Prescott`s Microbiology, 9th Edition Chapter 18 – Microbial
... Figure 18.15 How would determining the amino acid sequence of a 30 amino acid residue peptide differ from determining the amino acid sequence of a 200,000 dalton protein? The peptide would generate a few fragments, while the protein would generate dozens. Figure 18.18 Two strains of E. coli are show ...
... Figure 18.15 How would determining the amino acid sequence of a 30 amino acid residue peptide differ from determining the amino acid sequence of a 200,000 dalton protein? The peptide would generate a few fragments, while the protein would generate dozens. Figure 18.18 Two strains of E. coli are show ...
Microbial and Biofunctional Biotechnology for the Benefit of Human
... I have always interested in application of bacteria to human health since I started to study in field of life science. First, I have started research with bacteria and its bacteriphages and then extended my research to natural functional materials. The aim of this study is to establish the integrase ...
... I have always interested in application of bacteria to human health since I started to study in field of life science. First, I have started research with bacteria and its bacteriphages and then extended my research to natural functional materials. The aim of this study is to establish the integrase ...
Structural and Functional Characterization of Shrimp Viral Proteins
... Litopenaeus vannamei. Although selective breeding for improvement of TSV resistance in L. vannamei has been successfully developed and has led to a great benefit to the shrimp farming industry worldwide. The molecular mechanisms underlying the viral resistance in shrimp remain largely unknown. In th ...
... Litopenaeus vannamei. Although selective breeding for improvement of TSV resistance in L. vannamei has been successfully developed and has led to a great benefit to the shrimp farming industry worldwide. The molecular mechanisms underlying the viral resistance in shrimp remain largely unknown. In th ...
Abstract-Template-2016
... SNPs in many subjects, no heterozygotes were observed, despite the use of multiple PCRbased methods and several different primer pairs. Experiments with mixing the genomic DNA from different individuals proved that the assays were capable of detecting both alleles simultaneously. This indicates that ...
... SNPs in many subjects, no heterozygotes were observed, despite the use of multiple PCRbased methods and several different primer pairs. Experiments with mixing the genomic DNA from different individuals proved that the assays were capable of detecting both alleles simultaneously. This indicates that ...
Abstract-Template-2017 - Queenstown Research Week
... SNPs in many subjects, no heterozygotes were observed, despite the use of multiple PCRbased methods and several different primer pairs. Experiments with mixing the genomic DNA from different individuals proved that the assays were capable of detecting both alleles simultaneously. This indicates that ...
... SNPs in many subjects, no heterozygotes were observed, despite the use of multiple PCRbased methods and several different primer pairs. Experiments with mixing the genomic DNA from different individuals proved that the assays were capable of detecting both alleles simultaneously. This indicates that ...
Document
... Result: both heparin and repressor inhibits (re)association of polymerase with promoter. Analysis: (1) heparin binds polymerase preventing association with DNA (2) repressor does the same by binding to the operator adjacent to the promoter and blocking access to the promoter by RNA polymerase. Con ...
... Result: both heparin and repressor inhibits (re)association of polymerase with promoter. Analysis: (1) heparin binds polymerase preventing association with DNA (2) repressor does the same by binding to the operator adjacent to the promoter and blocking access to the promoter by RNA polymerase. Con ...
The Molecular Genetics of Gene Expression
... • Promoter = nucleotide sequence 20-200 bp long—is the initial binding site of RNA polymerase and transcription initiation factors ...
... • Promoter = nucleotide sequence 20-200 bp long—is the initial binding site of RNA polymerase and transcription initiation factors ...
Central Dogma
... • 2 molecules involved: microRNA and siRNA (small interfering RNA) that regulate gene expression. ...
... • 2 molecules involved: microRNA and siRNA (small interfering RNA) that regulate gene expression. ...
PowerPoint
... One of the longevity genes discovered encodes a protein called SIRT1, which is 1 of 7 proteins. These proteins are known as a class III histone deacetlyase, which means that they use NAD+ to remove Lysine acetyl from proteins or histones. Eventually the function of SIRT6 was discovered by researcher ...
