ERT 101 Biochemistry
... i) deduce the amino acids that would result from this sequence Arg-Met-Pro-Ile-Asp-Arg-Ser ii) if the first A is deleted from sequence, what new amino acid sequence would result? Arg-Cys-Pro-Stop iii) Determine the type of mutations that have occurred in the following altered mRNA segment CGAAUGGCCC ...
... i) deduce the amino acids that would result from this sequence Arg-Met-Pro-Ile-Asp-Arg-Ser ii) if the first A is deleted from sequence, what new amino acid sequence would result? Arg-Cys-Pro-Stop iii) Determine the type of mutations that have occurred in the following altered mRNA segment CGAAUGGCCC ...
Protein
... synthesis involves two types of nucleic acids: DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) RNA (ribonucleic acid) ...
... synthesis involves two types of nucleic acids: DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) RNA (ribonucleic acid) ...
E. coli
... with the plasma cell membrane where they release DNA into the cell • Shuttle plasmids are plasmids engineered to infect eukaryotic cells. • A selectable marker (antibiotic resistance gene) such as neomycin and a promotor from a mammalian virus to aid in DNA insertion • CMV (cytomegalovirus) is a hum ...
... with the plasma cell membrane where they release DNA into the cell • Shuttle plasmids are plasmids engineered to infect eukaryotic cells. • A selectable marker (antibiotic resistance gene) such as neomycin and a promotor from a mammalian virus to aid in DNA insertion • CMV (cytomegalovirus) is a hum ...
Gene Activity - Haiku Learning
... expose the bases of the sense strand The genetic information in the gene is transcribed (rewritten) into an mRNA molecule The exposed bases in the DNA determine the sequence in which the RNA bases will be connected together RNA polymerase connects the loose RNA nucleotides together ...
... expose the bases of the sense strand The genetic information in the gene is transcribed (rewritten) into an mRNA molecule The exposed bases in the DNA determine the sequence in which the RNA bases will be connected together RNA polymerase connects the loose RNA nucleotides together ...
CHAPTER 16
... Answer: The lacZ, lacY, and lacA genes are under the control of the lac promoter. FIGURE 16.5 Concept check: Under what conditions is the lac repressor bound to the lac operon? Answer: The lac repressor is bound to the lac operon when it is not exposed to lactose— when allolactose is not bound to th ...
... Answer: The lacZ, lacY, and lacA genes are under the control of the lac promoter. FIGURE 16.5 Concept check: Under what conditions is the lac repressor bound to the lac operon? Answer: The lac repressor is bound to the lac operon when it is not exposed to lactose— when allolactose is not bound to th ...
DNA Transcription
... This is the stage where the RNA is made from a strand of DNA using the enzyme RNA polymerase. This occurs in the nucleus of the eukaryotic cell. ...
... This is the stage where the RNA is made from a strand of DNA using the enzyme RNA polymerase. This occurs in the nucleus of the eukaryotic cell. ...
DNA Replication, Transcription and Translation assessment
... 2.7.1 Explain the process of DNA replication in eukaryotes, including the role of enzymes (helicase, DNA polymerase, RNA primase and DNA ligase), Okazaki fragments and deoxynucleoside triphosphates. 2.7.2 Explain the significance of complementary base pairing in the conservation of the base sequence ...
... 2.7.1 Explain the process of DNA replication in eukaryotes, including the role of enzymes (helicase, DNA polymerase, RNA primase and DNA ligase), Okazaki fragments and deoxynucleoside triphosphates. 2.7.2 Explain the significance of complementary base pairing in the conservation of the base sequence ...
Green Factory: Recombinant Protein Production in Chloroplasts
... is of major concern to the public. In order to address this problem, a novel visual selection system was developed [7]. Here an antibiotic resistance marker is still used for the initial selection, but the marker is automatically excluded later. New vectors were designed, that carry the marker gene ...
... is of major concern to the public. In order to address this problem, a novel visual selection system was developed [7]. Here an antibiotic resistance marker is still used for the initial selection, but the marker is automatically excluded later. New vectors were designed, that carry the marker gene ...
Bio1001Ch13W
... In the genetic code, nucleotide triplets specify amino acids • In the __________, three consecutive bases specify an amino acid, creating 43 (64) possible ________. • The genetic instructions for a polypeptide chain are written in DNA as a series of three__________words. ...
... In the genetic code, nucleotide triplets specify amino acids • In the __________, three consecutive bases specify an amino acid, creating 43 (64) possible ________. • The genetic instructions for a polypeptide chain are written in DNA as a series of three__________words. ...
vertebrate genome evolution and function illuminated by chicken
... – Examine interspecies alignments, noncoding regions – Evaluate likelihood of being under purifying selection, e.g. phastCons score – Some regulatory regions are deeply conserved, others are lineage-specific ...
... – Examine interspecies alignments, noncoding regions – Evaluate likelihood of being under purifying selection, e.g. phastCons score – Some regulatory regions are deeply conserved, others are lineage-specific ...
chapter_19
... Chapters 19 - Genetic Analysis of Development: Development Development refers to interaction of then genome with the cytoplasm and external environment to produce a programmed sequence of typically irreversible events. Differentiation Differentiation refers to the formation of cell types, tissues, a ...
