Overview
... The task is – for each circle in turn – to join every point to every other point with a straight line, and count the number of resulting regions. They should end up with the sequence 1, 2, 4, 8 – and most learners would agree that there is a straightforward pattern here. Now predict and test for the ...
... The task is – for each circle in turn – to join every point to every other point with a straight line, and count the number of resulting regions. They should end up with the sequence 1, 2, 4, 8 – and most learners would agree that there is a straightforward pattern here. Now predict and test for the ...
Lesson 1 Contents
... 5. If RS ST and SV is the angle bisector of RST, what is the m TSV? m TSV = ½ m RST = ½(90) = 45° ...
... 5. If RS ST and SV is the angle bisector of RST, what is the m TSV? m TSV = ½ m RST = ½(90) = 45° ...
Chapter5 Triangles.pptx
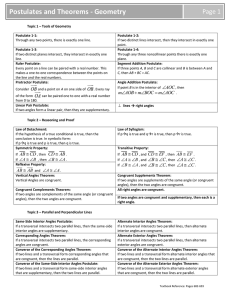
... • Students will define and use the Angle Sum Theorem. Angle Sum Theorem: The sum of the measures of the angles of a triangle is 180°. Theorem 5-2: The acute angles of a right angle triangle are complementary. An equilateral triangle is a triangle with all angles congruent. Theorem 5-3: The measure o ...
... • Students will define and use the Angle Sum Theorem. Angle Sum Theorem: The sum of the measures of the angles of a triangle is 180°. Theorem 5-2: The acute angles of a right angle triangle are complementary. An equilateral triangle is a triangle with all angles congruent. Theorem 5-3: The measure o ...
Geometry Collateral Constructions
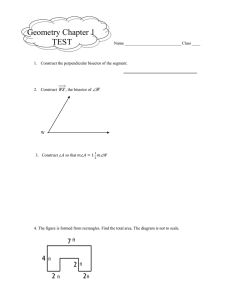
... b. Demonstrate once how to construct a line to a given line through a point not on the line. c. Draw a large scalene triangle. d. Bisect any 2 angles of the triangle. Draw the bisectors and label their point of intersection P. (This is the center of the circle and the incenter.) e. Construct a lin ...
... b. Demonstrate once how to construct a line to a given line through a point not on the line. c. Draw a large scalene triangle. d. Bisect any 2 angles of the triangle. Draw the bisectors and label their point of intersection P. (This is the center of the circle and the incenter.) e. Construct a lin ...
08:00 – 9:20 AM Monday - Thursday 6/22 – 7/30 - upwardbound-esu
... A combination of methods (including lecture, discussion, discovery techniques and problemsolving) is used in this course. Every effort is made to involve the student in the doing of mathematics, since it is only in the doing of mathematics that one can learn something of the nature and thought proce ...
... A combination of methods (including lecture, discussion, discovery techniques and problemsolving) is used in this course. Every effort is made to involve the student in the doing of mathematics, since it is only in the doing of mathematics that one can learn something of the nature and thought proce ...
Complementary Halfspaces and Trigonometric Ceva
... Honsberger [12] and Mitrinović, Pečarić and Volenec [18], the Brocard point was already known to Crelle [4], Jacobi and others at the beginning of the 19th century. Indeed, the historically more accurate name of Crelle-Brocard point is used in [18] (where other references to contemporary work are ...
... Honsberger [12] and Mitrinović, Pečarić and Volenec [18], the Brocard point was already known to Crelle [4], Jacobi and others at the beginning of the 19th century. Indeed, the historically more accurate name of Crelle-Brocard point is used in [18] (where other references to contemporary work are ...