... One of the longevity genes discovered encodes a protein called SIRT1, which is 1 of 7 proteins. These proteins are known as a class III histone deacetlyase, which means that they use NAD+ to remove Lysine acetyl from proteins or histones. Eventually the function of SIRT6 was discovered by researcher ...
Matt Reuter
... RNA can catalyze reactions like enzymes. RNA can control gene expression through riboswitches. ...
... RNA can catalyze reactions like enzymes. RNA can control gene expression through riboswitches. ...
Estimating the Recovery Kinetics of tER Sites
... Through fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) imaging techniques the rate proteins attached to specific genes transfer between tER sites is observable, allowing one to infer protein kinetics and behaviors. It is important to estimate a function accurately describing the recovery kinetics ...
... Through fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) imaging techniques the rate proteins attached to specific genes transfer between tER sites is observable, allowing one to infer protein kinetics and behaviors. It is important to estimate a function accurately describing the recovery kinetics ...
Investigating the effects of different types of mutations
... Q16. A 3.3 kbp gene encoding for a protein that produces melanin (hair pigment) in rats has 300 bases deleted from the middle of the sequence. Do you think the protein will still be functional? Explain your answer. Q17. If this mutation was in the only functional copy of this gene in the individual ...
... Q16. A 3.3 kbp gene encoding for a protein that produces melanin (hair pigment) in rats has 300 bases deleted from the middle of the sequence. Do you think the protein will still be functional? Explain your answer. Q17. If this mutation was in the only functional copy of this gene in the individual ...
DNA and RNA
... together by two types of bonds. Phosphodiester bonds link the phosphate group of one nucleotide to the sugar of an adjacent nucleotide along the side of the double helix. The nitrogenous bases are held together by hydrogen bonds across a rung. ...
... together by two types of bonds. Phosphodiester bonds link the phosphate group of one nucleotide to the sugar of an adjacent nucleotide along the side of the double helix. The nitrogenous bases are held together by hydrogen bonds across a rung. ...
Protein Synthesis Notes: Transcription and Translation
... Codon: group of ___________ nucleotides on the messenger RNA that specifies one amino acid. 3. _______________ (transfer RNA) carries amino acids to the mRNA. 4. This tRNA has an ________________ that matches the codon on the mRNA strand. _____________________: group of 3 unpaired nucleotides on a t ...
... Codon: group of ___________ nucleotides on the messenger RNA that specifies one amino acid. 3. _______________ (transfer RNA) carries amino acids to the mRNA. 4. This tRNA has an ________________ that matches the codon on the mRNA strand. _____________________: group of 3 unpaired nucleotides on a t ...
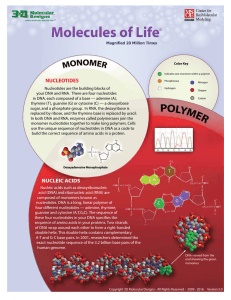
Nucleic Acids Placemat
... Nucleic acids such as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are composed of monomers known as nucleotides. DNA is a long, linear polymer of four different nucleotides — adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine (A,T,G,C). The sequence of these four nucleotides in your DNA specifies the ...
... Nucleic acids such as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are composed of monomers known as nucleotides. DNA is a long, linear polymer of four different nucleotides — adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine (A,T,G,C). The sequence of these four nucleotides in your DNA specifies the ...
Transformation Lab
... referred to by its common name, X-gal. X-gal is colorless, but when it is cleaved by beta-galactosidase, one of the products is dark blue. Therefore, if you grow bacteria that produce beta-galactosidase on media containing X-gal, the colonies will be bright blue. ...
... referred to by its common name, X-gal. X-gal is colorless, but when it is cleaved by beta-galactosidase, one of the products is dark blue. Therefore, if you grow bacteria that produce beta-galactosidase on media containing X-gal, the colonies will be bright blue. ...
Biotechnology
... taken from one organism and placed into the cells of another organism. As a result, for example, we can cause bacterial cells to produce human molecules. ...
... taken from one organism and placed into the cells of another organism. As a result, for example, we can cause bacterial cells to produce human molecules. ...
