* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson Plan Format
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Apollonian network wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Area of a circle wikipedia , lookup
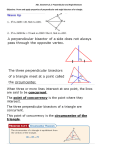
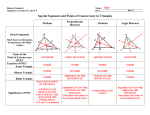
HW: pg. 311-312 (1-10) 5.1-5.3 Quiz Friday 12-14-12 www.westex.org HS, Teacher Website Name _________________________ Geometry CPA 5-2 Bisectors of Triangles GOAL: I will be able to: 1. prove and apply properties of perpendicular bisectors of a triangle. 2. prove and apply properties of angle bisectors of a triangle. Date ________ Part A---PERPENDICULAR BISECTORS Since a triangle has three sides, it has three perpendicular bisectors. When you construct the perpendicular bisectors, you find that they have an interesting property. When three or more lines intersect at one point, the lines are said to be ________________. The ______________ concurrency is the point where they intersect. In the demonstration, you saw that the three perpendicular bisectors of a triangle are concurrent. This point of concurrency is the ____________________ of the triangle. The circumcenter can be _________, __________, or ____ the triangle as illustrated below. The circumcenter of ΔABC is the center of its circumscribed circle. A circle that contains all the vertices of a polygon is _________________ about the polygon. Example 1: Using Properties of Perpendicular Bisectors YOU TRY: Z is the circumcenter of ∆GHJ . a. Find GM. b. Find JZ. Example 2: Finding the Circumcenter of a Triangle Find the circumcenter of ∆HJK with vertices H(0, 0), J(10, 0), and K(0, 6). YOU TRY: Find the circumcenter of ∆GOH with vertices G(0, –9), O(0, 0), and H(8, 0) . Part B---ANGLE BISECTORS A triangle has three angles, so it has three angle bisectors. The angle bisectors of a triangle are also concurrent. This point of concurrency is the _______________ of the triangle. Unlike the circumcenter, the incenter is always __________ the triangle. The incenter is the center of the triangle’s inscribed circle. A circle _______________ in a polygon intersects each line that contains a side of the polygon at exactly one point. Example 3: Using Properties of Angle Bisectors Find mPMN. YOU TRY: Find mPQX. 5-2 Practice 3. Lee’s job requires him to travel to X, Y, and Z. Draw a sketch to show where he should buy a home so it is the same distance from all three places.