Lecture 14 Gene Regulation
... with the goal of increasing in mass and dividing. • Genes that are continuously expressed are constitutive genes or housekeeping genes. Examples include protein synthesis and glucose metabolism. ...
... with the goal of increasing in mass and dividing. • Genes that are continuously expressed are constitutive genes or housekeeping genes. Examples include protein synthesis and glucose metabolism. ...
CHAPTER 10 - Protein Synthesis The DNA genotype is expressed
... of the cell or exported out of the cell Figure 10.20 • Summary of transcription and translation Review: The flow of genetic information in the cell is DNA→RNA→protein • The sequence of codons in DNA spells out the primary structure of a polypeptide – Polypeptides form proteins that cells and organis ...
... of the cell or exported out of the cell Figure 10.20 • Summary of transcription and translation Review: The flow of genetic information in the cell is DNA→RNA→protein • The sequence of codons in DNA spells out the primary structure of a polypeptide – Polypeptides form proteins that cells and organis ...
Gene Section RBM15 (RNA binding motif protein 15) in Oncology and Haematology
... Complete remission in only 50% of cases; median survival: 8 months. Cytogenetics 60% of cases have the t(1;22) as a single anomaly; the remaining cases exhibit complex and hyperploid clones. Hybrid/Mutated gene 5' OTT - 3' MAL, comprisng most of OTT fused to most of MAL; the reciprocal 5' MAL - 3' O ...
... Complete remission in only 50% of cases; median survival: 8 months. Cytogenetics 60% of cases have the t(1;22) as a single anomaly; the remaining cases exhibit complex and hyperploid clones. Hybrid/Mutated gene 5' OTT - 3' MAL, comprisng most of OTT fused to most of MAL; the reciprocal 5' MAL - 3' O ...
DNA Replication, Transcription and Translation assessment
... 2.7.2 Explain the significance of complementary base pairing in the conservation of the base sequence of DNA 2.7.3 State that DNA replication is semi-conservative 2.7.4 Compare the structure of DNA and RNA 2.7.5 Outline DNA transcription in terms of the formation of an RNA strand complementary to th ...
... 2.7.2 Explain the significance of complementary base pairing in the conservation of the base sequence of DNA 2.7.3 State that DNA replication is semi-conservative 2.7.4 Compare the structure of DNA and RNA 2.7.5 Outline DNA transcription in terms of the formation of an RNA strand complementary to th ...
Lecture 20
... transcription begins and ends. – RNA polymerase attaches and initiates transcription at the promotor ال ُم َحفـز, at the beginning of the transcription unit (gene) on the DNA. – The terminator منطقة النهايةends the transcription. • Bacteria have a single type of RNA polymerase that synthesizes ...
... transcription begins and ends. – RNA polymerase attaches and initiates transcription at the promotor ال ُم َحفـز, at the beginning of the transcription unit (gene) on the DNA. – The terminator منطقة النهايةends the transcription. • Bacteria have a single type of RNA polymerase that synthesizes ...
Recombinant DNA Technology Manipulation of Gene Expression in
... expressed in E. coli, resulting in production of eukaryotic proteins in transformed bacteria. ...
... expressed in E. coli, resulting in production of eukaryotic proteins in transformed bacteria. ...
Biology 212 General Genetics
... Similar to DNA Contains ribose sugar in place of deoxyribose Contains the base uracil (U) in place of thymine (T) Three types of RNA mRNA=messenger RNA Carries information from DNA Used as a template for protein synthesis rRNA=ribosomal RNA Several types of rRNA Major components of rib ...
... Similar to DNA Contains ribose sugar in place of deoxyribose Contains the base uracil (U) in place of thymine (T) Three types of RNA mRNA=messenger RNA Carries information from DNA Used as a template for protein synthesis rRNA=ribosomal RNA Several types of rRNA Major components of rib ...
