Lab 4 - Simple Op
... The 741 pinout (for 8-pin DIP package) is shown in Figure 4-2, along with a schematic. This information is taken straight from the component data-sheet; you should always review the datasheet before using any IC (the data sheet for the National Semiconductor version of the 741, the LM741, can be fou ...
... The 741 pinout (for 8-pin DIP package) is shown in Figure 4-2, along with a schematic. This information is taken straight from the component data-sheet; you should always review the datasheet before using any IC (the data sheet for the National Semiconductor version of the 741, the LM741, can be fou ...
Stresa, Italy, 25-27 April 2007 STEP-UP CONVERTER FOR ELECTROMAGNETIC VIBRATIONAL ENERGY SCAVENGER.
... A significant amount of research has already been done on vibrational power generators using electromagnetic [16], piezoelectric [3] [7-9], and electrostatic principles [3] [8]. These generators require the use of a converter circuit to convert the ac-generated voltage to a usable dc level. In parti ...
... A significant amount of research has already been done on vibrational power generators using electromagnetic [16], piezoelectric [3] [7-9], and electrostatic principles [3] [8]. These generators require the use of a converter circuit to convert the ac-generated voltage to a usable dc level. In parti ...
Timing Circuits Word Document
... When the switch is set to position 1, the power supply draws electrons off the top plate and transfers them onto the bottom plate. As a result, the bottom plate carries a negative charge and the top plate a positive charge. Transfer of charge continues until the voltage across the capacitor is equal ...
... When the switch is set to position 1, the power supply draws electrons off the top plate and transfers them onto the bottom plate. As a result, the bottom plate carries a negative charge and the top plate a positive charge. Transfer of charge continues until the voltage across the capacitor is equal ...
Calculation of a Shock Response Spectra
... Two main parameters of the SDOF system, which are specifying free oscillation, are the substructure natural frequency and damping. There are many measures of describing damping. This paper prefers the damping ratio Q = 1/(2ξ ) and the quality factor Q, which is approximately equal to a resonance gai ...
... Two main parameters of the SDOF system, which are specifying free oscillation, are the substructure natural frequency and damping. There are many measures of describing damping. This paper prefers the damping ratio Q = 1/(2ξ ) and the quality factor Q, which is approximately equal to a resonance gai ...
Chapter 27 - KFUPM Faculty List
... T042: Q#11: Three resistors are connected as shown in figure 3. The potential difference between points A and B is 26 V. How much current flows through the 4-Ohm resistor? (A1 2.0 A ) Q#12: In the circuit shown in figure 4, I=0.65A and R=15 Ohms. What is the value of the emf of the battery? (A1 39 ...
... T042: Q#11: Three resistors are connected as shown in figure 3. The potential difference between points A and B is 26 V. How much current flows through the 4-Ohm resistor? (A1 2.0 A ) Q#12: In the circuit shown in figure 4, I=0.65A and R=15 Ohms. What is the value of the emf of the battery? (A1 39 ...
Lecture 02 Resistance and Resistors Full
... such metals where they are intended to offer the least possible impediment to the flow of current. They are used only to provide a path for current to flow in an electric circuit and to connect points together electrically where the potential or emf is intended to be the same. However, practical ele ...
... such metals where they are intended to offer the least possible impediment to the flow of current. They are used only to provide a path for current to flow in an electric circuit and to connect points together electrically where the potential or emf is intended to be the same. However, practical ele ...
Parallel and Series Resistors, Kirchoff`s Law Introduction Objectives
... Loop rule: It states that: ”Algebraic sum of all the potential differences around any loop in a circuit is equal to zero”. The loop theorem is a restatement of energy conservation principle. Mathematically the rule is presented as follows ...
... Loop rule: It states that: ”Algebraic sum of all the potential differences around any loop in a circuit is equal to zero”. The loop theorem is a restatement of energy conservation principle. Mathematically the rule is presented as follows ...
Unit 16 Inductance in AC Circuits
... increases through a coil, a magnetic field is created around the coil. ...
... increases through a coil, a magnetic field is created around the coil. ...
Mechanism Operated Contacts
... device. In this version, the contacts only change state when the circuit breaker is opened/closed while it is in the “CONNECTED” position within the circuit breaker compartment. There are two distinct models of the “connect only” MOC, one for circuit breaker frame sizes 1 and 2 (WLMOCC), and a secon ...
... device. In this version, the contacts only change state when the circuit breaker is opened/closed while it is in the “CONNECTED” position within the circuit breaker compartment. There are two distinct models of the “connect only” MOC, one for circuit breaker frame sizes 1 and 2 (WLMOCC), and a secon ...
crystals and oscillators
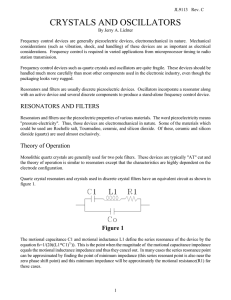
... specified by the load capacitance (CL) that they are intended to work into. The equivalent series resistance (the equivalent resistance at the load capacitance specified) of a parallel resonant crystal can be calculated by ESR=R1*((1+Co/CL)²). The shift in frequency from series to the parallel reson ...
... specified by the load capacitance (CL) that they are intended to work into. The equivalent series resistance (the equivalent resistance at the load capacitance specified) of a parallel resonant crystal can be calculated by ESR=R1*((1+Co/CL)²). The shift in frequency from series to the parallel reson ...
Trouble - MacMate
... these are primarily addressable analog devices report individual condition like accumulated dirt or environmental changes. address not part of the programmed data base will make generating a Trouble condition, and displaying a message on the Liquid Crystal Display as “unconfigured device”. ...
... these are primarily addressable analog devices report individual condition like accumulated dirt or environmental changes. address not part of the programmed data base will make generating a Trouble condition, and displaying a message on the Liquid Crystal Display as “unconfigured device”. ...
Chapter17
... Alternating current flows in a capacitive circuit with ac voltage applied. A smaller capacitance allows less current, which means more XC with more ohms of opposition. Lower frequencies for the applied voltage result in less current and more XC. With a steady dc voltage source (zero frequenc ...
... Alternating current flows in a capacitive circuit with ac voltage applied. A smaller capacitance allows less current, which means more XC with more ohms of opposition. Lower frequencies for the applied voltage result in less current and more XC. With a steady dc voltage source (zero frequenc ...
The JFET - W. Marshall Leach, Jr.
... VT O ≤ vGS ≤ 0. The slope of the curve is the small-signal transconductance gm . For vGS < VT O , the drain current is zero. For vGS > 0, gate current flows. Fig. 2 shows the typical variation of drain current iD with drain-to-source voltage vDS for eight values of VGS in the range VT O < VGS ≤ 0. T ...
... VT O ≤ vGS ≤ 0. The slope of the curve is the small-signal transconductance gm . For vGS < VT O , the drain current is zero. For vGS > 0, gate current flows. Fig. 2 shows the typical variation of drain current iD with drain-to-source voltage vDS for eight values of VGS in the range VT O < VGS ≤ 0. T ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.