Chapter 16 - HCC Learning Web
... 2. Fig. 17.5 page 339 shows the dictionary of the genetic code. Know how to use it. AUG has a dual function coding for methionine and also functioning as a “start” signal. ...
... 2. Fig. 17.5 page 339 shows the dictionary of the genetic code. Know how to use it. AUG has a dual function coding for methionine and also functioning as a “start” signal. ...
Presentation
... • Evaluated network reconstruction on the KEGG cell cycle pathway • Created a Receiver-Operator (ROC) Curve (True positive rate vs. False ...
... • Evaluated network reconstruction on the KEGG cell cycle pathway • Created a Receiver-Operator (ROC) Curve (True positive rate vs. False ...
Transcription
... initially synthesized‐‐a cut‐and‐paste job called RNA splicing. The average length of a transcription unit along a eukaryotic DNA molecule is about 8,000 nucleotides, so the primary RNA transcript is also that long. But it takes only about 1,200 nucleotides to code for an average‐sized protein of ...
... initially synthesized‐‐a cut‐and‐paste job called RNA splicing. The average length of a transcription unit along a eukaryotic DNA molecule is about 8,000 nucleotides, so the primary RNA transcript is also that long. But it takes only about 1,200 nucleotides to code for an average‐sized protein of ...
Biological vocabulary glossary, part 1
... The bases that occur in DNA are Cytosine (C), guanine (G), adenine (A), or thymine (T). Instead of Thymine, Uracil (U) is used in RNA; the other bases stay the same. A phosphate group links together sugar backbone and bases. Together, these three elements create a nucleotide - the basic ...
... The bases that occur in DNA are Cytosine (C), guanine (G), adenine (A), or thymine (T). Instead of Thymine, Uracil (U) is used in RNA; the other bases stay the same. A phosphate group links together sugar backbone and bases. Together, these three elements create a nucleotide - the basic ...
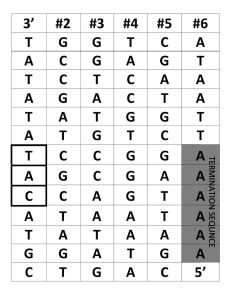
5` 3` - UTSA CS
... Has orientations Usually recorded from N-terminal to C-terminal Peptide vs protein: basically the same thing Conventions – Peptide is shorter (< 50aa), while protein is longer – Peptide refers to the sequence, while protein has 2D/3D structure ...
... Has orientations Usually recorded from N-terminal to C-terminal Peptide vs protein: basically the same thing Conventions – Peptide is shorter (< 50aa), while protein is longer – Peptide refers to the sequence, while protein has 2D/3D structure ...
Chapter 16 - drtracey.net
... clones with DNA fragment of interest identified from clone library preliminary screening - eliminate any clones without a vector and clones with vectors that do not contain DNA employ vector with gene for antibiotic resistance and lac Z’ gene expose to growth medium ...
... clones with DNA fragment of interest identified from clone library preliminary screening - eliminate any clones without a vector and clones with vectors that do not contain DNA employ vector with gene for antibiotic resistance and lac Z’ gene expose to growth medium ...
Genetics Video
... 5. How many times longer is DNA than it is wide? A b__________ times longer. 6. Your g____________ are strung out on c_________________. Thousands and thousands of g_____ are joined together to make a c___________. 7. DNA is contained in the n___________ of a cell. 8. G_________ are packed into c___ ...
... 5. How many times longer is DNA than it is wide? A b__________ times longer. 6. Your g____________ are strung out on c_________________. Thousands and thousands of g_____ are joined together to make a c___________. 7. DNA is contained in the n___________ of a cell. 8. G_________ are packed into c___ ...
CIS 595 Bioinformatics
... Figure 6-65. Translating an mRNA molecule. Each amino acid added to the growing end of a polypeptide chain is selected by complementary base-pairing between the anticodon on its attached tRNA molecule and the next codon on the mRNA chain. Because only one of the many types of tRNA molecules in a cel ...
... Figure 6-65. Translating an mRNA molecule. Each amino acid added to the growing end of a polypeptide chain is selected by complementary base-pairing between the anticodon on its attached tRNA molecule and the next codon on the mRNA chain. Because only one of the many types of tRNA molecules in a cel ...
ChIP-seq
... Histones (various types and modifications) RNA Polymerase (survey of transcription) DNA polymerase (investigate DNA replication) DNA repair enzymes ...
... Histones (various types and modifications) RNA Polymerase (survey of transcription) DNA polymerase (investigate DNA replication) DNA repair enzymes ...
Characteristics of Living Things (Essay
... Importance of each process Stages. What happens? When? Spermatogenesis & Oogenesis 2. DNA in different forms DNA basic structure. Remember nucleotides? Drawings? What is a gene? Centromere? Homologous Chromosomes 3. Mutations & Cancer & Aging Mutations: Good? Bad? Indifferent? Mutati ...
... Importance of each process Stages. What happens? When? Spermatogenesis & Oogenesis 2. DNA in different forms DNA basic structure. Remember nucleotides? Drawings? What is a gene? Centromere? Homologous Chromosomes 3. Mutations & Cancer & Aging Mutations: Good? Bad? Indifferent? Mutati ...
AP Biology 12
... Some of the enzymes responsible for acetylation or deacetylation are associated with or are components of transcription factors that bind to promoters. ...
