슬라이드 1
... b-Cat and other Wnt pathway-specific regulators cycle on and off the c-Myc enhacer in LiCl-treated cells To test whether b-cat regulates H3K4 trimethylation at Wnt target genes in vivo A ...
... b-Cat and other Wnt pathway-specific regulators cycle on and off the c-Myc enhacer in LiCl-treated cells To test whether b-cat regulates H3K4 trimethylation at Wnt target genes in vivo A ...
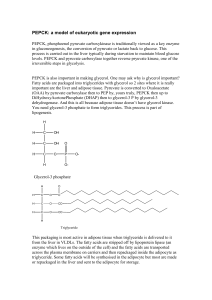
PEPCK: a model of eukaryotic gene expression
... In the fed state insulin is released by the pancreas and this suppresses transcription of PEPCK, the mRNA is unstable so very little PEPCK protein is synthesised. The protein is also rapidly turned over?? During fasting, a glucocorticoid, cortisol is released and this steroid activates the transcrip ...
... In the fed state insulin is released by the pancreas and this suppresses transcription of PEPCK, the mRNA is unstable so very little PEPCK protein is synthesised. The protein is also rapidly turned over?? During fasting, a glucocorticoid, cortisol is released and this steroid activates the transcrip ...
NF1X - BioMed Central
... could provide a direct link between the pineal clock, cellular redox state, and intermediary metabolism if the circadian clock regulated it. Future research exploring a redox dependent regulatory role of NF1X within the chick pineal clock is warranted. ...
... could provide a direct link between the pineal clock, cellular redox state, and intermediary metabolism if the circadian clock regulated it. Future research exploring a redox dependent regulatory role of NF1X within the chick pineal clock is warranted. ...
Medical Genetics, Lecture 3
... et al., 2001) estimated the number of human genes to be between 30,000-40,000, which is much less than the previous estimates . There are 130 thousands types of proteins. ...
... et al., 2001) estimated the number of human genes to be between 30,000-40,000, which is much less than the previous estimates . There are 130 thousands types of proteins. ...
Learning Objectives
... codons on mRNA and the linear sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide. 9. Explain the early techniques used to identify what amino acids are specified by the triplets UUU, AAA, GGG, and CCC. 10. Explain why polypeptides begin with methionine when they are synthesized. 11. Explain what it means to s ...
... codons on mRNA and the linear sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide. 9. Explain the early techniques used to identify what amino acids are specified by the triplets UUU, AAA, GGG, and CCC. 10. Explain why polypeptides begin with methionine when they are synthesized. 11. Explain what it means to s ...
Learning Objectives
... codons on mRNA and the linear sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide. 9. Explain the early techniques used to identify what amino acids are specified by the triplets UUU, AAA, GGG, and CCC. 10. Explain why polypeptides begin with methionine when they are synthesized. 11. Explain what it means to s ...
... codons on mRNA and the linear sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide. 9. Explain the early techniques used to identify what amino acids are specified by the triplets UUU, AAA, GGG, and CCC. 10. Explain why polypeptides begin with methionine when they are synthesized. 11. Explain what it means to s ...
Document
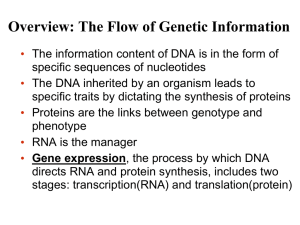
... • RNA is the bridge and the gatekeeper between genes and the proteins for which they code • Transcription is the synthesis of RNA using coded information in DNA • Transcription produces many classes of RNA • Translation is the synthesis of a polypeptide, using information in one class: messenger RNA ...
... • RNA is the bridge and the gatekeeper between genes and the proteins for which they code • Transcription is the synthesis of RNA using coded information in DNA • Transcription produces many classes of RNA • Translation is the synthesis of a polypeptide, using information in one class: messenger RNA ...
Comparison of DNA and RNA
... 1-DNA contains the sugar deoxyribose, while RNA contains the sugar ribose. The only difference between ribose and deoxyribose is that ribose has one more OH group than deoxyribose, which has -H attached to the second (2') carbon in the ring. 2-DNA is a double stranded molecule while RNA is a single ...
