charged
... and then cut back by an exonuclease to produce mature rRNA. Formation of RNA loops and binding of specific proteins leads to the formation of the active ribosomal subunit. ...
... and then cut back by an exonuclease to produce mature rRNA. Formation of RNA loops and binding of specific proteins leads to the formation of the active ribosomal subunit. ...
Amino Acids
... Seager SL, Slabaugh MR, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic and Biochemistry, 7 th Edition, 2011; Berg JM, Tymoczko JL, Stryer L, Biochemistry, 5th Edition, 2002 ...
... Seager SL, Slabaugh MR, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic and Biochemistry, 7 th Edition, 2011; Berg JM, Tymoczko JL, Stryer L, Biochemistry, 5th Edition, 2002 ...
Some General Information on CD of Proteins
... The approximate fraction of each secondary structure type that is present in any protein can thus be determined by analyzing its far-UV CD spectrum as a sum of fractional multiples of such reference spectra for each structural type. (e.g. For an alpha helical protein with increasing amounts of rando ...
... The approximate fraction of each secondary structure type that is present in any protein can thus be determined by analyzing its far-UV CD spectrum as a sum of fractional multiples of such reference spectra for each structural type. (e.g. For an alpha helical protein with increasing amounts of rando ...
Protein Synthesis Review
... Enzymes, which speed up chemical reactions Build and repair cell structures Determine the structure & function of living organisms ...
... Enzymes, which speed up chemical reactions Build and repair cell structures Determine the structure & function of living organisms ...
12.3 RNA and Protein Synthesis
... • The DNA of eukaryotic genes contains sequences of nucleotides, called introns, that are not involved in coding for proteins. • The DNA sequences that code for proteins are called exons because they are expressed in protein synthesis. ...
... • The DNA of eukaryotic genes contains sequences of nucleotides, called introns, that are not involved in coding for proteins. • The DNA sequences that code for proteins are called exons because they are expressed in protein synthesis. ...
From DNA to Protein
... causes them to clump together and form Van der Wall’s interactions • Dislufide bridges between two sulfhydryl groups ...
... causes them to clump together and form Van der Wall’s interactions • Dislufide bridges between two sulfhydryl groups ...
THREE POSSIBILE MODELS FOR REPLICATION
... may provide cross over places without interrupting code may facilitate evolution of new proteins by exon shuffling • EXONS - coding DNA segments; code for different DOMAINS =structural/functional regions snRNPs (small nuclear ribonucleoproteins) • Made of proteins and RNA • Part of SPLICEOSOME (comp ...
... may provide cross over places without interrupting code may facilitate evolution of new proteins by exon shuffling • EXONS - coding DNA segments; code for different DOMAINS =structural/functional regions snRNPs (small nuclear ribonucleoproteins) • Made of proteins and RNA • Part of SPLICEOSOME (comp ...
THREE POSSIBILE MODELS FOR REPLICATION
... may provide cross over places without interrupting code may facilitate evolution of new proteins by exon shuffling • EXONS - coding DNA segments; code for different DOMAINS =structural/functional regions snRNPs (small nuclear ribonucleoproteins) • Made of proteins and RNA • Part of SPLICEOSOME (comp ...
... may provide cross over places without interrupting code may facilitate evolution of new proteins by exon shuffling • EXONS - coding DNA segments; code for different DOMAINS =structural/functional regions snRNPs (small nuclear ribonucleoproteins) • Made of proteins and RNA • Part of SPLICEOSOME (comp ...
3.PROTEIN SYNTHESIS overview
... Translation: Overview This is also divided into three stages: Initiation: when a ribosome binds to a specific site on _________________________ Elongation: the ribosome moves along the mRNA _____________________at a time assembling a sequence of ____________________ Termination: the ribosome r ...
... Translation: Overview This is also divided into three stages: Initiation: when a ribosome binds to a specific site on _________________________ Elongation: the ribosome moves along the mRNA _____________________at a time assembling a sequence of ____________________ Termination: the ribosome r ...
PG1005 Lecture 17 Gene Transcription
... delivery of specific amino acids to the ribosome to provide each monomer of the polypeptide chain ...
... delivery of specific amino acids to the ribosome to provide each monomer of the polypeptide chain ...