Pre-post test questions
... 15. Individuals with the diseases -thalassemia and sickle cell anemia both have mutations in the gene for hemoglobin. How could mutations in the same gene cause two different disease phenotypes? The different mutations in the DNA would cause different amino acids to be changed in the protein. The ...
... 15. Individuals with the diseases -thalassemia and sickle cell anemia both have mutations in the gene for hemoglobin. How could mutations in the same gene cause two different disease phenotypes? The different mutations in the DNA would cause different amino acids to be changed in the protein. The ...
View PDF - Genetics
... animal kingdom. Cilia formation and function depends on kinesin 2 family motors and on intraflagellar transport (IFT) proteins, which mediate transport inside the ciliary shaft. The authors show that both the main ciliary motor (heterotrimetic kinesin 2) and IFT proteins display unexpected functions ...
... animal kingdom. Cilia formation and function depends on kinesin 2 family motors and on intraflagellar transport (IFT) proteins, which mediate transport inside the ciliary shaft. The authors show that both the main ciliary motor (heterotrimetic kinesin 2) and IFT proteins display unexpected functions ...
Viewpoint - Prof Ralf Metzler
... the fundamental processes of gene regulation, yet we know that genetic systems may be extremely stable. Facilitated diffusion—the interplay of three-dimensional and one-dimensional search of DNA binding proteins for their specific binding sites—has been proposed to explain the regulation speed and l ...
... the fundamental processes of gene regulation, yet we know that genetic systems may be extremely stable. Facilitated diffusion—the interplay of three-dimensional and one-dimensional search of DNA binding proteins for their specific binding sites—has been proposed to explain the regulation speed and l ...
Structure of cloned δ-globin genes from a normal subject and a
... H i n d H I , B ^ I I , PstI and BamHI (Takara Shuzo Co., Ltd, Japan) at 37°C in the buffer recommended by the manufacturer, and fractionated 1n 0.6 % agarose gel by electrophoresis. Tnen DNA fragments were transferred onto nitrocellulose f i l t e r s and hybridized to various DNA probes labelled w ...
... H i n d H I , B ^ I I , PstI and BamHI (Takara Shuzo Co., Ltd, Japan) at 37°C in the buffer recommended by the manufacturer, and fractionated 1n 0.6 % agarose gel by electrophoresis. Tnen DNA fragments were transferred onto nitrocellulose f i l t e r s and hybridized to various DNA probes labelled w ...
Genetic Engineering Techniques
... found in bacteria) is placed in a container with special restriction enzymes that cut the DNA at a certain recognizable sequence. The same enzyme is then used to treat the DNA sequence to be engin ...
... found in bacteria) is placed in a container with special restriction enzymes that cut the DNA at a certain recognizable sequence. The same enzyme is then used to treat the DNA sequence to be engin ...
Chapter 21 (part 1) - University of Nevada, Reno
... of the enzyme (up to 50 nm!) • Only RNA Pol II whose CTD is NOT phosphorylated can initiate transcription • TATA box (TATAAA) is a consensus promoter • 7 general transcription factors are ...
... of the enzyme (up to 50 nm!) • Only RNA Pol II whose CTD is NOT phosphorylated can initiate transcription • TATA box (TATAAA) is a consensus promoter • 7 general transcription factors are ...
Chapter 11 - useful links
... The principles of probability can be used to predict the outcomes of genetic crosses. Punnett squares are tables that can be used to calculate the different gene combinations that could result from a particular cross. There are some cases that exist where alleles are not completely dominant, ...
... The principles of probability can be used to predict the outcomes of genetic crosses. Punnett squares are tables that can be used to calculate the different gene combinations that could result from a particular cross. There are some cases that exist where alleles are not completely dominant, ...
The methanol oxidation genes mxaFJGIR(S)ACKLD in
... The genes mxaFJGI are transcribed from a promoter upstream of mxaF ; this is the only promoter so far de¢nitively identi¢ed in a methylotroph [4,7]. About 2 kb downstream from mxaI in Methylobacterium extorquens is another cluster of genes (mxaACKLD) some, if not all, of which are involved in the in ...
