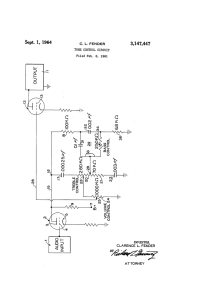
pat3147447_fender.pdf
... instruments such as electric guitars and the like. An object of the invention is to provide a tone control circuit which permits achievement of a brilliant highfrequency response without resulting in substantial distortion due to phase-shift and other effects. A further object is to provide a tone c ...
... instruments such as electric guitars and the like. An object of the invention is to provide a tone control circuit which permits achievement of a brilliant highfrequency response without resulting in substantial distortion due to phase-shift and other effects. A further object is to provide a tone c ...
Multisim Electronics Workbench Tutorial
... professional version, a demo version, a student version, and a textbook version. The professional version is available in the labs on the CECS network and has all of the Workbench features. The demo version may be downloaded from the Workbench website at http://www.electronicsworkbench.com/html/edup ...
... professional version, a demo version, a student version, and a textbook version. The professional version is available in the labs on the CECS network and has all of the Workbench features. The demo version may be downloaded from the Workbench website at http://www.electronicsworkbench.com/html/edup ...
A Design of CMOS Class-AB Differential Log-Companding Amplifier Kobkaew Opasjumruskit , Apisak Worapishet
... its operation at 1 V. This design utilizes a class-A amplifier which consumes large amount of power at zero input. A classAB integrator [2], which is also based on the log-companding technique, is proposed to reduce the power consumption. This circuit generates positive and negative voltages from a ...
... its operation at 1 V. This design utilizes a class-A amplifier which consumes large amount of power at zero input. A classAB integrator [2], which is also based on the log-companding technique, is proposed to reduce the power consumption. This circuit generates positive and negative voltages from a ...
Chapter Images
... take the path of least resistance. This is true, especially if there is a fault such as in the secondary (high-voltage) section of the ignition system. If there is a path to ground that is lower than the path to the spark plug, the highvoltage spark will take the path of least resistance. In a paral ...
... take the path of least resistance. This is true, especially if there is a fault such as in the secondary (high-voltage) section of the ignition system. If there is a path to ground that is lower than the path to the spark plug, the highvoltage spark will take the path of least resistance. In a paral ...
No Slide Title
... VR , VR and VL are all sinusoidally varying quantities with maximum values, VR,m (= im R), VC,m (= im XC ), and VL,m (= im XL) This equation is correct for every moment in time but it is not useful for calculating the current i. ...
... VR , VR and VL are all sinusoidally varying quantities with maximum values, VR,m (= im R), VC,m (= im XC ), and VL,m (= im XL) This equation is correct for every moment in time but it is not useful for calculating the current i. ...
Chapter 5 Protection Circuit Design
... Therefore, the time from overcurrent detection to the complete turn-off in each circuit must work effectively as fast as possible. Since the IGBT turns off very quickly, if the overcurrent is shut off using an ordinary drive signal, the collector-emitter voltage will rise due to the back-emf from pa ...
... Therefore, the time from overcurrent detection to the complete turn-off in each circuit must work effectively as fast as possible. Since the IGBT turns off very quickly, if the overcurrent is shut off using an ordinary drive signal, the collector-emitter voltage will rise due to the back-emf from pa ...
AN-679 APPLICATION NOTE
... However, there are some important considerations when selecting a shunt for an energy metering application. First, minimize the power dissipation in the shunt. The maximum rated current for this design is 30 A; therefore, the maximum power dissipated in the shunt is 30 A 2 350 = 315 mW. IEC 610 ...
... However, there are some important considerations when selecting a shunt for an energy metering application. First, minimize the power dissipation in the shunt. The maximum rated current for this design is 30 A; therefore, the maximum power dissipated in the shunt is 30 A 2 350 = 315 mW. IEC 610 ...
simplest chaotic circuit
... Fig. 6. In this figure, we compare experimental versus theoretical attractors. The top two sets of attractor plots y(t) (iL (t), current through the inductor) versus x(t) (vC (t), voltage across the capacitor). The axes scales for the experimental attractor on the top-left are 0.5 V/division. Hence f ...
... Fig. 6. In this figure, we compare experimental versus theoretical attractors. The top two sets of attractor plots y(t) (iL (t), current through the inductor) versus x(t) (vC (t), voltage across the capacitor). The axes scales for the experimental attractor on the top-left are 0.5 V/division. Hence f ...
Digital circuit blocks
... blocks. This is not so, however, since a current-drawing circuit can easily be converted into a current-delivering circuit by the addition of two resistors and a blocking diode (see fig. 6). In fig. 5 the current for the load is supplied via the collector resistance of the driving stage and in fig. ...
... blocks. This is not so, however, since a current-drawing circuit can easily be converted into a current-delivering circuit by the addition of two resistors and a blocking diode (see fig. 6). In fig. 5 the current for the load is supplied via the collector resistance of the driving stage and in fig. ...
Chapter 5 - Oscillators (Part 1)
... • When oscillation starts at t0, the condition ACL > 1 causes the sinusoidal output voltage amplitude to build up to a ...
... • When oscillation starts at t0, the condition ACL > 1 causes the sinusoidal output voltage amplitude to build up to a ...
Introduction to OrCAD Capture and PSpice Notes for demonstrators
... it in PSpice. You will get error messages about floating nodes if you forget this, which is very easy! The reason is that all voltages in PSpice are measured from a particular node, numbered zero, and this must be defined as ground. Your circuit should now look something like figure 7 on page 7 alth ...
... it in PSpice. You will get error messages about floating nodes if you forget this, which is very easy! The reason is that all voltages in PSpice are measured from a particular node, numbered zero, and this must be defined as ground. Your circuit should now look something like figure 7 on page 7 alth ...
Design and Layout Guidelines for the
... used with distributed loads. The CDCVF2505 can be used to drive one or two 50-Ω transmission lines each. In the dual-transmission-line case, there is no need to add any external series resistor to the outputs because the CDCVF2505 has an integrated 25-Ω resistor included on chip. Conversely, in the ...
... used with distributed loads. The CDCVF2505 can be used to drive one or two 50-Ω transmission lines each. In the dual-transmission-line case, there is no need to add any external series resistor to the outputs because the CDCVF2505 has an integrated 25-Ω resistor included on chip. Conversely, in the ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.