Document
... as well as the presence of other genetic conditions and known disorders. The most widely used methods are: – Amniocentesis – Chorionic villi sampling (CVS) – Fetal cells are isolated and cultured ...
... as well as the presence of other genetic conditions and known disorders. The most widely used methods are: – Amniocentesis – Chorionic villi sampling (CVS) – Fetal cells are isolated and cultured ...
Assembling the nuclear receptor genesets
... in the DGAP expression data and protein-protein interaction network. The sizes of the three genesets were 35, 32, and 49, respectively. Assembling the IS-HD gene set Because type 2 diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance, the insulin signaling pathway is a natural candidate for testing for a ...
... in the DGAP expression data and protein-protein interaction network. The sizes of the three genesets were 35, 32, and 49, respectively. Assembling the IS-HD gene set Because type 2 diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance, the insulin signaling pathway is a natural candidate for testing for a ...
3/27
... Genomics I: The Transcriptome RNA Expression Analysis Determining genomewide RNA expression levels ...
... Genomics I: The Transcriptome RNA Expression Analysis Determining genomewide RNA expression levels ...
Viral genomes
... Viral genomes: ssRNA, dsRNA, ssDNA, dsDNA, linear or circular Viruses with RNA genomes: • Almost all plant viruses and some bacterial and animal viruses • Genomes are rather small (a few thousand nucleotides) Viruses with DNA genomes (e.g. lambda = 48,502 bp): • Often a circular genome. Replicative ...
... Viral genomes: ssRNA, dsRNA, ssDNA, dsDNA, linear or circular Viruses with RNA genomes: • Almost all plant viruses and some bacterial and animal viruses • Genomes are rather small (a few thousand nucleotides) Viruses with DNA genomes (e.g. lambda = 48,502 bp): • Often a circular genome. Replicative ...
Research Focused Undergraduate Education - GCG-42
... Transfer Golden Rice Grains such as rice, produce all but two of the enzymes needed to produce beta carotene (vit A precursor) Rice feeds half the world’s population Vit A deficiencies are associated with blindness, night blindness, diabetes, anemia and easy infections WHO estimates 220 mi ...
... Transfer Golden Rice Grains such as rice, produce all but two of the enzymes needed to produce beta carotene (vit A precursor) Rice feeds half the world’s population Vit A deficiencies are associated with blindness, night blindness, diabetes, anemia and easy infections WHO estimates 220 mi ...
glossary - Diabetes Care
... It is increasingly being used to study host-pathogen interactions and has helped identify basic evolutionarily conserved pathways associated with microbial pathogenesis. In particular, this has revealed important factors of the host response with remarkable parallels in higher organisms. This organi ...
... It is increasingly being used to study host-pathogen interactions and has helped identify basic evolutionarily conserved pathways associated with microbial pathogenesis. In particular, this has revealed important factors of the host response with remarkable parallels in higher organisms. This organi ...
Chapter 12-13 Notes
... DNA polymerase: joins nucleotides to produce a new strand of DNA -“proofreads” new DNA strand. ...
... DNA polymerase: joins nucleotides to produce a new strand of DNA -“proofreads” new DNA strand. ...
Chapter 5 Genetic Models
... region and the other for the C region • These genes come together during at the DNA level to form a continuous message • There are thousands of V genes in germ line but only one gene for the C region ...
... region and the other for the C region • These genes come together during at the DNA level to form a continuous message • There are thousands of V genes in germ line but only one gene for the C region ...
Traditional and Modern Breeding Methods
... Achieving all these goals will require not only traditional breeder skills, but will be accelerated by the use of novel molecular techniques and biotechnology ...
... Achieving all these goals will require not only traditional breeder skills, but will be accelerated by the use of novel molecular techniques and biotechnology ...
Bio-261-chapter-7
... • The immediate product of this transcription is a resultant initial RNA transcript, which contains a sequence of nucleotides that is identical to the that of the sense strand. The exception to this is that uracil is used for nucleotide sequencing of RNA molecules rather than thymine. ...
... • The immediate product of this transcription is a resultant initial RNA transcript, which contains a sequence of nucleotides that is identical to the that of the sense strand. The exception to this is that uracil is used for nucleotide sequencing of RNA molecules rather than thymine. ...
C - TeacherWeb
... • The immediate product of this transcription is a resultant initial RNA transcript, which contains a sequence of nucleotides that is identical to the that of the sense strand. The exception to this is that uracil is used for nucleotide sequencing of RNA molecules rather than thymine. ...
... • The immediate product of this transcription is a resultant initial RNA transcript, which contains a sequence of nucleotides that is identical to the that of the sense strand. The exception to this is that uracil is used for nucleotide sequencing of RNA molecules rather than thymine. ...
Automate Function Prediction
... (http://genome.cshlp.org/content/early/2011/07/22/gr.104687.109) ...
... (http://genome.cshlp.org/content/early/2011/07/22/gr.104687.109) ...
Genetics: The Science of Heredity
... This is where mRNA will come into the picture - to provide new instructions that will be used by the workers. ...
... This is where mRNA will come into the picture - to provide new instructions that will be used by the workers. ...
