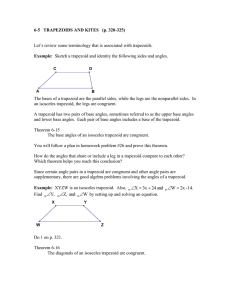
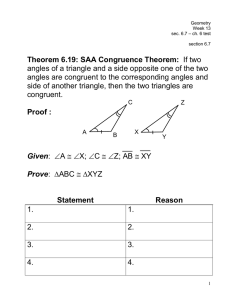
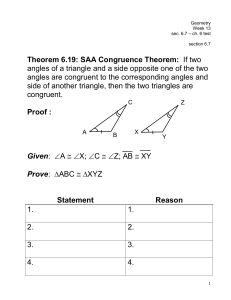
g - Perry Local Schools
... S.CP.3 Understand the conditional probability of A given B as P(A and B)/P(B), and interpret independence of A and B as saying that the conditional probability of A given B is the same as the probability of A, and the conditional probability of B given A is the same as the probability of B. S.CP.4 C ...
... S.CP.3 Understand the conditional probability of A given B as P(A and B)/P(B), and interpret independence of A and B as saying that the conditional probability of A given B is the same as the probability of A, and the conditional probability of B given A is the same as the probability of B. S.CP.4 C ...
Triangles - Oliveboard
... PA x PB = PC x PD = ½ [ m(Arc AC) – m(Arc BD) ] The radius and tangent are perpendicular to each other. There can only be two tangents from an external point, which are equal in length PA = PB ...
... PA x PB = PC x PD = ½ [ m(Arc AC) – m(Arc BD) ] The radius and tangent are perpendicular to each other. There can only be two tangents from an external point, which are equal in length PA = PB ...
KVS TGT syllabus
... To deduce the meaning of unfamiliar lexical items in a given text and provide synonyms / antonyms etc. To organize thoughts coherently in a piece of writing using a variety of cohesive devices. To write a short composition, e.g. notice, message or report in a given context and word limit. To write a ...
... To deduce the meaning of unfamiliar lexical items in a given text and provide synonyms / antonyms etc. To organize thoughts coherently in a piece of writing using a variety of cohesive devices. To write a short composition, e.g. notice, message or report in a given context and word limit. To write a ...