... Chapters 19 - Genetic Analysis of Development: Development Development refers to interaction of then genome with the cytoplasm and external environment to produce a programmed sequence of typically irreversible events. Differentiation Differentiation refers to the formation of cell types, tissues, a ...
Unit 2 Review: Molecular Genetics
... Control Mechanisms -42,000 human proteins, needed at specific times in different locations, and amounts -gene regulation controlled at four different levels: -transcriptional- transcription factors turn genes on/off -post-transcriptional- introns removed from mRNA, exons spliced together -translatio ...
... Control Mechanisms -42,000 human proteins, needed at specific times in different locations, and amounts -gene regulation controlled at four different levels: -transcriptional- transcription factors turn genes on/off -post-transcriptional- introns removed from mRNA, exons spliced together -translatio ...
REGULATION OF GENES INVOLVED IN LIPID CATABOLISM
... Real-Time Quantitative PCR was used to obtain a more precise estimate of mRNA levels. Data were normalized using reference dye (ROX) in the PCR mix and normalized to ACT2 mRNA as an internal standard. At 21 dpi, the time at which virus accumulation reaches a maximum, levels of ACX1 and ACX2 mRNA wer ...
... Real-Time Quantitative PCR was used to obtain a more precise estimate of mRNA levels. Data were normalized using reference dye (ROX) in the PCR mix and normalized to ACT2 mRNA as an internal standard. At 21 dpi, the time at which virus accumulation reaches a maximum, levels of ACX1 and ACX2 mRNA wer ...
Lab Manual: Week 8
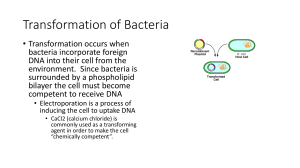
... In this lab you will perform a procedure known as a genetic transformation. Remember that a gene is a piece of DNA which provides the instructions for making (coding for) a protein, which gives an organism a particular trait. Genetic transformation literally means change caused by genes; it involves ...
... In this lab you will perform a procedure known as a genetic transformation. Remember that a gene is a piece of DNA which provides the instructions for making (coding for) a protein, which gives an organism a particular trait. Genetic transformation literally means change caused by genes; it involves ...
Who am I?
... What is cloning? Clones are identical copies of living things. Humans have cloned a lot of things already. ...
... What is cloning? Clones are identical copies of living things. Humans have cloned a lot of things already. ...
Document
... Mutant alleles of trpA gene differed in the position of the mutation at the DNA level, which corresponded to position of amino acid substitution in the gene product. Colinearity of mutations and altered amino acids in a subunit of tryptophan synthetase from E. coli C. Yanofsky, 1967. Scientific Amer ...
... Mutant alleles of trpA gene differed in the position of the mutation at the DNA level, which corresponded to position of amino acid substitution in the gene product. Colinearity of mutations and altered amino acids in a subunit of tryptophan synthetase from E. coli C. Yanofsky, 1967. Scientific Amer ...
Final review questions: ch 13-15 How does RNA differ from DNA
... reducing the amount of land that is required to grow them. A introducing chemicals into the environment. B increasing an animal's resistance to antibiotics. C changing the genomes of other crop plants. D 24. Genetic markers allow scientists to ...
... reducing the amount of land that is required to grow them. A introducing chemicals into the environment. B increasing an animal's resistance to antibiotics. C changing the genomes of other crop plants. D 24. Genetic markers allow scientists to ...
Genetic Technology
... Organisms whose genetic characteristics have been altered using the techniques of genetic engineering. Examples ...
... Organisms whose genetic characteristics have been altered using the techniques of genetic engineering. Examples ...
principles of gene control
... cells was controlled at a genetic level. The theory also predicted the existence of mRNA-an unstable intermediate between the genome and the expressed protein. Before this work the prevailing model was called the instruction hypothesis that stated that all proteins were present in a cell, but that i ...
... cells was controlled at a genetic level. The theory also predicted the existence of mRNA-an unstable intermediate between the genome and the expressed protein. Before this work the prevailing model was called the instruction hypothesis that stated that all proteins were present in a cell, but that i ...
Protein Synthesis
... mRNA: A U G C C U C A C G A G C G U G C G C U A U G A Codons and anticodons consist of 3 nucleotides. How many codons are on the above mRNA strand? 8 Now mRNA can take it’s copy of the DNA code to the ribosome ...
... mRNA: A U G C C U C A C G A G C G U G C G C U A U G A Codons and anticodons consist of 3 nucleotides. How many codons are on the above mRNA strand? 8 Now mRNA can take it’s copy of the DNA code to the ribosome ...
Document
... serve as templates to produce complementary RNA molecules. In prokaryotes, RNA synthesis and protein synthesis takes place in the cytoplasm. In eukaryotes, RNA is produced in the cell’s nucleus and then moves to the cytoplasm to play a role in the production of protein. The following focuses on tran ...
... serve as templates to produce complementary RNA molecules. In prokaryotes, RNA synthesis and protein synthesis takes place in the cytoplasm. In eukaryotes, RNA is produced in the cell’s nucleus and then moves to the cytoplasm to play a role in the production of protein. The following focuses on tran ...