that are the main players in regulatory networks or cascades. By binding to the promoter region at the start of other genes they turn them on, initiating the production of another protein, and so on. Some transcription factors are inhibitory.In single-celled organisms, regulatory networks respond to the external environment, optimising the cell at a given time for survival in this environment. Thus a yeast cell, finding itself in a sugar solution, will turn on genes to make enzymes that process the sugar to alcohol. This process, which we associate with wine-making, is how the yeast cell makes its living, gaining energy to multiply, which under normal circumstances would enhance its survival prospects.In multicellular animals the same principle has been put in the service of gene cascades that control body-shape. Each time a cell divides, two cells result which, although they contain the same genome in full, can differ in which genes are turned on and making proteins. Sometimes a 'self-sustaining feedback loop' ensures that a cell maintains its identity and passes it on. Less understood is the mechanism of epigenetics by which chromatin modification may provide cellular memory by blocking or allowing transcription. A major feature of multicellular animals is the use of morphogen gradients, which in effect provide a positioning system that tells a cell where in the body it is, and hence what sort of cell to become. A gene that is turned on in one cell may make a product that leaves the cell and diffuses through adjacent cells, entering them and turning on genes only when it is present above a certain threshold level. These cells are thus induced into a new fate, and may even generate other morphogens that signal back to the original cell. Over longer distances morphogens may use the active process of signal transduction. Such signalling controls embryogenesis, the building of a body plan from scratch through a series of sequential steps. They also control and maintain adult bodies through feedback processes, and the loss of such feedback because of a mutation can be responsible for the cell proliferation that is seen in cancer. In parallel with this process of building structure, the gene cascade turns on genes that make structural proteins that give each cell the physical properties it needs.It has been suggested that, because biological molecular interactions are intrinsically stochastic, gene networks are the result of cellular processes and not their cause (i.e. cellular Darwinism). However, recent experimental evidence has favored the attractor view of cell fates.