Fibrous proteins
... - Ferritin: Main store of iron in the body in non toxic form, because free iron is toxic and oxidize cells (form reactive oxygen species). Ferritin is present in liver, spleen and bone marrow. The amount of ferritin stored reflects the amount of iron stored. Ferritin releases iron to areas where it ...
... - Ferritin: Main store of iron in the body in non toxic form, because free iron is toxic and oxidize cells (form reactive oxygen species). Ferritin is present in liver, spleen and bone marrow. The amount of ferritin stored reflects the amount of iron stored. Ferritin releases iron to areas where it ...
Trafficking of Proteins to Membranes
... Trafficking of Proteins to Membranes 1. Protein fate is determined by N-terminal signal sequences 15-30 amino acids long. All contain ~10 hydrophobic residues. 2. When 70-80 amino acids have been polymerised during translation, and the signal sequence has emerged into the cytosol, it is recognised b ...
... Trafficking of Proteins to Membranes 1. Protein fate is determined by N-terminal signal sequences 15-30 amino acids long. All contain ~10 hydrophobic residues. 2. When 70-80 amino acids have been polymerised during translation, and the signal sequence has emerged into the cytosol, it is recognised b ...
Catalysis - University of California, Davis
... Dielectric Constant Availability of solvent water and the ability of water to decrease intermolecular attraction keeps globular proteins in ...
... Dielectric Constant Availability of solvent water and the ability of water to decrease intermolecular attraction keeps globular proteins in ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... 3.Transfer RNA (tRNA)—transfers each amino acid and anticodon to the appropriate place on the mRNA strand. ...
... 3.Transfer RNA (tRNA)—transfers each amino acid and anticodon to the appropriate place on the mRNA strand. ...
Gene to protein
... may provide cross over places without interrupting code may facilitate evolution of new proteins by exon shuffling • EXONS - coding DNA segments; code for different DOMAINS =structural/functional regions snRNPs (small nuclear ribonucleoproteins) • Made of proteins and RNA • Part of SPLICEOSOME (comp ...
... may provide cross over places without interrupting code may facilitate evolution of new proteins by exon shuffling • EXONS - coding DNA segments; code for different DOMAINS =structural/functional regions snRNPs (small nuclear ribonucleoproteins) • Made of proteins and RNA • Part of SPLICEOSOME (comp ...
Ch 1617 Study Guide - Dublin City Schools
... may provide cross over places without interrupting code may facilitate evolution of new proteins by exon shuffling • EXONS - coding DNA segments; code for different DOMAINS =structural/functional regions snRNPs (small nuclear ribonucleoproteins) • Made of proteins and RNA • Part of SPLICEOSOME (comp ...
... may provide cross over places without interrupting code may facilitate evolution of new proteins by exon shuffling • EXONS - coding DNA segments; code for different DOMAINS =structural/functional regions snRNPs (small nuclear ribonucleoproteins) • Made of proteins and RNA • Part of SPLICEOSOME (comp ...
Chapter 11: DNA and Genes
... ribosomes for protein manufacturing. In the nucleus, enzymes make an RNA copy of a portion of a DNA strand by this process. Forms a single-stranded RNA molecule rather than a double-stranded DNA molecule. Page 296, Figure 11.6 has a diagram and step-bystep information for this process. http://www.dn ...
... ribosomes for protein manufacturing. In the nucleus, enzymes make an RNA copy of a portion of a DNA strand by this process. Forms a single-stranded RNA molecule rather than a double-stranded DNA molecule. Page 296, Figure 11.6 has a diagram and step-bystep information for this process. http://www.dn ...
protein synthesis
... ________________________________________________________________ List below are the steps involved in the attachment of the amino acid to its tRNA. Put them in the correct order. ______ ATP loses phosphates ______ AMP attaches to amino acid ______ Enzyme active site binds to amino acid and ATP _____ ...
... ________________________________________________________________ List below are the steps involved in the attachment of the amino acid to its tRNA. Put them in the correct order. ______ ATP loses phosphates ______ AMP attaches to amino acid ______ Enzyme active site binds to amino acid and ATP _____ ...
Acrylamide -gel patterns of total soluble proteins at different stages +
... The omogenate was centrifuged at 20,000 x g for 15’ and the clear supernatant was used as sample for the electrophoretic analysis as well as for the parallel protein content determination (Lowry et al. method). For the analysis of the hemolymph proteins, larvae were dissected in a cold centrifuge tu ...