... Some of the enzymes responsible for acetylation or deacetylation are associated with or are components of transcription factors that bind to promoters. ...
Fig. 7 Cancer cell signaling pathways and the cellular processes
... What all cancers have in common is DNA damage that leads to run-away cell division. It is a kind of cellular evolution where natural selection favors those that divide most rapidly. The DNA damage results in altered proteins, the interactions of which often promote more DNA damage. It is much easie ...
... What all cancers have in common is DNA damage that leads to run-away cell division. It is a kind of cellular evolution where natural selection favors those that divide most rapidly. The DNA damage results in altered proteins, the interactions of which often promote more DNA damage. It is much easie ...
CHIP-seq and RNA-seq
... Provides the mRNA level of thousands of genes (sometimes almost all known genes in a genome) in a given sample Sample=tissue (e.g., liver, brain), tissue in a specific environment or state (e.g., brain with cancer), etc. ...
... Provides the mRNA level of thousands of genes (sometimes almost all known genes in a genome) in a given sample Sample=tissue (e.g., liver, brain), tissue in a specific environment or state (e.g., brain with cancer), etc. ...
Chapter 13: Genetic Engineering
... Radiation & Chemicals Not a sure bet nor do you know what you are going to get Polyploidy (3N or 4N) plants have resulted from this – larger & hardier ...
... Radiation & Chemicals Not a sure bet nor do you know what you are going to get Polyploidy (3N or 4N) plants have resulted from this – larger & hardier ...
Molecular genetics (cloning)
... -The original chromosome with the special gene is distributed into small pieces in the bacterial clone. ...
... -The original chromosome with the special gene is distributed into small pieces in the bacterial clone. ...
Microbial Genomics
... Bacteria, 19 Archaea) 521 Ongoing prokaryote genome projects: (494 Bacteria, 27 Archaea) 28 Eukaryote genomes fully sequenced and annotated. 453 ongoing eukaryote projects. 7 vertebrates, 9 invertebrates, 7 fungii, 10 protozoa and 2 flys. 1674 virus genomes have been sequenced and annotated ...
... Bacteria, 19 Archaea) 521 Ongoing prokaryote genome projects: (494 Bacteria, 27 Archaea) 28 Eukaryote genomes fully sequenced and annotated. 453 ongoing eukaryote projects. 7 vertebrates, 9 invertebrates, 7 fungii, 10 protozoa and 2 flys. 1674 virus genomes have been sequenced and annotated ...
Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis
... complementary bases using uracil instead of thymine • Continues until the polymerase reaches the termination signal • What do you think a termination signal does? • Termination signal causes the polymerase to release the DNA and RNA ...
... complementary bases using uracil instead of thymine • Continues until the polymerase reaches the termination signal • What do you think a termination signal does? • Termination signal causes the polymerase to release the DNA and RNA ...
BI_1_Yang
... events, SNPs located in gene structure, mitochondrial proteins, micro-RNA elements, biological pathways, and PPI networks ...
... events, SNPs located in gene structure, mitochondrial proteins, micro-RNA elements, biological pathways, and PPI networks ...
Explain the importance of gene regulation in both prokaryotes and
... ¾ In prokaryotes, functionally related genes are often located next to each other and are transcribed as a unit. ¾ For example, in E. coli 5 different enzymes are needed to synthesize the amino acid tryptophan. The genes that code for these enzymes are located together. ...
... ¾ In prokaryotes, functionally related genes are often located next to each other and are transcribed as a unit. ¾ For example, in E. coli 5 different enzymes are needed to synthesize the amino acid tryptophan. The genes that code for these enzymes are located together. ...
Structural and functional characterization of the promoter regions of
... Based on the nucleotide sequence of cDNA clones and the 5' flanking genomlc region of the NFKB2 gene, RT-PCR analysis in a number of human cell lines demonstrated the presence of two alternative noncoding first exons (la and Ib). Two distinct promoter regions, P1 and P2, were identified upstream of ...
... Based on the nucleotide sequence of cDNA clones and the 5' flanking genomlc region of the NFKB2 gene, RT-PCR analysis in a number of human cell lines demonstrated the presence of two alternative noncoding first exons (la and Ib). Two distinct promoter regions, P1 and P2, were identified upstream of ...
Transcription and Translation
... transcription is numbered “+1” and is called the transcription start site. • Transcription factors that are required at every promoter site for RNA polymerase interaction are called basal transcription factors. ...
... transcription is numbered “+1” and is called the transcription start site. • Transcription factors that are required at every promoter site for RNA polymerase interaction are called basal transcription factors. ...
A Gene Coexpression Network for Global Discovery of Conserved
... ► Would the multi-species network be as useful for species that are more closely related? ► Gene orthology is based on protein sequence similarity. Does sequence conservation equate to conserved function? ► Are 12 clusters of meta-genes sufficient to hypothesize function for 3416 metagenes? ► How ca ...
... ► Would the multi-species network be as useful for species that are more closely related? ► Gene orthology is based on protein sequence similarity. Does sequence conservation equate to conserved function? ► Are 12 clusters of meta-genes sufficient to hypothesize function for 3416 metagenes? ► How ca ...
Promoter (genetics)
In genetics, a promoter is a region of DNA that initiates transcription of a particular gene. Promoters are located near the transcription start sites of genes, on the same strand and upstream on the DNA (towards the 5' region of the sense strand).Promoters can be about 100–1000 base pairs long.