Exercise 2: Sentence length Determine the distribution of words per
... detects eavesdroppers and errors almost immediately---to ensure not only that votes are kept secret but also that they are all counted. In quantum cryptography, as in most long-distance data transmission, the information is carried by photons, the particles which compose light and other sorts of ele ...
... detects eavesdroppers and errors almost immediately---to ensure not only that votes are kept secret but also that they are all counted. In quantum cryptography, as in most long-distance data transmission, the information is carried by photons, the particles which compose light and other sorts of ele ...
problem set
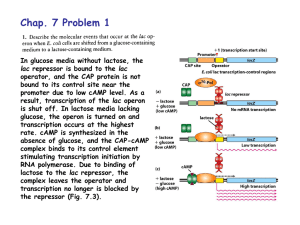
... transcription start site for genes. The TATA box is found in genes that are strongly expressed, and therefore was the first promoter element to be identified by in vitro transcription assays. In addition, the transcription start site occurs at a fixed location downstream of a TATA box (Fig. 7.14). ...
... transcription start site for genes. The TATA box is found in genes that are strongly expressed, and therefore was the first promoter element to be identified by in vitro transcription assays. In addition, the transcription start site occurs at a fixed location downstream of a TATA box (Fig. 7.14). ...
Dr. Jacob. P. L. Brand Statement of Research philosophy (205)
... basis of predictive information from surrounding genes and specifies for each gene the individual type 1 error allowed in declaring this gene significant. If a highly differentially expressed gene is strongly correlated to many non-differentially expressed genes, than this gene is acting “out of ord ...
... basis of predictive information from surrounding genes and specifies for each gene the individual type 1 error allowed in declaring this gene significant. If a highly differentially expressed gene is strongly correlated to many non-differentially expressed genes, than this gene is acting “out of ord ...
Alan Wolffe (1959-2001) - Journal of Cell Science
... solve or wasting any time getting moving with a new project. Even as a busy PhD student, he was always ready to help others around him, especially those having difficulties with their research, and always with that wonderful smile of his. No wonder he made innumerable friends - friendships that he n ...
... solve or wasting any time getting moving with a new project. Even as a busy PhD student, he was always ready to help others around him, especially those having difficulties with their research, and always with that wonderful smile of his. No wonder he made innumerable friends - friendships that he n ...
sample
... 8. Alkyltransferase is required for direct reversal of photodimers. 9. A mutation that leads to the overexpression of a normal protein can lead to a dominant oncogenic mutation. 10. The normal activity of the RB protein is to negatively regulate the progression from G1 to S of the cell cycle. ...
... 8. Alkyltransferase is required for direct reversal of photodimers. 9. A mutation that leads to the overexpression of a normal protein can lead to a dominant oncogenic mutation. 10. The normal activity of the RB protein is to negatively regulate the progression from G1 to S of the cell cycle. ...
Prokaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives)
... 4. Compare and contrast the molecular mechanism (on/off switches) controlling expression of repressible and inducible operons. ...
... 4. Compare and contrast the molecular mechanism (on/off switches) controlling expression of repressible and inducible operons. ...
chapter 19 the organization and control of eukaryotic
... Eukaryotic repressors can cause inhibition of gene expression by blocking the binding of activators to their control elements or to components of the transcription machinery or by turning off transcription even in the presence of activators. Some activators and repressors act indirectly to influen ...
... Eukaryotic repressors can cause inhibition of gene expression by blocking the binding of activators to their control elements or to components of the transcription machinery or by turning off transcription even in the presence of activators. Some activators and repressors act indirectly to influen ...
Regulation of virulence gene expression
... In contrast, temperature and iron availability have long been recognised as triggers for modulating gene expression in bacterial pathogens. Induction of virulence gene expression as a result of a shift to 37oC or a depletion of extracellular iron is a common theme in bacterial pathogenicity. Many re ...
... In contrast, temperature and iron availability have long been recognised as triggers for modulating gene expression in bacterial pathogens. Induction of virulence gene expression as a result of a shift to 37oC or a depletion of extracellular iron is a common theme in bacterial pathogenicity. Many re ...
Slide 1
... Half of the world’s cotton is GM. Around half of you are probably wearing TRUEGMorpants! FALSE ...
... Half of the world’s cotton is GM. Around half of you are probably wearing TRUEGMorpants! FALSE ...
industrial biotechnology basics
... Enzymes are proteins that catalyze (i.e., increase the rates of) chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates, and the enzyme converts them into different molecules, called the products. products Almost all processes in a biological ...
... Enzymes are proteins that catalyze (i.e., increase the rates of) chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates, and the enzyme converts them into different molecules, called the products. products Almost all processes in a biological ...
