Honors Geometry Final Exam Study Guide Please complete this
... 9. Catherine is flying a plane north at a speed of 350 mph, but the wind is blowing east at a speed of 70 mph. What are Catherine's resultant speed and direction? Give speed in mph and direction as an angle measure with compass directions. Round your answers to the nearest hundredth. 10. Guy wants h ...
... 9. Catherine is flying a plane north at a speed of 350 mph, but the wind is blowing east at a speed of 70 mph. What are Catherine's resultant speed and direction? Give speed in mph and direction as an angle measure with compass directions. Round your answers to the nearest hundredth. 10. Guy wants h ...
MIDTERM DEFINITIONS THEOREM ETC Old Word PDF
... then their measures are equal! (and vice versa!) Can be applied to angles as well! A value will always equal itself! On overlapping segments and angles when we need to add the same thing to both sides we use this reason first. Basically, this is just for switching sides of an equation if necessary t ...
... then their measures are equal! (and vice versa!) Can be applied to angles as well! A value will always equal itself! On overlapping segments and angles when we need to add the same thing to both sides we use this reason first. Basically, this is just for switching sides of an equation if necessary t ...
MTH 362: Study Guide for the Exam 2
... a. Discuss the following students’ definitions of polygons. Are they valid? How would you respond to them? i. Polygon is a simple closed shape that contains straight lines. ii. Polygon is a union of several line segments that form angles. iii. Polygon is several line segments meeting at their endpoi ...
... a. Discuss the following students’ definitions of polygons. Are they valid? How would you respond to them? i. Polygon is a simple closed shape that contains straight lines. ii. Polygon is a union of several line segments that form angles. iii. Polygon is several line segments meeting at their endpoi ...
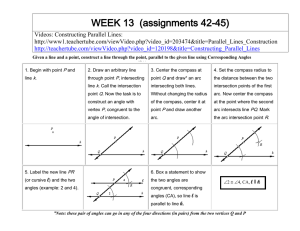
Week_13
... four by constructing congruent angles for each pair of Alternate Interior Angles (AIA's) - doing both the obtuse and acute angles (two times each). Make two by constructing supplementary angles for each pair of Same Side Interior Angles (SSIA's). Make two more by constructing a perpendicular transve ...
... four by constructing congruent angles for each pair of Alternate Interior Angles (AIA's) - doing both the obtuse and acute angles (two times each). Make two by constructing supplementary angles for each pair of Same Side Interior Angles (SSIA's). Make two more by constructing a perpendicular transve ...
Geometry - Harrison High School
... Congruent Triangles Congruent triangles have three congruent sides and and three congruent angles. However, triangles can be proved congruent without showing 3 pairs of congruent sides and angles. ...
... Congruent Triangles Congruent triangles have three congruent sides and and three congruent angles. However, triangles can be proved congruent without showing 3 pairs of congruent sides and angles. ...