Four processes were needed for the spontaneous
... 2. Why RNA? RNA can act as a catalyst to: a. Bind ____________________ together to form _______________ b. ______________________ itself to create more RNA 3. __________ can be transcribed to __________ (using reverse transcriptase); this could have given rise to the first DNA 4. DNA is more stable ...
... 2. Why RNA? RNA can act as a catalyst to: a. Bind ____________________ together to form _______________ b. ______________________ itself to create more RNA 3. __________ can be transcribed to __________ (using reverse transcriptase); this could have given rise to the first DNA 4. DNA is more stable ...
Lecture 5
... determine the amino acid sequence of the protein. • mRNA (“Messenger RNA”) associates with the ribosome (mRNA and protein portion). • RNA (“Transfer RNA”) also required • Codons are 3 base mRNA segments that specify a certain amino acid. • Most amino acids are coded for by more than one codon. • Tra ...
... determine the amino acid sequence of the protein. • mRNA (“Messenger RNA”) associates with the ribosome (mRNA and protein portion). • RNA (“Transfer RNA”) also required • Codons are 3 base mRNA segments that specify a certain amino acid. • Most amino acids are coded for by more than one codon. • Tra ...
Materials and methods (Supplement)
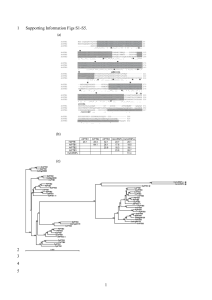
... The Tol2 element is flanked by an 8-bp direct repeat unit, TCAAGAAC, resulting from target site duplications during its integration. After the excision of the Tol2 element, this direct repeat is cancelled to restore the original sequence, possibly via a ‘cut-and-paste’ mechanism (Fig. 2D, type I) [1 ...
... The Tol2 element is flanked by an 8-bp direct repeat unit, TCAAGAAC, resulting from target site duplications during its integration. After the excision of the Tol2 element, this direct repeat is cancelled to restore the original sequence, possibly via a ‘cut-and-paste’ mechanism (Fig. 2D, type I) [1 ...
Teacher`s Name: ___Julie
... 2014-15 LESSON “SNAPSHOT” Teacher’s Name: B. Dunn Course Title and Periods Taught: Bio B – 4th ...
... 2014-15 LESSON “SNAPSHOT” Teacher’s Name: B. Dunn Course Title and Periods Taught: Bio B – 4th ...
Microbial diversity
... Why use rDNA for phylogeny? * Present in all organisms * Has highly conserved and weakly conserved regions ...
... Why use rDNA for phylogeny? * Present in all organisms * Has highly conserved and weakly conserved regions ...
Replication - UniMAP Portal
... Synthesis of the Leading Strand A cell synthesizes a leading strand toward the replication fork in the following series of five steps 1) An enzyme called primase synthesizes a short RNA molecule that is complementary to the template DNA strand. This RNA primer provides the 3' hydroxyl group requir ...
... Synthesis of the Leading Strand A cell synthesizes a leading strand toward the replication fork in the following series of five steps 1) An enzyme called primase synthesizes a short RNA molecule that is complementary to the template DNA strand. This RNA primer provides the 3' hydroxyl group requir ...
T7 In Vitro Transcription Kit esiSCRIBE 100 Reactions (10 µl each
... generation of double-stranded (ds)RNA and guide (g)RNA for RNA interference (RNAi) experiments and CRISPR/Cas systems, respectively. Ready-totransfect esiRNAs (endoribonuclease-prepared siRNAs) and gRNAs are also available from Eupheria Biotech (www.eupheria.com). Reaction Conditions This kit contai ...
... generation of double-stranded (ds)RNA and guide (g)RNA for RNA interference (RNAi) experiments and CRISPR/Cas systems, respectively. Ready-totransfect esiRNAs (endoribonuclease-prepared siRNAs) and gRNAs are also available from Eupheria Biotech (www.eupheria.com). Reaction Conditions This kit contai ...
Lecture 11 - Horizontal Gene Transfer S11 2 slides per page
... •Enzymes cut DNA into smaller fragments (5 - 15 kb) •Single strand is taken up by cell ...
... •Enzymes cut DNA into smaller fragments (5 - 15 kb) •Single strand is taken up by cell ...
here
... This course will provide background knowledge of five basic units of Biochemistry and the relationship between genes and proteins within the cell. Unit 1 deals with the molecules of life, DNA, RNA, nucleotides and the central dogma of molecular biology. Unit 2 covers the decoding of the genetic code ...
... This course will provide background knowledge of five basic units of Biochemistry and the relationship between genes and proteins within the cell. Unit 1 deals with the molecules of life, DNA, RNA, nucleotides and the central dogma of molecular biology. Unit 2 covers the decoding of the genetic code ...
AtPTB-like 1 negatively regulates splicing inclusion of a plant
... Arabidopsis with other plant species show clustering of genes into three distinct groups and a ...
... Arabidopsis with other plant species show clustering of genes into three distinct groups and a ...