... The genes mxaFJGI are transcribed from a promoter upstream of mxaF ; this is the only promoter so far de¢nitively identi¢ed in a methylotroph [4,7]. About 2 kb downstream from mxaI in Methylobacterium extorquens is another cluster of genes (mxaACKLD) some, if not all, of which are involved in the in ...
Fusion protein
... expressed in E. coli, resulting in production of eukaryotic proteins in transformed bacteria. ...
... expressed in E. coli, resulting in production of eukaryotic proteins in transformed bacteria. ...
Recombinant DNA Technology Manipulation of Gene Expression in
... expressed in E. coli, resulting in production of eukaryotic proteins in transformed bacteria. ...
... expressed in E. coli, resulting in production of eukaryotic proteins in transformed bacteria. ...
The Proteomics of Epigenetics
... Differences in Histones: Variant • All histones have variants except H4 • The varients are subject to posttranslational modification as well • Some are very similar with subtle differences (ex. H3 and H3.3) • Others are very different (ex. H2A and macroH2A) • Specific tasks: Transcription activatin ...
... Differences in Histones: Variant • All histones have variants except H4 • The varients are subject to posttranslational modification as well • Some are very similar with subtle differences (ex. H3 and H3.3) • Others are very different (ex. H2A and macroH2A) • Specific tasks: Transcription activatin ...
DNA and RNA review
... How do the purines and pyrimidines differ structurally? What type of bond holds the 2 strands of DNA together? Describe this type of bond. Explain the complementary base pairing of the nitrogen bases in DNA. What is produced in DNA replication? Why is DNA replication necessary? What important roles ...
... How do the purines and pyrimidines differ structurally? What type of bond holds the 2 strands of DNA together? Describe this type of bond. Explain the complementary base pairing of the nitrogen bases in DNA. What is produced in DNA replication? Why is DNA replication necessary? What important roles ...
Recombinant DNA Technology Manipulation of Gene Expression in
... expressed in E. coli, resulting in production of eukaryotic proteins in transformed bacteria. ...
... expressed in E. coli, resulting in production of eukaryotic proteins in transformed bacteria. ...
Biology
... 3. Describe what occurs in each step of the cell cycle.(Interphase, Mitosis, and Cytokinesis) 4. Describe what occurs in each phase of mitosis. 5. Contrast cytokinesis in plant and animal cells. 6. What are the two reasons why cells undergo mitosis and cytokinesis? 7. How is cell division controlled ...
... 3. Describe what occurs in each step of the cell cycle.(Interphase, Mitosis, and Cytokinesis) 4. Describe what occurs in each phase of mitosis. 5. Contrast cytokinesis in plant and animal cells. 6. What are the two reasons why cells undergo mitosis and cytokinesis? 7. How is cell division controlled ...
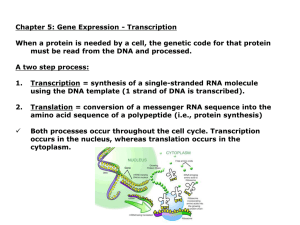
Gene expression: Transcription
... When a protein is needed by a cell, the genetic code for that protein must be read from the DNA and processed. A two step process: ...
... When a protein is needed by a cell, the genetic code for that protein must be read from the DNA and processed. A two step process: ...
C - NCSU Bioinformatics Research Center
... • The transcribed mRNA (pre-mRNA) must first be processed into mature mRNA • The protein-coding regions (exons) are interspersed with non-coding regions (introns) which must be excised ...
... • The transcribed mRNA (pre-mRNA) must first be processed into mature mRNA • The protein-coding regions (exons) are interspersed with non-coding regions (introns) which must be excised ...
Promoter (genetics)
In genetics, a promoter is a region of DNA that initiates transcription of a particular gene. Promoters are located near the transcription start sites of genes, on the same strand and upstream on the DNA (towards the 5' region of the sense strand).Promoters can be about 100–1000 base pairs long.