PDF - Biotechnology for Biofuels
... various anaerobic and facultative anaerobic bacteria capable of fermentative hydrogen production [4]. H2 production in living organisms is always dependent on the presence of H2-producing enzymes such as hydrogenases and nitrogenases. [FeFe] hydrogenases, which are especially abundant in clostridia, ...
... various anaerobic and facultative anaerobic bacteria capable of fermentative hydrogen production [4]. H2 production in living organisms is always dependent on the presence of H2-producing enzymes such as hydrogenases and nitrogenases. [FeFe] hydrogenases, which are especially abundant in clostridia, ...
Identification, molecular characterization, and tissue
... with no hydrophobic transmembrane regions, and to exert its function in the cell nucleus. A conserved domain of parathyroid superfamily from amino acids 34-114 was observed in the polypeptide. Sequence comparison and the phylogenetic analysis showed that the sequence of the water buffalo PTHrP prote ...
... with no hydrophobic transmembrane regions, and to exert its function in the cell nucleus. A conserved domain of parathyroid superfamily from amino acids 34-114 was observed in the polypeptide. Sequence comparison and the phylogenetic analysis showed that the sequence of the water buffalo PTHrP prote ...
Rules, regulations, and policies for breeding and biotechnology
... example noticeable in traits related to disease resistance in animals and to biomass in plants. A decade after the discovery of heterosis, the fact that many traits depend on many genes, so called quantitative traits, was understood and statistical models were developed to account for such traits in ...
... example noticeable in traits related to disease resistance in animals and to biomass in plants. A decade after the discovery of heterosis, the fact that many traits depend on many genes, so called quantitative traits, was understood and statistical models were developed to account for such traits in ...
Essential Outcomes Biology
... a) Students will explain how anatomical and molecular similarities among organisms suggest that life on earth began as simple, one-celled organisms and that multicellular organisms evolved later. (B.8.1) b) Students will explain how organisms are classified and named based on their evolutionary rela ...
... a) Students will explain how anatomical and molecular similarities among organisms suggest that life on earth began as simple, one-celled organisms and that multicellular organisms evolved later. (B.8.1) b) Students will explain how organisms are classified and named based on their evolutionary rela ...
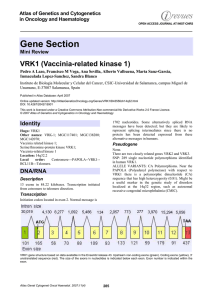
Gene Section VRK1 (Vaccinia-related kinase 1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... hypersensitive site located between VRK1 and BCL11B genes; but the structure, or expression, of VRK1 does not appear to be affected. In this translocation there is a dysregulation of TLX3 and NKX2-5 homeobox genes (both on chromosome 5). ...
... hypersensitive site located between VRK1 and BCL11B genes; but the structure, or expression, of VRK1 does not appear to be affected. In this translocation there is a dysregulation of TLX3 and NKX2-5 homeobox genes (both on chromosome 5). ...
Molecular cloning of Drosophila Rh6 rhodopsin: the
... rhodopsin palmitylation has not yet been provided [20]. In ...
... rhodopsin palmitylation has not yet been provided [20]. In ...
Glutamate synthase and nitrogen
... indicates that cyanobacteria might, like plants, have both Fd- and result is reminiscent of evidence obtained with E. coli NADPHNAD(P)H-GOGAT enzymes. However, significant Synecho- GOGAT showing that the gltA-encoded subunit alone can catacystis Fd-GOGAT activity was retained in mutants that contain ...
... indicates that cyanobacteria might, like plants, have both Fd- and result is reminiscent of evidence obtained with E. coli NADPHNAD(P)H-GOGAT enzymes. However, significant Synecho- GOGAT showing that the gltA-encoded subunit alone can catacystis Fd-GOGAT activity was retained in mutants that contain ...
Novel domains and orthologues of eukaryotic
... factors are known to facilitate elongation through chromatin (3) (Table 1). These are Rad26p, CP (a heterodimeric factor of Cdc68p/Spt16p and Pob3p), Elongator (containing two subcomplexes, each of three subunits), the Spt4p±Spt5p heterodimer and Spt6p. The molecular functions of these 12 differ gre ...
... factors are known to facilitate elongation through chromatin (3) (Table 1). These are Rad26p, CP (a heterodimeric factor of Cdc68p/Spt16p and Pob3p), Elongator (containing two subcomplexes, each of three subunits), the Spt4p±Spt5p heterodimer and Spt6p. The molecular functions of these 12 differ gre ...