Lecture 11 - Horizontal Gene Transfer Chapt. 8 S11
... Observed in only certain species Example - Streptococcus pneumoniae (GPC) •Becomes Becomes competent in late log phase •Competent cell binds ds DNA •Enzymes cut DNA into smaller fragments (5 - 15 kb) •Single strand is taken up by cell Example - Haemophilus influenzae (GNR) •Cell binds DNA only from ...
... Observed in only certain species Example - Streptococcus pneumoniae (GPC) •Becomes Becomes competent in late log phase •Competent cell binds ds DNA •Enzymes cut DNA into smaller fragments (5 - 15 kb) •Single strand is taken up by cell Example - Haemophilus influenzae (GNR) •Cell binds DNA only from ...
Announcements DNA Invertebrates DNA DNA DNA Code
... Two anatomical structures are considered to be analogous when they serve similar functions but are not evolutionarily related. Analogous structures are the result of convergent evolution and are contrasted with homologous structures. Convergent evolution or homoplasious characters show phenotypic si ...
... Two anatomical structures are considered to be analogous when they serve similar functions but are not evolutionarily related. Analogous structures are the result of convergent evolution and are contrasted with homologous structures. Convergent evolution or homoplasious characters show phenotypic si ...
gene therapy
... 3. What types of diseases can gene therapy be used to treat? Gene therapy can be used to treat diseases like cys$c fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and muscular dystrophy. 4. How are viruses used in g ...
... 3. What types of diseases can gene therapy be used to treat? Gene therapy can be used to treat diseases like cys$c fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and muscular dystrophy. 4. How are viruses used in g ...
Transcriptome Atlas
... short reads of RNA present in biological samples, including coding and non-coding RNA. These reads are short, but long enough to be aligned uniquely to genes lying on a reference genome. Thus, reads can be assigned to their respective gene. ...
... short reads of RNA present in biological samples, including coding and non-coding RNA. These reads are short, but long enough to be aligned uniquely to genes lying on a reference genome. Thus, reads can be assigned to their respective gene. ...
DNA Technology
... Farm animals that are genetically altered to synthesize marketable proteins. Mice that urinate human growth hormone (HGH) Goats that produce the malaria antigen for use in ...
... Farm animals that are genetically altered to synthesize marketable proteins. Mice that urinate human growth hormone (HGH) Goats that produce the malaria antigen for use in ...
Folate and DNA methylation during in utero development and aging
... dinucleotides occur at low abundance throughout the human DNA genome and tend to concentrate in regions known as CpG islands found in the promoter regions of genes. A CpG island is a region of DNA with more than 200 bp, a high G-C content and an observed/expected ratio of CpGs greater than 0.6 [2]. ...
... dinucleotides occur at low abundance throughout the human DNA genome and tend to concentrate in regions known as CpG islands found in the promoter regions of genes. A CpG island is a region of DNA with more than 200 bp, a high G-C content and an observed/expected ratio of CpGs greater than 0.6 [2]. ...
Part III PLANT TRANSFORMATION
... used by the bacteria as carbon and nitrogen source. The Ti-plasmid contains genes that help in the break-down of these opines. The T-DNA, which is transferred to the plant cell, contains two types of genes: oncogenic genes, which are responsible for tumor formation, and genes encoding enzymes that s ...
... used by the bacteria as carbon and nitrogen source. The Ti-plasmid contains genes that help in the break-down of these opines. The T-DNA, which is transferred to the plant cell, contains two types of genes: oncogenic genes, which are responsible for tumor formation, and genes encoding enzymes that s ...
Biotechnology student NOTES
... 1) Selective breeding = The process by which desired traits of certain plants and animals are selected and passed on to their future generations. 2) Human Genome Project = (1988-2003) the mapping and sequencing of all the genes in the human genome 3) Genome is the total DNA in the nucleus of each ce ...
... 1) Selective breeding = The process by which desired traits of certain plants and animals are selected and passed on to their future generations. 2) Human Genome Project = (1988-2003) the mapping and sequencing of all the genes in the human genome 3) Genome is the total DNA in the nucleus of each ce ...
RNA interference - genemol de Jean
... In such cases, the formation of the double-stranded RNA through the binding of the miRNA triggers the degradation of the mRNA transcript through a process similar to RNA interference (RNAi), though in other cases it is believed that the miRNA complex blocks the protein translation machinery or other ...
... In such cases, the formation of the double-stranded RNA through the binding of the miRNA triggers the degradation of the mRNA transcript through a process similar to RNA interference (RNAi), though in other cases it is believed that the miRNA complex blocks the protein translation machinery or other ...
Jan 19
... Sanger (di-deoxy chain termination) 1) anneal primer to template 2) elongate with DNA polymerase 3) cause chain termination with di-deoxy nucleotides will be incorporated but cannot be elongated 4 separate reactions: A, C, G, T ...
... Sanger (di-deoxy chain termination) 1) anneal primer to template 2) elongate with DNA polymerase 3) cause chain termination with di-deoxy nucleotides will be incorporated but cannot be elongated 4 separate reactions: A, C, G, T ...
Promoter (genetics)
In genetics, a promoter is a region of DNA that initiates transcription of a particular gene. Promoters are located near the transcription start sites of genes, on the same strand and upstream on the DNA (towards the 5' region of the sense strand).Promoters can be about 100–1000 base pairs long.