Organic Chemistry
... Primary Structure – straight chain of aa – not functional Secondary Structure – starts to fold – alphahelix and beta pleated sheats – uncharged parts probably start of collapse together and the O of the acid groups form H bonds with the H from the amino group ...
... Primary Structure – straight chain of aa – not functional Secondary Structure – starts to fold – alphahelix and beta pleated sheats – uncharged parts probably start of collapse together and the O of the acid groups form H bonds with the H from the amino group ...
Lecture_11_2005
... Folds/motifs - tertiary structure • How these secondary structure elements come together to form structure. – Helix-turn-helix ...
... Folds/motifs - tertiary structure • How these secondary structure elements come together to form structure. – Helix-turn-helix ...
Protein Synthesis
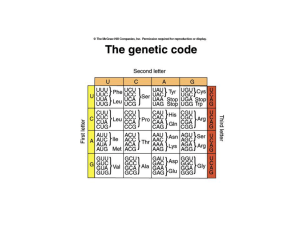
... • The three-nucleotide sequence of RNA is called a codon. • Each 3-nucleotide codon codes for a specific amino acid. • A codon chart is used to find what amino acid each codon codes for. ...
... • The three-nucleotide sequence of RNA is called a codon. • Each 3-nucleotide codon codes for a specific amino acid. • A codon chart is used to find what amino acid each codon codes for. ...
Glossary
... complexes (RISCs) is formed. RISCs recognize complementary sites in the 3’ UTR of their target mRNAs, and induce translational repression and/or poly(A) shortening and decay of these mRNAs. RNA-binding proteins :【RNA 結合蛋白質】Proteins that bind to RNA directly through regions that can bind to RNA. This ...
... complexes (RISCs) is formed. RISCs recognize complementary sites in the 3’ UTR of their target mRNAs, and induce translational repression and/or poly(A) shortening and decay of these mRNAs. RNA-binding proteins :【RNA 結合蛋白質】Proteins that bind to RNA directly through regions that can bind to RNA. This ...
File
... fMet-tRNAf is placed in the P site during formation of the 70S initiation complex Initiation factors IF1 and IF3 join the 30S subunit to preventing 30S from prematurely binding 50S IF2, a GTPase, binds GTP to change shape and enable binding of IF2 to fMet-tRNAf. The IF2-GTP- fMet-tRNAf complex bi ...
... fMet-tRNAf is placed in the P site during formation of the 70S initiation complex Initiation factors IF1 and IF3 join the 30S subunit to preventing 30S from prematurely binding 50S IF2, a GTPase, binds GTP to change shape and enable binding of IF2 to fMet-tRNAf. The IF2-GTP- fMet-tRNAf complex bi ...
Peptides - Alfred State College
... • Naming starts from the N-terminus • Sequence is written as: Ala-Glu-Gly-Lys • Sometimes the one-letter code is used: AEGK ...
... • Naming starts from the N-terminus • Sequence is written as: Ala-Glu-Gly-Lys • Sometimes the one-letter code is used: AEGK ...
File - Ms. Poole`s Biology
... Warm Up (In Notes) • Create a list of 10 specific proteins we have studied this year ...
... Warm Up (In Notes) • Create a list of 10 specific proteins we have studied this year ...
Features of the genetic code
... transcript by a poly-A-polymerase. Tailing is believed to stabilize mRNA so it remains for longer time to be translated to many polypeptide molecules before it is degraded and increase the efficiency of the initial steps of translation. • RNA splicing and removal of introns from the primary transcri ...
... transcript by a poly-A-polymerase. Tailing is believed to stabilize mRNA so it remains for longer time to be translated to many polypeptide molecules before it is degraded and increase the efficiency of the initial steps of translation. • RNA splicing and removal of introns from the primary transcri ...
Study Questions for Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein
... spliced out and exons are then joined together to make a continuous coding sequence 12) Introns (non-coding regions) were once thought to be “junk DNA” but now it is thought that they do have biological and/or evolutionary importance. List 3 potential functions of introns. 1. Increase opportunity fo ...