... The omogenate was centrifuged at 20,000 x g for 15’ and the clear supernatant was used as sample for the electrophoretic analysis as well as for the parallel protein content determination (Lowry et al. method). For the analysis of the hemolymph proteins, larvae were dissected in a cold centrifuge tu ...
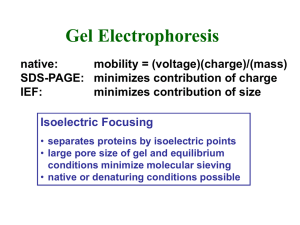
No Slide Title
... • separates proteins by isoelectric points • large pore size of gel and equilibrium conditions minimize molecular sieving • native or denaturing conditions possible ...
... • separates proteins by isoelectric points • large pore size of gel and equilibrium conditions minimize molecular sieving • native or denaturing conditions possible ...
RNA
... which is RNA. DNA molecule stays safely in the cell’s nucleus RNA molecules go to protein-building sites in the cytoplasm ...
... which is RNA. DNA molecule stays safely in the cell’s nucleus RNA molecules go to protein-building sites in the cytoplasm ...
Total Bacterial Protein Isolation
... Bacterial proteins features • Bacterial proteins has the ability to bind with other protein. Protein binding involves the formation of very strong links between tow different proteins . Once proteins bind , they can trigger a reaction which may vary from an immune system response to an infection to ...
... Bacterial proteins features • Bacterial proteins has the ability to bind with other protein. Protein binding involves the formation of very strong links between tow different proteins . Once proteins bind , they can trigger a reaction which may vary from an immune system response to an infection to ...
Chapter 9 Expressing Genetic Information Learning Targets
... Codons and Antocodons Use of the amino acid chart Proteins potential for variation ...
... Codons and Antocodons Use of the amino acid chart Proteins potential for variation ...
12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Types of RNA RNA Used For Protein Synthesis Three Types of RNA Messenger RNA, mRNA Ribosomal RNA, rRNA Transfer RNA, ...
... Types of RNA RNA Used For Protein Synthesis Three Types of RNA Messenger RNA, mRNA Ribosomal RNA, rRNA Transfer RNA, ...
Supporting Information File SF5
... ependorf tube and precipitate from the phenol-ethanol supernatants using 1.5ml isopropanol per 1ml reagent. Light vertex, and incubation (10 min., room temp.), and then centrifuged (10,254g, 10 min at 4 °C). In-gel proteolysis Proteins subjected to gel electrophoresis were reduced with 10 mM DTT (60 ...
... ependorf tube and precipitate from the phenol-ethanol supernatants using 1.5ml isopropanol per 1ml reagent. Light vertex, and incubation (10 min., room temp.), and then centrifuged (10,254g, 10 min at 4 °C). In-gel proteolysis Proteins subjected to gel electrophoresis were reduced with 10 mM DTT (60 ...
LSm
In molecular biology, LSm proteins are a family of RNA-binding proteins found in virtually every cellular organism. LSm is a contraction of 'like Sm', because the first identified members of the LSm protein family were the Sm proteins. LSm proteins are defined by a characteristic three-dimensional structure and their assembly into rings of six or seven individual LSm protein molecules, and play a large number of various roles in mRNA processing and regulation.The Sm proteins were first discovered as antigens targeted by so-called Anti-Sm antibodies in a patient with a form of Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), a debilitating autoimmune disease. They were named Sm proteins in honor of Stephanie Smith, a patient who suffered from SLE. Other proteins with very similar structures were subsequently discovered and named LSm proteins. New members of the LSm protein family continue to be identified and reported.Proteins with similar structures are grouped into a hierarchy of protein families, superfamilies, and folds. The LSm protein structure is an example of a small beta sheet folded into a short barrel. Individual LSm proteins assemble into a six or seven member doughnut ring (more properly termed a torus), which usually binds to a small RNA molecule to form a ribonucleoprotein complex. The LSm torus assists the RNA molecule to assume and maintain its proper three-dimensional structure. Depending on which LSm proteins and RNA molecule are involved, this ribonucleoprotein complex facilitates a wide variety of RNA processing including degradation, editing, splicing, and regulation.Alternate terms for LSm family are LSm fold and Sm-like fold, and alternate capitalization styles such as lsm, LSM, and Lsm are common and equally acceptable.