Experiment SIG1: Active Low-Pass Filter Design
... shown in Figure 4, the output sine-wave frequency can be linearly swept from a lowfrequency value to a high-frequency value. This frequency sweep signal can be connected to the filter under test to evaluate the frequency response. The AC-DC converter is essentially a peak-detector circuit which conv ...
... shown in Figure 4, the output sine-wave frequency can be linearly swept from a lowfrequency value to a high-frequency value. This frequency sweep signal can be connected to the filter under test to evaluate the frequency response. The AC-DC converter is essentially a peak-detector circuit which conv ...
Reduction of coupling capacitance, using a capacitor
... is shown in Figure 2 (b). In this figure Rb is the output resistance of bias circuit and Ri is the amplifier input resistance. ...
... is shown in Figure 2 (b). In this figure Rb is the output resistance of bias circuit and Ri is the amplifier input resistance. ...
MAX7033 315MHz/433MHz ASK Superheterodyne Receiver with AGC Lock General Description
... frequency range. The receiver has an RF input signal range of -114dBm to 0dBm. With few external components and a low-current power-down mode, it is ideal for cost-sensitive and power-sensitive applications typical in the automotive and consumer markets. The MAX7033 consists of a low-noise amplifier ...
... frequency range. The receiver has an RF input signal range of -114dBm to 0dBm. With few external components and a low-current power-down mode, it is ideal for cost-sensitive and power-sensitive applications typical in the automotive and consumer markets. The MAX7033 consists of a low-noise amplifier ...
Network Theorems -
... circuit voltage of around 13.5 V. Similarly, if we take 7 pen-torch batteries, they too will have a terminal voltage of 7×1.5 = 13.5 V. However, you would also be aware, that if your car battery is dead, you cannot go to the nearest shop, buy 7 pen-torch batteries and start your car. Why is that ? B ...
... circuit voltage of around 13.5 V. Similarly, if we take 7 pen-torch batteries, they too will have a terminal voltage of 7×1.5 = 13.5 V. However, you would also be aware, that if your car battery is dead, you cannot go to the nearest shop, buy 7 pen-torch batteries and start your car. Why is that ? B ...
Vinf
... continuos form, (d) discrete form. In case of the output term with fuzzy singleton, the max composition is represented in figure 3. This approach is referred to TSK fuzzy inference method as mentioned before. It only uses five fuzzy singleton terms that could be determined by the designer. It is use ...
... continuos form, (d) discrete form. In case of the output term with fuzzy singleton, the max composition is represented in figure 3. This approach is referred to TSK fuzzy inference method as mentioned before. It only uses five fuzzy singleton terms that could be determined by the designer. It is use ...
CONTROL BY A TRIAC FOR AN INDUCTIVE LOAD
... e.g. speed-control circuit for AC motors. - Narrow conducting angle ; broad lag angle. The flow of current in one direction is a function of the control and thus of the duration of the current flow in the previous direction. The triac can be triggered at the end of the mains half-cycle. In this case ...
... e.g. speed-control circuit for AC motors. - Narrow conducting angle ; broad lag angle. The flow of current in one direction is a function of the control and thus of the duration of the current flow in the previous direction. The triac can be triggered at the end of the mains half-cycle. In this case ...
hmc424lp3 product note
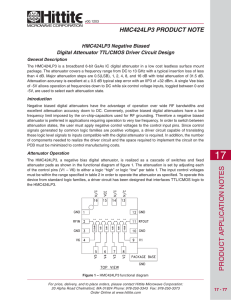
... excellent attenuation accuracy down to DC. Conversely, positive biased digital attenuators have a low frequency limit imposed by the on-chip-capacitors used for RF grounding. Therefore a negative biased attenuator is preferred in applications requiring operation to very low frequency. In order to sw ...
... excellent attenuation accuracy down to DC. Conversely, positive biased digital attenuators have a low frequency limit imposed by the on-chip-capacitors used for RF grounding. Therefore a negative biased attenuator is preferred in applications requiring operation to very low frequency. In order to sw ...
topics - no simpler
... law for voltage across a component - Calculate the voltage given the values of current and resistance V = IxR (iii) Apply ohm's law for Resistance in a circuit. - calculate the resistance of a circuit given the values of voltage and current. (iv) State formular for quantities. Draw the symbol for oh ...
... law for voltage across a component - Calculate the voltage given the values of current and resistance V = IxR (iii) Apply ohm's law for Resistance in a circuit. - calculate the resistance of a circuit given the values of voltage and current. (iv) State formular for quantities. Draw the symbol for oh ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.