Multiple Molecular Mechanisms Cause Reproductive Isolation
... interspecific F2 hybrid sterility [14]. To examine whether nuclearmitochondrial incompatibility represents a general mechanism of reproductive isolation in yeast, a systematic screen for such genes was conducted in three closely related yeast species: S. cerevisiae (Sc), S. paradoxus (Sp), and S. ba ...
... interspecific F2 hybrid sterility [14]. To examine whether nuclearmitochondrial incompatibility represents a general mechanism of reproductive isolation in yeast, a systematic screen for such genes was conducted in three closely related yeast species: S. cerevisiae (Sc), S. paradoxus (Sp), and S. ba ...
Document
... (Clark and Kao, 1991). Last, the S locus of Lycopersicon peruvianum has been shown by genetic mapping to be located close to the centromere of chromosome I (Bernatzky, 1993), and the S locus of Petunia hybrida has been shown by fluorescence in situ hybridization to be located close to the centromere ...
... (Clark and Kao, 1991). Last, the S locus of Lycopersicon peruvianum has been shown by genetic mapping to be located close to the centromere of chromosome I (Bernatzky, 1993), and the S locus of Petunia hybrida has been shown by fluorescence in situ hybridization to be located close to the centromere ...
TE classification and submission guide
... genome-scale characterization of TEs and to provide a user-friendly interface for biologists to take full advantage of the compiled information. Within any genome, a TE consists of multiple copies generated by transposition events. Here we call the collection of these copies an Element. Although the ...
... genome-scale characterization of TEs and to provide a user-friendly interface for biologists to take full advantage of the compiled information. Within any genome, a TE consists of multiple copies generated by transposition events. Here we call the collection of these copies an Element. Although the ...
... on a dry paper towel to remove excess liquid, transferred to another Petri dish, and rapidly frozedthawed twice with liquid nitrogen. A 1-ml acyl-CoA reaction mixture containing 0.1 M Tris-HC1, pH 8.0, 10 m~ ATP, 2 m~ dithiothreitol, 20 p i [3Hlpalmitic acid (specific activity 60 Wmmol), and 2% Trit ...
Emerging real-time PCR applications.
... to test for known sequence variations. Applications include SNP genotyping for allelic prevalence in a population for the identification of candidate predisposition genes, DNA fingerprinting, screening for loss of heterozygosity, association (case/control) studies, characterisation of haplotype bloc ...
... to test for known sequence variations. Applications include SNP genotyping for allelic prevalence in a population for the identification of candidate predisposition genes, DNA fingerprinting, screening for loss of heterozygosity, association (case/control) studies, characterisation of haplotype bloc ...
access full article - Caister Academic Press
... clustered and range in size from five to greater than 100 kilobases (Malpartida and Hopwood 1984; August et al., 1998). As these natural product biosynthetic pathways become elucidated, more innovative efforts have been placed on producing these molecules in heterologous hosts such as E. coli, that ...
... clustered and range in size from five to greater than 100 kilobases (Malpartida and Hopwood 1984; August et al., 1998). As these natural product biosynthetic pathways become elucidated, more innovative efforts have been placed on producing these molecules in heterologous hosts such as E. coli, that ...
Block III - Madhya Pradesh Bhoj Open University
... ions by roots. Although trace amounts of sulphur dioxide gas are absorbed and assimilated by leaves, but it is also converted to sulphate ions. Most of the sulphate absorbed by the roots is carried upward in the transpiration stream to leaves, where it is assimilated. In fact, sulphate assimilation ...
... ions by roots. Although trace amounts of sulphur dioxide gas are absorbed and assimilated by leaves, but it is also converted to sulphate ions. Most of the sulphate absorbed by the roots is carried upward in the transpiration stream to leaves, where it is assimilated. In fact, sulphate assimilation ...
Understanding phage, the viruses that infect
... d'Hérelle, working at the Pasteur Institute in Paris, announced on September 3, 1917 that he discovered "an invisible, antagonistic microbe of the dysentery bacillus". For d’Herelle, there was no question as to the nature of his discovery: "In a flash I had understood: what caused my clear spots was ...
... d'Hérelle, working at the Pasteur Institute in Paris, announced on September 3, 1917 that he discovered "an invisible, antagonistic microbe of the dysentery bacillus". For d’Herelle, there was no question as to the nature of his discovery: "In a flash I had understood: what caused my clear spots was ...
Functional genomics analysis of foliar condensed tannin and
... 2002) using GeneSpring 6.2 software (Silicon Genetics, Redwood City, CA). For each experiment (between-line comparisons or within-line N effects), differentially expressed genes were selected by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with multiple-testing correction at a false discovery rate of P = 0. ...