Tools_and_Methods_of_Genetic_Engineering
... 2. human DNA is cut (with restriction enzymes) into thousand of short fragments and then each of those short fragments is inserted to separate bacteria 3. a “complete” copy of human genome has been accomplished in 2002 = human genomic library (human genome project) 4. problems: expensive to maintain ...
... 2. human DNA is cut (with restriction enzymes) into thousand of short fragments and then each of those short fragments is inserted to separate bacteria 3. a “complete” copy of human genome has been accomplished in 2002 = human genomic library (human genome project) 4. problems: expensive to maintain ...
11/01 Molecular genetic analysis and biotechnology
... chromosomal location and to visualize a gene while it is in a cell • May also be used to detect localization of mRNA expression in multicellular organisms. ...
... chromosomal location and to visualize a gene while it is in a cell • May also be used to detect localization of mRNA expression in multicellular organisms. ...
21 356 Molecular Biology
... 3. Describe the intermolecular forces used to promote interactions between DNA, RNA, proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates. 4. Discuss the roles of non-coding RNAs in regulating gene expression 5. Describe how DNA, RNA, and proteins are synthesized, regulated, and degraded in cells ...
... 3. Describe the intermolecular forces used to promote interactions between DNA, RNA, proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates. 4. Discuss the roles of non-coding RNAs in regulating gene expression 5. Describe how DNA, RNA, and proteins are synthesized, regulated, and degraded in cells ...
Solutions for Practice Problems for Molecular Biology, Session 3
... f) A mutation occurs which results in the insertion of an extra G/C (top strand/bottom strand) base- pair immediately after base pair 11 (shown in bold). What effect will this insertion mutation have on the mRNA transcript and resulting protein? The mRNA will be longer by one nucleotide, but because ...
... f) A mutation occurs which results in the insertion of an extra G/C (top strand/bottom strand) base- pair immediately after base pair 11 (shown in bold). What effect will this insertion mutation have on the mRNA transcript and resulting protein? The mRNA will be longer by one nucleotide, but because ...
Supporting Information S1: 1. Establishment of hSMP30 transcription
... cooled to room temp and was reverse transcribed at 42ºC for 1hour using primer extension system (Promega, USA) according to manufacturer’s instruction. The same primer was used for the sequencing reactions of cloned SMP30 promoter containing exon 1. Sequencing reactions and primer extension product ...
... cooled to room temp and was reverse transcribed at 42ºC for 1hour using primer extension system (Promega, USA) according to manufacturer’s instruction. The same primer was used for the sequencing reactions of cloned SMP30 promoter containing exon 1. Sequencing reactions and primer extension product ...
Sequence of events in formation of eukaryotic mRNA
... splicing to occur? What would happen if there was a mutation in a splice site consensus sequence? •What is the significance of the lariat structure in splicing out introns? ...
... splicing to occur? What would happen if there was a mutation in a splice site consensus sequence? •What is the significance of the lariat structure in splicing out introns? ...
RNA processing - Faculty Web Pages
... splicing to occur? What would happen if there was a mutation in a splice site consensus sequence? •What is the significance of the lariat structure in splicing out introns? ...
... splicing to occur? What would happen if there was a mutation in a splice site consensus sequence? •What is the significance of the lariat structure in splicing out introns? ...
HUMAN-CHIMP DNA
... only 13 nucleotides, a far larger number of changes than would be expected had the mutations been the result of drift rather than selection. The location of enhancer activity highlights the importance of the difference. Our hands, with their opposable thumbs*, our feet, evolved for bipedal locomotio ...
... only 13 nucleotides, a far larger number of changes than would be expected had the mutations been the result of drift rather than selection. The location of enhancer activity highlights the importance of the difference. Our hands, with their opposable thumbs*, our feet, evolved for bipedal locomotio ...
Promoter (genetics)
In genetics, a promoter is a region of DNA that initiates transcription of a particular gene. Promoters are located near the transcription start sites of genes, on the same strand and upstream on the DNA (towards the 5' region of the sense strand).Promoters can be about 100–1000 base pairs long.