1. Overview of Gene Expression Overview of Gene Expression Chapter 10B:
... Genes are segments of DNA that code for a particular protein (or RNA molecule) • the human genome contains ~3 billion base pairs (bps) and ~25,000 genes • almost all genes encode proteins • when we talk about “genes” we will focus on those that express proteins ( the “end products” for a small perce ...
... Genes are segments of DNA that code for a particular protein (or RNA molecule) • the human genome contains ~3 billion base pairs (bps) and ~25,000 genes • almost all genes encode proteins • when we talk about “genes” we will focus on those that express proteins ( the “end products” for a small perce ...
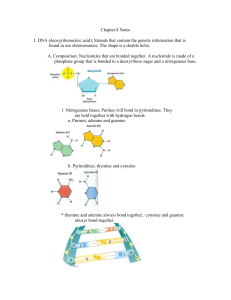
Chapter 11 Notes
... IV. Mutations; May be caused by errors in replication, transcription, cell division, or by external factors. Mutations may have negative effects, or beneficial effects. A. Cell types 1. Body cells; mutations that occur in body cells might cause problems for the individual that has the mutation. 2. R ...
... IV. Mutations; May be caused by errors in replication, transcription, cell division, or by external factors. Mutations may have negative effects, or beneficial effects. A. Cell types 1. Body cells; mutations that occur in body cells might cause problems for the individual that has the mutation. 2. R ...
L16 - sRNA Overview
... The task of establishing microRNA properties and function of individual miRs is ongoing and already there are indications that each miR can modulate the activity of up to 100 mRNAs to influence a large number of key biological processes: ...
... The task of establishing microRNA properties and function of individual miRs is ongoing and already there are indications that each miR can modulate the activity of up to 100 mRNAs to influence a large number of key biological processes: ...
Section J
... protein can be produced. If post-translational modifications are critical, the gene may have to be expressed in aeukaryotic cell. ...
... protein can be produced. If post-translational modifications are critical, the gene may have to be expressed in aeukaryotic cell. ...
21 356 Molecular Biology Spring 2017
... 1. Describe how the structure of DNA, RNA, Proteins, Lipids, and Carbohydrates contributes to their specific functions. 2. Describe the central dogma of the flow of genetic information. 3. Describe the intermolecular forces used to regulate interactions between DNA, RNA, Proteins, Lipids, and Carboh ...
... 1. Describe how the structure of DNA, RNA, Proteins, Lipids, and Carbohydrates contributes to their specific functions. 2. Describe the central dogma of the flow of genetic information. 3. Describe the intermolecular forces used to regulate interactions between DNA, RNA, Proteins, Lipids, and Carboh ...
Chapter 1 - Introduction
... the function of that protein; alternatively, the mutated copy of the human gene may be introduced into the mouse genome and the resultant physiology of the mouse closely studied. This entire sequence of events might require one or two years to complete, which is quite different from the decades of i ...
... the function of that protein; alternatively, the mutated copy of the human gene may be introduced into the mouse genome and the resultant physiology of the mouse closely studied. This entire sequence of events might require one or two years to complete, which is quite different from the decades of i ...
Standard
... livestock that have DNA from different organisms. As you already know, inserting genes (sections of DNA) into the genome of another organism is called recombinant DNA. These inserted genes are intended to make the organisms bigger, stronger, and more resistant to disease. ...
... livestock that have DNA from different organisms. As you already know, inserting genes (sections of DNA) into the genome of another organism is called recombinant DNA. These inserted genes are intended to make the organisms bigger, stronger, and more resistant to disease. ...
A New Plant Breeding Technique: Gene Editing
... Traits by editing plant genes instead of adding new genes ...
... Traits by editing plant genes instead of adding new genes ...
Systems Microbiology 1
... a. Describe the stringent response, and at what level and what components of cellular activity it regulates. The stringent response is triggered in response to two modified nucleotides called alarmones—guanosine tetraphostpate (ppGpp) and guanosine pentaphosphate (pppGpp). These nucleotides accumula ...
... a. Describe the stringent response, and at what level and what components of cellular activity it regulates. The stringent response is triggered in response to two modified nucleotides called alarmones—guanosine tetraphostpate (ppGpp) and guanosine pentaphosphate (pppGpp). These nucleotides accumula ...
Bio 211 Quiz 1 practice test answers
... 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 [email protected] http://www.si.iastate.edu ...
... 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 [email protected] http://www.si.iastate.edu ...
DNA - Laboratory of Theory of Biopolymers
... Fig. 6.2. Neutral, non-polar (hydrophobic) amino acids. ...
... Fig. 6.2. Neutral, non-polar (hydrophobic) amino acids. ...
Histone Methylation
... Transcriptional - These mechanisms prevent transcription. Posttranscriptional - These mechanisms control or regulate mRNA after it has been produced. Translational - These mechanisms prevent translation. They often involve protein factors needed for translation. Posttranslational - These mechanism ...
... Transcriptional - These mechanisms prevent transcription. Posttranscriptional - These mechanisms control or regulate mRNA after it has been produced. Translational - These mechanisms prevent translation. They often involve protein factors needed for translation. Posttranslational - These mechanism ...
Self-Replication
... • After one week, the initial amino acids began to be polymerized into simple carbohydrates and peptides. What had been transparent reactants took on a ...
... • After one week, the initial amino acids began to be polymerized into simple carbohydrates and peptides. What had been transparent reactants took on a ...
The Genetic Science Glossary - Canadian Council of Churches
... The cellular structure containing the DNA molecule carrying genes. There are 46 chromosomes in the human genome. Each person receives 23 chromosomes from each parent: 22 autosomal chromosomes plus an X chromosome from the mother and either an X or a Y sex determining chromosome from the father. Each ...
... The cellular structure containing the DNA molecule carrying genes. There are 46 chromosomes in the human genome. Each person receives 23 chromosomes from each parent: 22 autosomal chromosomes plus an X chromosome from the mother and either an X or a Y sex determining chromosome from the father. Each ...
Genomes 3/e
... But keeping it in mind that global ocean water could have 106 biomolecules/liter that may be associated with very different geological regions remained for billions of years give good chances to think or imagine any possible scenarios that could lead to the ordered assembly of these biomolecules. ...
... But keeping it in mind that global ocean water could have 106 biomolecules/liter that may be associated with very different geological regions remained for billions of years give good chances to think or imagine any possible scenarios that could lead to the ordered assembly of these biomolecules. ...
Gene Expression Analysis, DNA Chips and Genetic Networks
... Transcriptional Regulation • RNA polymerase – protein machinery that transcribes genes • Transcription factors (TFs) bind to specific binding sites in the promoter region of a gene • After binding to DNA TFs either enhance (activator) or disrupt (repressor) RNA polymerase binding to DNA ...
... Transcriptional Regulation • RNA polymerase – protein machinery that transcribes genes • Transcription factors (TFs) bind to specific binding sites in the promoter region of a gene • After binding to DNA TFs either enhance (activator) or disrupt (repressor) RNA polymerase binding to DNA ...
Gene expression (central dogma)
... During translation, the nucleotide sequence of an mRNA is translated into the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide. Specifically, the nucleotides of the mRNA are read in triplets (groups of three) called codons. There are 616161codons that specify amino acids. One codon is a "start" codon that indic ...
... During translation, the nucleotide sequence of an mRNA is translated into the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide. Specifically, the nucleotides of the mRNA are read in triplets (groups of three) called codons. There are 616161codons that specify amino acids. One codon is a "start" codon that indic ...