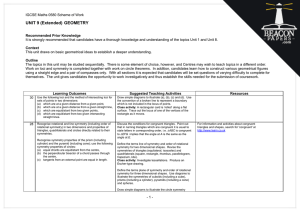
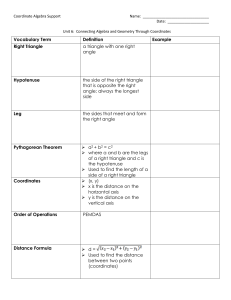
Lesson Plan
... parallelogram can be applied to a rhombus plus three other characteristics: The diagonals of a rhombus are perpendicular Each diagonal of a rhombus bisects a pair of opposite angles. Square a quadrilateral with four right angles and four sides that are congruent. Squares have all of the properties o ...
... parallelogram can be applied to a rhombus plus three other characteristics: The diagonals of a rhombus are perpendicular Each diagonal of a rhombus bisects a pair of opposite angles. Square a quadrilateral with four right angles and four sides that are congruent. Squares have all of the properties o ...
Rules of Geometry
... - the bisector of a pair of opposite angles of a 11gm are : intersecting at a point - if diagnols AC = diagonal BD and AC is perpendicular to BD in a parallelogram ABCD then it is : rhombus - area of s rectangle and area of || gm standing on the same base and b/w the same || have relation b/w them a ...
... - the bisector of a pair of opposite angles of a 11gm are : intersecting at a point - if diagnols AC = diagonal BD and AC is perpendicular to BD in a parallelogram ABCD then it is : rhombus - area of s rectangle and area of || gm standing on the same base and b/w the same || have relation b/w them a ...
Geometry 10.3-10.4 Chords and Arcs + Inscribed Angles
... Geometry 10.310.4 Chords and Arcs + Inscribed Angles Notes ...
... Geometry 10.310.4 Chords and Arcs + Inscribed Angles Notes ...