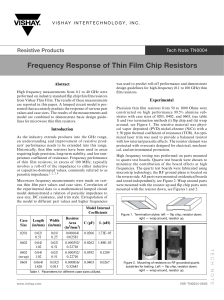
Introduction and Digital Images
... with Lenz’s law. The instantaneous current is zero, so the resistor voltage is initially zero. The induced voltage across L opposes the V ...
... with Lenz’s law. The instantaneous current is zero, so the resistor voltage is initially zero. The induced voltage across L opposes the V ...
Switched - Vicphysics
... transistor itself is small compared to the other resistors (X & Y) in the circuit, and makes very little difference in that regard. But, if you make the resistance of X very large, so that the current through that path in the circuit almost stops, then no current will flow through Y either. A small ...
... transistor itself is small compared to the other resistors (X & Y) in the circuit, and makes very little difference in that regard. But, if you make the resistance of X very large, so that the current through that path in the circuit almost stops, then no current will flow through Y either. A small ...
Series Circuit - Spring Branch ISD
... a. What happened to the current in the circuit as the number of bulbs is reduced? Explain why this occur using Ohm’s law and the concept of resistance. b. What happens to the other two bulbs when one bulb is removed from the threebulb circuit? Try it and explain why the circuit behaves as it does. P ...
... a. What happened to the current in the circuit as the number of bulbs is reduced? Explain why this occur using Ohm’s law and the concept of resistance. b. What happens to the other two bulbs when one bulb is removed from the threebulb circuit? Try it and explain why the circuit behaves as it does. P ...
Transmission Line Theory
... SWR, and sharply defined voltage minima recorded at z=0.2 cm, 2.2cm, 4.2cm The short circuit is removed, and replaced with the unknown load. The SWR is measured as 1.5, and voltage minima are recorded at z=0.72cm, 2.72cm, 4.72cm. ...
... SWR, and sharply defined voltage minima recorded at z=0.2 cm, 2.2cm, 4.2cm The short circuit is removed, and replaced with the unknown load. The SWR is measured as 1.5, and voltage minima are recorded at z=0.72cm, 2.72cm, 4.72cm. ...
Power Electronics 2 Flyback SMPS
... by rectifying the utility ac voltage followed by a simple capacitor filter. • The circuit can offer single or multiple isolated output voltages and can operate over wide range of input voltage variation. In respect of energy-efficiency, flyback power supplies are inferior to many other SMPS circuits ...
... by rectifying the utility ac voltage followed by a simple capacitor filter. • The circuit can offer single or multiple isolated output voltages and can operate over wide range of input voltage variation. In respect of energy-efficiency, flyback power supplies are inferior to many other SMPS circuits ...
4 RC Circuits Experiment 4.1
... capacitor will charge up and its voltage will increase. During this time, a current will flow producing a voltage across the resistor according to Ohm’s Law, V = IR. As the capacitor is charging up the current is actually decreasing due to the stored charge on the capacitor producing a voltage that ...
... capacitor will charge up and its voltage will increase. During this time, a current will flow producing a voltage across the resistor according to Ohm’s Law, V = IR. As the capacitor is charging up the current is actually decreasing due to the stored charge on the capacitor producing a voltage that ...
RC Circuits
... begins to build across the plates, thus opposing the action of the battery. As a consequence, the current flowing in the circuit gets less and less (i.e. it decays), falling to zero when the “back-voltage” on the capacitor is exactly equal and opposite to the battery voltage. If we were to quickly d ...
... begins to build across the plates, thus opposing the action of the battery. As a consequence, the current flowing in the circuit gets less and less (i.e. it decays), falling to zero when the “back-voltage” on the capacitor is exactly equal and opposite to the battery voltage. If we were to quickly d ...
ZM013666670
... settling performance of the gain-boosted op amp [3] and the effort of pushing up the doublet can raise stability problem [4]. For high gain, the architecture of a single stage amplifier with gain-boosted amplifier is a nice choice compare to telescopic topology. However, the folded-cascode topology ...
... settling performance of the gain-boosted op amp [3] and the effort of pushing up the doublet can raise stability problem [4]. For high gain, the architecture of a single stage amplifier with gain-boosted amplifier is a nice choice compare to telescopic topology. However, the folded-cascode topology ...
Ch 19all 20.2
... In practice: need to know P to select right size resistor – capable of dissipating thermal energy created by current. What is the power output of the battery? ...
... In practice: need to know P to select right size resistor – capable of dissipating thermal energy created by current. What is the power output of the battery? ...
Circuit Construction Kit (CCK) Lesson Plans A series of three labs
... Connecting parts with wires Deleting wires or parts to add parts. You can’t just add after the circuit is built. Using the voltmeter and ammeter. The non-contact ammeter is especially handy, but the other one is realistic. 5. The difference between schematic and lifelike views. In all my student dir ...
... Connecting parts with wires Deleting wires or parts to add parts. You can’t just add after the circuit is built. Using the voltmeter and ammeter. The non-contact ammeter is especially handy, but the other one is realistic. 5. The difference between schematic and lifelike views. In all my student dir ...
pat2680231_reed.pdf
... order of 800 cycles per second. Then, in effectkinds. I n general, any device which has an elecing tone control, it is usual to provide an attenuating network which attenuates the fretrical output with a range of frequencies in the aud.ible region may employ a tone control. Also 10 quencies at the m ...
... order of 800 cycles per second. Then, in effectkinds. I n general, any device which has an elecing tone control, it is usual to provide an attenuating network which attenuates the fretrical output with a range of frequencies in the aud.ible region may employ a tone control. Also 10 quencies at the m ...
EVALUATION AND DESIGN SUPPORT
... strong desire on the part of industrial and medical equipment manufacturers to use this bus as well, but adoption has been slow because there has not been a good way to provide the isolation required for connections to machines that control dangerous voltages or low leakage defibrillation proof conn ...
... strong desire on the part of industrial and medical equipment manufacturers to use this bus as well, but adoption has been slow because there has not been a good way to provide the isolation required for connections to machines that control dangerous voltages or low leakage defibrillation proof conn ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.