... 1-DNA contains the sugar deoxyribose, while RNA contains the sugar ribose. The only difference between ribose and deoxyribose is that ribose has one more OH group than deoxyribose, which has -H attached to the second (2') carbon in the ring. 2-DNA is a double stranded molecule while RNA is a single ...
STUDY GUIDE SEMESTER 2 EXAM 4 Dr. Marks Name: Class
... Refer to the illustration above. Suppose that you are given a protein containing the following sequence of amino acids: tyrosine, proline, aspartic acid, isoleucine, and cysteine. Use the portion of the genetic code given to determine which of the following contains a DNA sequence that codes for thi ...
... Refer to the illustration above. Suppose that you are given a protein containing the following sequence of amino acids: tyrosine, proline, aspartic acid, isoleucine, and cysteine. Use the portion of the genetic code given to determine which of the following contains a DNA sequence that codes for thi ...
Ribosome - Mrs. J. Malito
... • A 5’ cap is added to protect the mRNA from degradation and to help small ribosomal subunits recognize the attachment site on mRNA’s 5’ end. • A poly-A tail is sequence of 30 – 200 A nucleotides added to the 3’ end of mRNA before it exits to: • Prevent degradation • Facilitate attachment • Regulate ...
... • A 5’ cap is added to protect the mRNA from degradation and to help small ribosomal subunits recognize the attachment site on mRNA’s 5’ end. • A poly-A tail is sequence of 30 – 200 A nucleotides added to the 3’ end of mRNA before it exits to: • Prevent degradation • Facilitate attachment • Regulate ...
mind-blowing similarities in the way that information is stored
... signals, the outer one, specifies where to start and stop compiling the DNA sequence for use; the other set, the inner one, specifies where to start and stop the SP conversion for translation into protein. DNA serves as a repository of genetic information, and can be thought of as the hard drive whe ...
... signals, the outer one, specifies where to start and stop compiling the DNA sequence for use; the other set, the inner one, specifies where to start and stop the SP conversion for translation into protein. DNA serves as a repository of genetic information, and can be thought of as the hard drive whe ...
Class Topics - Seneca High School
... “Let the farmer forevermore be honored in his calling; for they who labor in the earth are the chosen people of God.” ...
... “Let the farmer forevermore be honored in his calling; for they who labor in the earth are the chosen people of God.” ...
CIS 595 Bioinformatics
... very large set of measurements in which the mRNA levels of 1800 selected genes (arranged top to bottom) were determined for 142 different human tumors (arranged left to right), each from a different patient. Each small red bar indicates that the given gene in the given tumor is transcribed at a leve ...
... very large set of measurements in which the mRNA levels of 1800 selected genes (arranged top to bottom) were determined for 142 different human tumors (arranged left to right), each from a different patient. Each small red bar indicates that the given gene in the given tumor is transcribed at a leve ...
manual HiScribe T7 In Vitro Transcription Kit E2030
... purification. For unpurified, heat-killed restriction digests, include no more than 13 µl of template per 40 µl reaction. For unpurified PCR product, include no more than 7 µl per 40 µl reaction. In all cases, the amount of added template DNA should not exceed 2 µg per 40 µl reaction, as RNA yields ...
... purification. For unpurified, heat-killed restriction digests, include no more than 13 µl of template per 40 µl reaction. For unpurified PCR product, include no more than 7 µl per 40 µl reaction. In all cases, the amount of added template DNA should not exceed 2 µg per 40 µl reaction, as RNA yields ...
Genetic regulation in eukaryotes 0. Introduction
... Small interfering RNA (siRNA), are a class of 20-25 nucleotide-long RNA molecules that interfere with the expression of genes. They are naturally produced as part of the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway by the enzyme Dicer. They can also be exogenously (artificially) introduced by investigators to br ...
... Small interfering RNA (siRNA), are a class of 20-25 nucleotide-long RNA molecules that interfere with the expression of genes. They are naturally produced as part of the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway by the enzyme Dicer. They can also be exogenously (artificially) introduced by investigators to br ...
Bio4751signaltransductionTechniques
... If use anti-phosphoERK (anti-p-ERK) antibody… ….observe only phosphorylated ERK If use anti-ERK (anti-p-ERK) antibody… ….observe total ERK ...
