Lect11
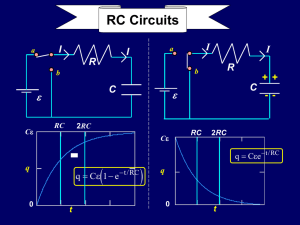
... • I personally find it easier to think about the circuit as if C was discharging than charging; I imagine that the capacitor is charged, and that the battery is replaced by a wire (which also has no resistance or capacitance). Since the battery supplies a constant voltage, it doesn’t affect the time ...
... • I personally find it easier to think about the circuit as if C was discharging than charging; I imagine that the capacitor is charged, and that the battery is replaced by a wire (which also has no resistance or capacitance). Since the battery supplies a constant voltage, it doesn’t affect the time ...
doorbell extender
... Live and Neutral supply the primary of a miniature 1·5VA mains transformer (T1) which has parallel-wired, 9V dual secondaries. The resulting low voltage a.c. output is rectified by the bridge rectifier, REC1, smoothed by capacitor C2 and reduced to a stable and ripple-free 5V d.c. by voltage regulat ...
... Live and Neutral supply the primary of a miniature 1·5VA mains transformer (T1) which has parallel-wired, 9V dual secondaries. The resulting low voltage a.c. output is rectified by the bridge rectifier, REC1, smoothed by capacitor C2 and reduced to a stable and ripple-free 5V d.c. by voltage regulat ...
Experiment Title
... 3. The current in the circuit is changed by varying the rheostat resistance Rh. This is done by sliding the rider to a new position. Activate the circuit and take three different readings of the ammeter and the voltmeter corresponding to the different rheostat settings. Be sure to use one scale sett ...
... 3. The current in the circuit is changed by varying the rheostat resistance Rh. This is done by sliding the rider to a new position. Activate the circuit and take three different readings of the ammeter and the voltmeter corresponding to the different rheostat settings. Be sure to use one scale sett ...
Solution to Assignment 4
... Solution: Since the current through the 3R resistor is 12 A, the voltage across it is V = I R = 12 * 3R= 36R. Since the 6R and 3R resistors are in parallel, the voltage across the 6R resistor is also 36R. It follows that the current through the 6R resistor is 36R/6R=6A. The current that flows throug ...
... Solution: Since the current through the 3R resistor is 12 A, the voltage across it is V = I R = 12 * 3R= 36R. Since the 6R and 3R resistors are in parallel, the voltage across the 6R resistor is also 36R. It follows that the current through the 6R resistor is 36R/6R=6A. The current that flows throug ...
Microphone Circuit
... A typical vocal signal is comprised mostly of frequencies in the 300-3000 Hz range. Therefore, any frequencies outside of this range are unnecessary in our system and hence represent unwanted noise. Thus one improvement might be to include a bandpass “speech filter” in the system to pass only freque ...
... A typical vocal signal is comprised mostly of frequencies in the 300-3000 Hz range. Therefore, any frequencies outside of this range are unnecessary in our system and hence represent unwanted noise. Thus one improvement might be to include a bandpass “speech filter” in the system to pass only freque ...
Name Date Partners HOMEWORK FOR LAB 3 VOLTAGE IN
... Real Time Physics Electric Circuits HW for Lab 3: Voltage in Simple DC Circuits and Ohm's Law ...
... Real Time Physics Electric Circuits HW for Lab 3: Voltage in Simple DC Circuits and Ohm's Law ...
C7802 Ohms Law 2005_newer
... As we have found, the current decreases when the resistance increases. This makes sense because more resistance means more opposition to current flow which reduces the current flowing in a circuit. Therefore we can say that the amount of current in a circuit is inversely proportional to the amount o ...
... As we have found, the current decreases when the resistance increases. This makes sense because more resistance means more opposition to current flow which reduces the current flowing in a circuit. Therefore we can say that the amount of current in a circuit is inversely proportional to the amount o ...
Lab1: Resistors
... for all numerical values. Figures must be neat and easy to read and understand. Data. Data is to be taken in ink. It must be clear as to what the data refers to. Do not forget units. The use of Tables is frequently convenient. Tables. Tables are used to present information. They must be neat and eas ...
... for all numerical values. Figures must be neat and easy to read and understand. Data. Data is to be taken in ink. It must be clear as to what the data refers to. Do not forget units. The use of Tables is frequently convenient. Tables. Tables are used to present information. They must be neat and eas ...
A Circuit Model for ESD Performance Analysis of
... it is low and its resistance is low when the magnitude of the voltage across it is high [7], [8]. A varistor circuit model can be created using SPICE components. The accuracy and simulation time of the varistor model in a SPICE-like circuit simulator will be restricted by the non-linear block expres ...
... it is low and its resistance is low when the magnitude of the voltage across it is high [7], [8]. A varistor circuit model can be created using SPICE components. The accuracy and simulation time of the varistor model in a SPICE-like circuit simulator will be restricted by the non-linear block expres ...
Complex Resistor Combinations
... Review the path taken to find the equivalent resistance in the figure at right, and work backward through this path. The equivalent resistance for the entire circuit is the same as the equivalent resistance for group (d). The center resistor in group (d) in turn is the equivalent resistance for grou ...
... Review the path taken to find the equivalent resistance in the figure at right, and work backward through this path. The equivalent resistance for the entire circuit is the same as the equivalent resistance for group (d). The center resistor in group (d) in turn is the equivalent resistance for grou ...
STEVAL-TDR022V1
... Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any time, without notic ...
... Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any time, without notic ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.