* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Current Measurements using Shunt
Mechanical filter wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Valve audio amplifier technical specification wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
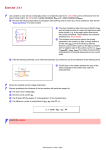
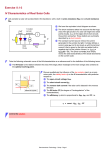
Current Measurements using Shunt 1. Explanation of ”Shunt” “Shunt” is the resistor used for the measurements of circuit currents in electric circuits. Actually, shunt was previously taken as the resistor connecting up to the ammeters in parallel to expand the measuring range of electric indicating instruments (indicating meters). *See Diagram1 However, recently shunt is more commonly used as the sensor that detects the circuit currents.*See Diagram2 There are various ways to detect the currents, but using shunts is the most simple to just connect up to the measuring circuits in series. This is the method for measuring and detecting the voltage commensurate with the currents generated in the shunt connecting up to the circuits. In order to insert the shunt to the circuit in series, adequate resistance value setting for circuit operation is needed. Shunt Power Supply Load Side Ammeter (Diagram1) Secondary Output Terminal Shunt Power Supply Load Side Detecting Circuit / Transducer Control Circuit (Diagram2) 1/3 123 Digital Panel Meter or other equipment 2. Proper Usage 3 typical case examples in measuring DC10A 1) Indicating meter Product Shunt : 10A/60mV (*Example : YS-1-10A60mV) Meter : Sensitivity 60mV Scale 0-10(A) (*Example : Y-80 60mV) [Connecting Diagram] Shunt : YS-1 Meter : Y-80 2) Digital Panel Meter Product Shunt : 10A/100mV (*Example : YS-1-10A100mV) Digital Panel Meter : Input Sensitivity : 200mV (*Example : YAP-101 : Maximum Display 1999) [Connecting Diagram] Shunt : YS-1 Digital Panel Meter : YAP-101 *Decimal Point Lighting : Triple Digits 2/3 3) Transducer or other equipment Product Shunt : 10A/60mV (*Example : YS-1-10A60mV) Transducer : DC Voltage Transducer (*Example CSV-「03」 「11」 「E」 / Input : 60mV, Output : 5V) [Connecting Diagram] Shunt : YS-1 Transducer Control Device <Scale Conversion> In this case, scale conversion is needed. In short, 10A⇒Shunt secondary output : 60mV⇒Transducer output 5V That means Current 1A goes 0.5V at transducer output. Double value of transducer output Voltage means Current Value at 10(A)/5(V). Adjustment like this (Scale Conversion) is needed at control device side. 3. Other Caution in setting up the current measurement circuit using shunt 1) Shunt is connected to the measuring circuit directly, please take care the risk of electrical shock in insulation. 2) In case of scale conversion between shunt secondary Voltage and measuring Voltage is needed, please specify the value of shunt output and measuring instruments input In ordering. 3/3