A gene trap Dissociation insertion line, associated with a RING
... Real interesting new gene (RING) finger proteins act as E3 ubiquitin-protein ligases and play critical roles in targeting the destruction of proteins of diverse functions in all eukaryotes, ranging from yeast to mammals. Arabidopsis genome contains a large number of genes encoding RING finger protei ...
... Real interesting new gene (RING) finger proteins act as E3 ubiquitin-protein ligases and play critical roles in targeting the destruction of proteins of diverse functions in all eukaryotes, ranging from yeast to mammals. Arabidopsis genome contains a large number of genes encoding RING finger protei ...
Facts for Consumers - Physicians and Scientists for Global
... The isolated genetic information is then inserted into the genome of a new host. This is done by constructing a VECTOR that can invade the genome of the new host and insert the foreign DNA sequences into it. The inserted DNA sequence is usually made up of the TRANSGENE (the chosen genetic informatio ...
... The isolated genetic information is then inserted into the genome of a new host. This is done by constructing a VECTOR that can invade the genome of the new host and insert the foreign DNA sequences into it. The inserted DNA sequence is usually made up of the TRANSGENE (the chosen genetic informatio ...
AP review
... • There should be a correlation between amino acid sequence and secondary structure. Short aa sequence is more likely to form one type of SS than another. • Local interactions determine SS. SS of a residues is determined by their neighbors (usually a sequence window of 13-17 residues is used). ...
... • There should be a correlation between amino acid sequence and secondary structure. Short aa sequence is more likely to form one type of SS than another. • Local interactions determine SS. SS of a residues is determined by their neighbors (usually a sequence window of 13-17 residues is used). ...
Control of intra-cellular (enzyme regulator)
... Control of metabolism can be simplified into: a) Control of intra-cellular (enzymes regulator) b) Systemic control (blood glucose) ...
... Control of metabolism can be simplified into: a) Control of intra-cellular (enzymes regulator) b) Systemic control (blood glucose) ...
Genome Anatomy - K
... further subdivided to produce a hierarchy of increasingly specific functional descriptions for smaller and smaller sets of genes. • The weakness : functions have not yet been assigned to many eukaryotic genes. ...
... further subdivided to produce a hierarchy of increasingly specific functional descriptions for smaller and smaller sets of genes. • The weakness : functions have not yet been assigned to many eukaryotic genes. ...
DNA
... related metabolic functions is organized as a unit - Operon – Promoter (sequence), operator (sequence) and structural genes ( sequence) are called an operon. • The promoter and operator are sites that control structural gene transcription. • Structural genes are expressed as a single messenger RNA. ...
... related metabolic functions is organized as a unit - Operon – Promoter (sequence), operator (sequence) and structural genes ( sequence) are called an operon. • The promoter and operator are sites that control structural gene transcription. • Structural genes are expressed as a single messenger RNA. ...
Learning objectives
... 6. Describe the role of an expression vector. 7. Describe two advantages of using yeast cells instead of bacteria as hosts for cloning or expressing eukaryotic genes. 8. Describe the structure and function of a yeast artificial chromosome (YAC). 9. Describe two techniques to introduce recombinant DN ...
... 6. Describe the role of an expression vector. 7. Describe two advantages of using yeast cells instead of bacteria as hosts for cloning or expressing eukaryotic genes. 8. Describe the structure and function of a yeast artificial chromosome (YAC). 9. Describe two techniques to introduce recombinant DN ...
Chapter 16 Practice Problems
... (considering birds) represent an example of paraphyly or polyphyly? Are reptiles monophyletic in our currently-accepted classification (Figure 16.3)? ...
... (considering birds) represent an example of paraphyly or polyphyly? Are reptiles monophyletic in our currently-accepted classification (Figure 16.3)? ...
Learning objectives
... 6. Describe the role of an expression vector. 7. Describe two advantages of using yeast cells instead of bacteria as hosts for cloning or expressing eukaryotic genes. 8. Describe the structure and function of a yeast artificial chromosome (YAC). 9. Describe two techniques to introduce recombinant DN ...
... 6. Describe the role of an expression vector. 7. Describe two advantages of using yeast cells instead of bacteria as hosts for cloning or expressing eukaryotic genes. 8. Describe the structure and function of a yeast artificial chromosome (YAC). 9. Describe two techniques to introduce recombinant DN ...
Genome_annotation
... wore a ball dress and her badge as maid of honor. The youthful little Princess Bolkonskaya, known as la femme la plus seduisante de Petersbourg, was also there. She had been married during the previous winter, and being pregnant did not go to any large gatherings, but only to small receptions. Princ ...