From RNA to protein
... The sequence of a coding (sense, non-template) strand of DNA, read 5’ – 3’, specifies a sequence of amino acids (read Nterminus to C-terminus) via a triplet code. Each triplet is called a codon and 4 bases give 43 possible combinations. Reading the DNA code: There are 64 codons; 61 represent amino a ...
... The sequence of a coding (sense, non-template) strand of DNA, read 5’ – 3’, specifies a sequence of amino acids (read Nterminus to C-terminus) via a triplet code. Each triplet is called a codon and 4 bases give 43 possible combinations. Reading the DNA code: There are 64 codons; 61 represent amino a ...
Epigenetics
... transcriptional machinery to gene promoter regions, thus altering gene expression levels. Therefore, promoter rmethylation of CpG islands is commonly associated with gene silencing and promoter demethylation with gene expression, though several exceptions to this rule are known. ...
... transcriptional machinery to gene promoter regions, thus altering gene expression levels. Therefore, promoter rmethylation of CpG islands is commonly associated with gene silencing and promoter demethylation with gene expression, though several exceptions to this rule are known. ...
Gene Regulation
... (b) Acetylation of histone tails promotes loose chromatin structure that permits transcription ...
... (b) Acetylation of histone tails promotes loose chromatin structure that permits transcription ...
Protein Synthesis Notes
... b. Single-stranded, not double. c. Thymine is replaced by URACIL. - Adenine binds with Uracil. ...
... b. Single-stranded, not double. c. Thymine is replaced by URACIL. - Adenine binds with Uracil. ...
THE CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION
... THE CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION • ATTEMPTING TO EXPLAIN THE PROCESS OF DIFFERENTATION LIES IN DISCOVERING HOW EUKARYOTIC CELLS CONTROL GENE EXPRESSION • THIS IS DIFFICULT, BECAUSE EUKARYOTIC GENOMES ARE LARGE AND COMPLEX; BUT WE SHALL DO OUR BEST!!! (VICTORY WILL BE OURS!!) ...
... THE CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION • ATTEMPTING TO EXPLAIN THE PROCESS OF DIFFERENTATION LIES IN DISCOVERING HOW EUKARYOTIC CELLS CONTROL GENE EXPRESSION • THIS IS DIFFICULT, BECAUSE EUKARYOTIC GENOMES ARE LARGE AND COMPLEX; BUT WE SHALL DO OUR BEST!!! (VICTORY WILL BE OURS!!) ...
Gene7-04
... 1. Almost all genes belong to families, defined by the possession of related sequences in the exons of individual members. 2. An evolving set of genes may remain together in a cluster or may be dispersed to new locations by chromosomal rearrangement. 3. Mutations accumulate more rapidly in silent si ...
... 1. Almost all genes belong to families, defined by the possession of related sequences in the exons of individual members. 2. An evolving set of genes may remain together in a cluster or may be dispersed to new locations by chromosomal rearrangement. 3. Mutations accumulate more rapidly in silent si ...
Microbial Genetics
... • Initiator proteins (IP; about 30) bind at repetitive sequences within the OriC site. • DNA winds around IP-complex; induces separation of strand at adjacent AT rich site. • Single strand binding proteins & helicases attach. • Formation of two replication forks that open in opposite ...
... • Initiator proteins (IP; about 30) bind at repetitive sequences within the OriC site. • DNA winds around IP-complex; induces separation of strand at adjacent AT rich site. • Single strand binding proteins & helicases attach. • Formation of two replication forks that open in opposite ...
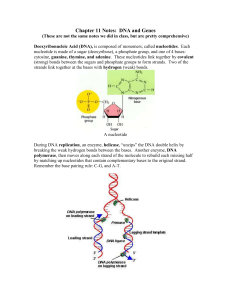
Chapter 11 Notes: DNA and Genes
... In transcription, a single strand of mRNA is copied from DNA, by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. In this case, however, thymine is replaced with uracil, so the “new” base pairing rule is C-G & A-U. The mRNA is then able to move through the nuclear membrane into the cytosol. Remember that all RNA i ...
... In transcription, a single strand of mRNA is copied from DNA, by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. In this case, however, thymine is replaced with uracil, so the “new” base pairing rule is C-G & A-U. The mRNA is then able to move through the nuclear membrane into the cytosol. Remember that all RNA i ...
Bio102 Problems
... 22A. Label the 5′ and 3′ ends on the DNA sequence and indicate which one is the template strand. 22B. Label and name both UTRs. 22C. The promoter consists of two key sequences. Name both of them and show where on the DNA or RNA sequence they would be expected. (You do not have to know or find their ...
... 22A. Label the 5′ and 3′ ends on the DNA sequence and indicate which one is the template strand. 22B. Label and name both UTRs. 22C. The promoter consists of two key sequences. Name both of them and show where on the DNA or RNA sequence they would be expected. (You do not have to know or find their ...
Promoter (genetics)
In genetics, a promoter is a region of DNA that initiates transcription of a particular gene. Promoters are located near the transcription start sites of genes, on the same strand and upstream on the DNA (towards the 5' region of the sense strand).Promoters can be about 100–1000 base pairs long.