... If use anti-phosphoERK (anti-p-ERK) antibody… ….observe only phosphorylated ERK If use anti-ERK (anti-p-ERK) antibody… ….observe total ERK ...
DNA replication to translation
... Steps in transcription: 1. initiation RNA polymerase recognizes and binds to promoter sequence - these contain TATAAA and TTGACA or CCAAT codes 2. elongation - similar to DNA replication - only one strand (template) is used 3. termination - transcription keeps going for 1000-2000 bases beyond end o ...
... Steps in transcription: 1. initiation RNA polymerase recognizes and binds to promoter sequence - these contain TATAAA and TTGACA or CCAAT codes 2. elongation - similar to DNA replication - only one strand (template) is used 3. termination - transcription keeps going for 1000-2000 bases beyond end o ...
RNA Polymerase II Subunit Rpb9 Regulates Transcription
... elongation properties. Occasionally, the pol II⌬9 enzyme did form arrested elongation complexes at the histone H3.3 arrest site. Unlike wild-type arrested complexes, these arrested pol II⌬9 complexes were unable to be rescued by the addition of the elongation factor TFIIS. In general, these studies ...
... elongation properties. Occasionally, the pol II⌬9 enzyme did form arrested elongation complexes at the histone H3.3 arrest site. Unlike wild-type arrested complexes, these arrested pol II⌬9 complexes were unable to be rescued by the addition of the elongation factor TFIIS. In general, these studies ...
Chapter 13
... - RNA has __________________________ instead of deoxyribose - RNA has the base _______________ instead of Thymine - it still has A, C, & G - ____________will pair with __________ (Uracil is a pyrimidine) ...
... - RNA has __________________________ instead of deoxyribose - RNA has the base _______________ instead of Thymine - it still has A, C, & G - ____________will pair with __________ (Uracil is a pyrimidine) ...
Unit 4
... DNA functions as a template fro transcription – the synthesis of an mRNA molecule of complementary sequence. The same base-pairing rule that apply to DNA synthesis also guide transcription, but the base uracil (U) takes the place of thymine (T) in RNA. During the translation, the genetic message, mR ...
... DNA functions as a template fro transcription – the synthesis of an mRNA molecule of complementary sequence. The same base-pairing rule that apply to DNA synthesis also guide transcription, but the base uracil (U) takes the place of thymine (T) in RNA. During the translation, the genetic message, mR ...
The Organization and Control of Eukaryotic Genomes
... Alternative RNA splicing – where different mRNA molecules are produced from the same primary transcript, depending on which RNA segments are treated as exons and which as introns. Regulatory proteins specific to a cell type control intron-exon choices by binding to regulatory sequences within the pr ...
... Alternative RNA splicing – where different mRNA molecules are produced from the same primary transcript, depending on which RNA segments are treated as exons and which as introns. Regulatory proteins specific to a cell type control intron-exon choices by binding to regulatory sequences within the pr ...
Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation
... When a gene is expressed, DNA is transcribed to produce RNA and RNA is then translated to produce proteins. ...
... When a gene is expressed, DNA is transcribed to produce RNA and RNA is then translated to produce proteins. ...
E1-3 NotesProtein Synth
... C. Transcription – 1. RNA carries genetic info from DNA in nucleus to cytosol to make proteins. 2. Transcription – where genetic info copies from DNA to RNA 3. Steps – a. RNA binds to regions of DNA that make a single gene (in eukaryotes) b. Nitrogen bases pair up (Uracil with adenine/ guanine with ...
... C. Transcription – 1. RNA carries genetic info from DNA in nucleus to cytosol to make proteins. 2. Transcription – where genetic info copies from DNA to RNA 3. Steps – a. RNA binds to regions of DNA that make a single gene (in eukaryotes) b. Nitrogen bases pair up (Uracil with adenine/ guanine with ...
Ch 17 Protein Synthesis
... polymerase II bind to promoter upstream from gene 2. Promoter region contains a TATA box which indicates non-template strand ...
... polymerase II bind to promoter upstream from gene 2. Promoter region contains a TATA box which indicates non-template strand ...