... wore a ball dress and her badge as maid of honor. The youthful little Princess Bolkonskaya, known as la femme la plus seduisante de Petersbourg, was also there. She had been married during the previous winter, and being pregnant did not go to any large gatherings, but only to small receptions. Princ ...
Transcription additions
... AUG, the start codon. Each transfer RNA has an anticodon whose bases are complementary to a codon on the mRNA strand. The ribosome positions the start codon to attract its anticodon, which is part of the tRNA that binds methionine. The ribosome also binds the next codon and its anticodon. ...
... AUG, the start codon. Each transfer RNA has an anticodon whose bases are complementary to a codon on the mRNA strand. The ribosome positions the start codon to attract its anticodon, which is part of the tRNA that binds methionine. The ribosome also binds the next codon and its anticodon. ...
3 " ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ - 1 - G 2 ¢ 2 2 – 1. Biological catalysts are (A
... (B) glutamate and glutamine (D) alanine and phenylalanine ...
... (B) glutamate and glutamine (D) alanine and phenylalanine ...
Abstract
... validation based on quantitative measurement and perturbation of network behavior, and (3) design and implementation of biological networks driven by the same logic as the original network. Mammalian circadian clock system is such a system consisting of complexly integrated regulatory loops and disp ...
... validation based on quantitative measurement and perturbation of network behavior, and (3) design and implementation of biological networks driven by the same logic as the original network. Mammalian circadian clock system is such a system consisting of complexly integrated regulatory loops and disp ...
Denotation of E.coli Genotypes
... Name of genes : Genes are named in three italic lowercase letters according to their functions. For example, the dam gene comes from the first three letters of DNA adenine methylase. Many genes related to their function can be distinguished by a different capital letter at their end. For example, re ...
... Name of genes : Genes are named in three italic lowercase letters according to their functions. For example, the dam gene comes from the first three letters of DNA adenine methylase. Many genes related to their function can be distinguished by a different capital letter at their end. For example, re ...
Gene regulatory network

A gene regulatory network or genetic regulatory network (GRN) is a collection of regulators thatinteract with each other and with other substances in the cell to govern the gene expression levels of mRNA and proteins.The regulator can be DNA, RNA, protein and their complex. The interaction can be direct or indirect (through their transcribed RNA or translated protein).In general, each mRNA molecule goes on to make a specific protein (or set of proteins). In some cases this protein will be structural, and will accumulate at the cell membrane or within the cell to give it particular structural properties. In other cases the protein will be an enzyme, i.e., a micro-machine that catalyses a certain reaction, such as the breakdown of a food source or toxin. Some proteins though serve only to activate other genes, and these are the transcription factors that are the main players in regulatory networks or cascades. By binding to the promoter region at the start of other genes they turn them on, initiating the production of another protein, and so on. Some transcription factors are inhibitory.In single-celled organisms, regulatory networks respond to the external environment, optimising the cell at a given time for survival in this environment. Thus a yeast cell, finding itself in a sugar solution, will turn on genes to make enzymes that process the sugar to alcohol. This process, which we associate with wine-making, is how the yeast cell makes its living, gaining energy to multiply, which under normal circumstances would enhance its survival prospects.In multicellular animals the same principle has been put in the service of gene cascades that control body-shape. Each time a cell divides, two cells result which, although they contain the same genome in full, can differ in which genes are turned on and making proteins. Sometimes a 'self-sustaining feedback loop' ensures that a cell maintains its identity and passes it on. Less understood is the mechanism of epigenetics by which chromatin modification may provide cellular memory by blocking or allowing transcription. A major feature of multicellular animals is the use of morphogen gradients, which in effect provide a positioning system that tells a cell where in the body it is, and hence what sort of cell to become. A gene that is turned on in one cell may make a product that leaves the cell and diffuses through adjacent cells, entering them and turning on genes only when it is present above a certain threshold level. These cells are thus induced into a new fate, and may even generate other morphogens that signal back to the original cell. Over longer distances morphogens may use the active process of signal transduction. Such signalling controls embryogenesis, the building of a body plan from scratch through a series of sequential steps. They also control and maintain adult bodies through feedback processes, and the loss of such feedback because of a mutation can be responsible for the cell proliferation that is seen in cancer. In parallel with this process of building structure, the gene cascade turns on genes that make structural proteins that give each cell the physical properties it needs.It has been suggested that, because biological molecular interactions are intrinsically stochastic, gene networks are the result of cellular processes and not their cause (i.e. cellular Darwinism). However, recent experimental evidence has favored the attractor view of cell fates.