... spliced out and exons are then joined together to make a continuous coding sequence 12) Introns (non-coding regions) were once thought to be “junk DNA” but now it is thought that they do have biological and/or evolutionary importance. List 3 potential functions of introns. 1. Increase opportunity fo ...
9 Week
... 2. Can it be broken down completely by the digestive system (can it free all the AA to be used by the organism?) Protein Digestibility Corrected Amino Acid Score (PDCAAS) This is a rating adopted by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Na ...
... 2. Can it be broken down completely by the digestive system (can it free all the AA to be used by the organism?) Protein Digestibility Corrected Amino Acid Score (PDCAAS) This is a rating adopted by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Na ...
Lecture_11
... Structural proteomics Two handouts for this week. Proteomics section from book already assigned. ...
... Structural proteomics Two handouts for this week. Proteomics section from book already assigned. ...
Protein Chemistry
... in structures on the protein - peptide backbone. The side chains are not considered here, even though they have an affect on the secondary structure. Two common secondary structures - alpha helix and beta pleated sheet Non- regular repeating structure is called a random coil. - no specific repeata ...
... in structures on the protein - peptide backbone. The side chains are not considered here, even though they have an affect on the secondary structure. Two common secondary structures - alpha helix and beta pleated sheet Non- regular repeating structure is called a random coil. - no specific repeata ...
A little less conjugation, a little more accuracy
... this issue focuses on methods to modify proteins in a site-selective manner. Proteins can fold into an incredibly diverse range of structures despite being made from only a limited number of building blocks — the twenty-or-so proteinogenic amino acids. The modular nature of proteins has enabled thei ...
... this issue focuses on methods to modify proteins in a site-selective manner. Proteins can fold into an incredibly diverse range of structures despite being made from only a limited number of building blocks — the twenty-or-so proteinogenic amino acids. The modular nature of proteins has enabled thei ...
Proteins 1 - Dr Rob's A
... Most important role of aa’s is as monomers for protein synthesis Green plants can synthesis all they need from photosynthesis and nitrate from soil Animals can synthesise some, but need to obtain 8 from their diet. These are the essential amino acids Amino acids are also involved in synthesis of ot ...
... Most important role of aa’s is as monomers for protein synthesis Green plants can synthesis all they need from photosynthesis and nitrate from soil Animals can synthesise some, but need to obtain 8 from their diet. These are the essential amino acids Amino acids are also involved in synthesis of ot ...
RNA editing of cytochrome c maturation transcripts is highly
... MORF4 or MORF7. We compared the organellar transcripts of the AtPAP2 OE line with that of the wild‐type at three time points using RNA‐sequencing analysis. In total, 34 editing sites were identified in chloroplast transcripts and 510 editing sites were identified in mitoc ...
... MORF4 or MORF7. We compared the organellar transcripts of the AtPAP2 OE line with that of the wild‐type at three time points using RNA‐sequencing analysis. In total, 34 editing sites were identified in chloroplast transcripts and 510 editing sites were identified in mitoc ...
No Slide Title
... acid specified by it’s anticodon and transfers it to the ribisome where it meets up with mRNA to assemble a protein. ...
... acid specified by it’s anticodon and transfers it to the ribisome where it meets up with mRNA to assemble a protein. ...
Book Reviews - Cancer Research
... Two papers deal with the cytochemistry of proteins. J. F. Danielli describes the use of chromogenic reagents along with specific blocking reagents, and B. P. Kauf man, H. Gay, and M. R. McDonald ...
... Two papers deal with the cytochemistry of proteins. J. F. Danielli describes the use of chromogenic reagents along with specific blocking reagents, and B. P. Kauf man, H. Gay, and M. R. McDonald ...