... 2002) using GeneSpring 6.2 software (Silicon Genetics, Redwood City, CA). For each experiment (between-line comparisons or within-line N effects), differentially expressed genes were selected by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with multiple-testing correction at a false discovery rate of P = 0. ...
Sequences of the Nucleocapsid Genes from Two Strains of Avian
... independently derived clones. In the case of Beaudette eight independently derived clones have restriction maps which show that they have this stretch of sequence, all containing a HindlII site at position 1436, which is within the 184 base region (data not shown). The deletion in M41 occurs only fo ...
... independently derived clones. In the case of Beaudette eight independently derived clones have restriction maps which show that they have this stretch of sequence, all containing a HindlII site at position 1436, which is within the 184 base region (data not shown). The deletion in M41 occurs only fo ...
PACS-2 (Q-20): sc-160645 - Santa Cruz Biotechnology
... mitochondrion and the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and belongs to the PACS (phosphofurin acidic cluster sorting) family. Expressed in a broad range of tissues with highest expression in skeletal muscle, brain, heart, testis and pancreas, PACS-2 interacts with Polycystin-2 and BID and func ...
... mitochondrion and the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and belongs to the PACS (phosphofurin acidic cluster sorting) family. Expressed in a broad range of tissues with highest expression in skeletal muscle, brain, heart, testis and pancreas, PACS-2 interacts with Polycystin-2 and BID and func ...
7.2 Nucleic acids
... Secondary and tertiary DNA structure. DNA stores genetic information. RNA: Structure and function. Physico-chemical properties of the nucleic acids. DNA denaturation and ...
... Secondary and tertiary DNA structure. DNA stores genetic information. RNA: Structure and function. Physico-chemical properties of the nucleic acids. DNA denaturation and ...
Fig. 1.12
... Secondary and tertiary DNA structure. DNA stores genetic information. RNA: Structure and function. Physico-chemical properties of the nucleic acids. DNA denaturation and ...
... Secondary and tertiary DNA structure. DNA stores genetic information. RNA: Structure and function. Physico-chemical properties of the nucleic acids. DNA denaturation and ...
the pdf - p53 WEB SITE
... Both 9E4 and 6B10 recognized wild-type p53 expressed in HepG2 cells, but 7D3 reacted only weakly. All three antibodies also reacted with two dierent mutant p53 proteins, p53-Y220C and p53-R249S, expressed in Huh-7 and Mahlavu cells, respectively. p53-deleted Hep3B cells were used as a negative cont ...
... Both 9E4 and 6B10 recognized wild-type p53 expressed in HepG2 cells, but 7D3 reacted only weakly. All three antibodies also reacted with two dierent mutant p53 proteins, p53-Y220C and p53-R249S, expressed in Huh-7 and Mahlavu cells, respectively. p53-deleted Hep3B cells were used as a negative cont ...
Divergence time estimates for the early history of animal phyla and
... sediments at Joggins, Nova Scotia (Benton 1997). It is one of the best calibration points within vertebrates for several reasons: (i) the unique conditions of preservation at this site, in fossilized tree stump holes (natural pitfall traps), has yielded an unusually good fossil record of early amnio ...
... sediments at Joggins, Nova Scotia (Benton 1997). It is one of the best calibration points within vertebrates for several reasons: (i) the unique conditions of preservation at this site, in fossilized tree stump holes (natural pitfall traps), has yielded an unusually good fossil record of early amnio ...
Abundant Expression of ras Proteins in Aplysia Neurons
... Aplysia tissues. This antibody reacts with the products of all three known mammalian ras proto-oncogenes as well as with the products of ras genes in S. cerevisiae, Dictyostelium, and Drosophila (36, 37, 38). The most abundant fluorescence was observed in neurons; little or no fluorescence was detec ...
... Aplysia tissues. This antibody reacts with the products of all three known mammalian ras proto-oncogenes as well as with the products of ras genes in S. cerevisiae, Dictyostelium, and Drosophila (36, 37, 38). The most abundant fluorescence was observed in neurons; little or no fluorescence was detec ...
Endogenous retrovirus
Endogenous retroviruses (ERVs) are endogenous viral elements in the genome that closely resemble and can be derived from retroviruses. They are abundant in the genomes of jawed vertebrates, and they comprise up to 5–8% of the human genome (lower estimates of ~1%). ERVs are a subclass of a type of gene called a transposon, which can be packaged and moved within the genome to serve a vital role in gene expression and in regulation. Researchers have suggested that retroviruses evolved from a type of transposable gene called a retrotransposon, which includes ERVs; these genes can mutate and instead of moving to another location in the genome they can become exogenous or pathogenic. This means that all ERVs may not have originated as an insertion by a retrovirus but that some may have been the source for the genetic information in the retroviruses they resemble.