Most human genes are composed of coding sequences (exons) that
... Most human genes are composed of coding sequences (exons) that are interrupted by non-coding sequences (introns). After gene transcription into pre-mRNA, these introns have to be removed in a process called splicing. Splicing is mediated by a very complex and dynamic complex called the spliceosome, ...
... Most human genes are composed of coding sequences (exons) that are interrupted by non-coding sequences (introns). After gene transcription into pre-mRNA, these introns have to be removed in a process called splicing. Splicing is mediated by a very complex and dynamic complex called the spliceosome, ...
Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation
... Protein Folding and Function As the amino acid chain grows, it folds into a three-dimensional (3-D) structure, which depends on both the chemical nature and order of the different amino acids. The 3-D structure determines the function of the protein. When there is a change in one or more amino acid ...
... Protein Folding and Function As the amino acid chain grows, it folds into a three-dimensional (3-D) structure, which depends on both the chemical nature and order of the different amino acids. The 3-D structure determines the function of the protein. When there is a change in one or more amino acid ...
Chapter 3 Section 4 Protein Synthesis
... The mRNA consists of the nitrogen bases A,U,C,G arranged in a specific order. • Proteins consist of chains of the 20 amino acids arranged in a specific order. • So what is the link between the two? ...
... The mRNA consists of the nitrogen bases A,U,C,G arranged in a specific order. • Proteins consist of chains of the 20 amino acids arranged in a specific order. • So what is the link between the two? ...
Protein Synthesis Notes: Transcription and Translation
... o Transcription Practice: Transcribe this strand of DNA into RNA (no T‟s in RNA!) DNA: A A T C T A G A T C A T T A RNA:______________________________ Step 2- Translation o Function: Pieces of RNA make _____________________, which then make ___________. o Location: In the ____________________________ ...
... o Transcription Practice: Transcribe this strand of DNA into RNA (no T‟s in RNA!) DNA: A A T C T A G A T C A T T A RNA:______________________________ Step 2- Translation o Function: Pieces of RNA make _____________________, which then make ___________. o Location: In the ____________________________ ...
Model Description Sheet
... According to the World Health Organization, 8.6 million people became ill and 1.3 million died in 2012 from tuberculosis (TB). Thioredoxin A (TrxA) is a binding protein in the bacterium, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the causative agent for TB. TB is prevalent in countries where infectious diseases ha ...
... According to the World Health Organization, 8.6 million people became ill and 1.3 million died in 2012 from tuberculosis (TB). Thioredoxin A (TrxA) is a binding protein in the bacterium, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the causative agent for TB. TB is prevalent in countries where infectious diseases ha ...
LSm
In molecular biology, LSm proteins are a family of RNA-binding proteins found in virtually every cellular organism. LSm is a contraction of 'like Sm', because the first identified members of the LSm protein family were the Sm proteins. LSm proteins are defined by a characteristic three-dimensional structure and their assembly into rings of six or seven individual LSm protein molecules, and play a large number of various roles in mRNA processing and regulation.The Sm proteins were first discovered as antigens targeted by so-called Anti-Sm antibodies in a patient with a form of Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), a debilitating autoimmune disease. They were named Sm proteins in honor of Stephanie Smith, a patient who suffered from SLE. Other proteins with very similar structures were subsequently discovered and named LSm proteins. New members of the LSm protein family continue to be identified and reported.Proteins with similar structures are grouped into a hierarchy of protein families, superfamilies, and folds. The LSm protein structure is an example of a small beta sheet folded into a short barrel. Individual LSm proteins assemble into a six or seven member doughnut ring (more properly termed a torus), which usually binds to a small RNA molecule to form a ribonucleoprotein complex. The LSm torus assists the RNA molecule to assume and maintain its proper three-dimensional structure. Depending on which LSm proteins and RNA molecule are involved, this ribonucleoprotein complex facilitates a wide variety of RNA processing including degradation, editing, splicing, and regulation.Alternate terms for LSm family are LSm fold and Sm-like fold, and alternate capitalization styles such as lsm, LSM, and Lsm are common and equally acceptable.