Chapt16_lecture
... This project is funded by a grant awarded under the President’s Community Based Job Training Grant as implemented by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration (CB-15-162-06-60). NCC is an equal opportunity employer and does not discriminate on the following basis: agains ...
... This project is funded by a grant awarded under the President’s Community Based Job Training Grant as implemented by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration (CB-15-162-06-60). NCC is an equal opportunity employer and does not discriminate on the following basis: agains ...
Genes
... Genes for metabolic pathways linked together in operons with a common switch mechanism (operator). ...
... Genes for metabolic pathways linked together in operons with a common switch mechanism (operator). ...
Topics covered on this exam include: cellular respiration
... their functions different? 2. What are the components of a single nucleotide? Dow we find nucleotides in both RNA and DNA? 3. Be able to go between DNA DNA, DNA RNA and RNA RNA. 4. What are the three types of RNA? What is the function of each? 5. What is the difference between transcription an ...
... their functions different? 2. What are the components of a single nucleotide? Dow we find nucleotides in both RNA and DNA? 3. Be able to go between DNA DNA, DNA RNA and RNA RNA. 4. What are the three types of RNA? What is the function of each? 5. What is the difference between transcription an ...
GENES
... coding RNA molecules like mRNA and tRNA. Exons in RNA are the sequences in the primary transcript that are found in the mRNA, Introns are RNA sequences between exons that are removed by splicing. ...
... coding RNA molecules like mRNA and tRNA. Exons in RNA are the sequences in the primary transcript that are found in the mRNA, Introns are RNA sequences between exons that are removed by splicing. ...
Name:
... 7. Our next step is translation. What happens during translation and where does this occur? 8. Match the amino acid anticodons with the mRNA codons. (Mr. Mason will ...
... 7. Our next step is translation. What happens during translation and where does this occur? 8. Match the amino acid anticodons with the mRNA codons. (Mr. Mason will ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis Notes Organizer
... 2. RNA, like DNA, is a nucleic acid made of nucleotides. What are the four differences between DNA and RNA? a. ...
... 2. RNA, like DNA, is a nucleic acid made of nucleotides. What are the four differences between DNA and RNA? a. ...
Protein Synthesis - East Aurora Schools
... Three kinds of RNA will be made from the DNA template 1. Messenger RNA (mRNA) directs protein synthesis 2. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) joins with ribosomal proteins to make ribosomes 3. Transfer RNA (tRNA) binds to an amino acid and holds it in place on a ribosome until it is incorporated into a protein du ...
... Three kinds of RNA will be made from the DNA template 1. Messenger RNA (mRNA) directs protein synthesis 2. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) joins with ribosomal proteins to make ribosomes 3. Transfer RNA (tRNA) binds to an amino acid and holds it in place on a ribosome until it is incorporated into a protein du ...
RNA, Protein Synthesis, Transcription, and Translation
... • When mRNA is produced. • Part of a DNA nucleotide sequence is copied. • Starts at places called promoter. • Stops when a specific code is given. • Occurs in the nucleus of the cell • Purpose – copy instructions onto mRNA ...
... • When mRNA is produced. • Part of a DNA nucleotide sequence is copied. • Starts at places called promoter. • Stops when a specific code is given. • Occurs in the nucleus of the cell • Purpose – copy instructions onto mRNA ...
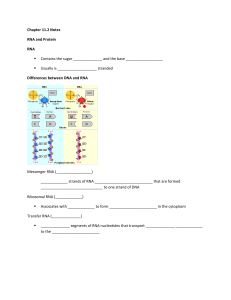
Chapter 11.2 Notes RNA and Protein RNA Contains the sugar and
... ____________________ – the process of ________________________ the info in a sequence of nitrogenous ______________ in mRNA into a sequence of amino acids in _______________ ...
... ____________________ – the process of ________________________ the info in a sequence of nitrogenous ______________ in mRNA into a sequence of amino acids in _______________ ...
Transcription Translation.notebook
... minimal media supplemented with various substances 1. Found mutant mold could grow in minimal media supplemented with arginine (amino acid) 2. Mutation in the genetic pathway that creates an essential molecule the mold required to survive (arginine) 3. Mutation in enzyme that help to produce argin ...
... minimal media supplemented with various substances 1. Found mutant mold could grow in minimal media supplemented with arginine (amino acid) 2. Mutation in the genetic pathway that creates an essential molecule the mold required to survive (arginine) 3. Mutation in enzyme that help to produce argin ...
Molecular_files/Translation Transcription
... – Each codon codes for an amino acid – Should have 64 different codons (4 nucleotide choices, 3 bases) but only 20 amino acids- why? ...
... – Each codon codes for an amino acid – Should have 64 different codons (4 nucleotide choices, 3 bases) but only 20 amino acids- why? ...
max 6
... 2. Breaks hydrogen bonds; 3. Only one DNA strand acts as template; 4. RNA nucleotides attracted to exposed bases; 5. (Attraction) according to base pairing rule; 6. RNA polymerase joins (RNA) nucleotides together; 7. Pre-mRNA spliced to remove introns. 6 max ...
... 2. Breaks hydrogen bonds; 3. Only one DNA strand acts as template; 4. RNA nucleotides attracted to exposed bases; 5. (Attraction) according to base pairing rule; 6. RNA polymerase joins (RNA) nucleotides together; 7. Pre-mRNA spliced to remove introns. 6 max ...
nuclear receptors - Guide to Pharmacology
... Overview:- Nuclear receptors are specialised transcription factors with commonalities of sequence and structure, which bind as homo- or heterodimers to specific consensus sequences of DNA (response elements) in the promoter region of particular target genes. They regulate (either promoting or repres ...
... Overview:- Nuclear receptors are specialised transcription factors with commonalities of sequence and structure, which bind as homo- or heterodimers to specific consensus sequences of DNA (response elements) in the promoter region of particular target genes. They regulate (either promoting or repres ...
Transcription
... Converting a gene from the DNA blueprint into a complementary single-stranded RNA sequence ...
... Converting a gene from the DNA blueprint into a complementary single-stranded RNA sequence ...
DNA-binding motifs
... Eukaryotic Regulation • Controlling the expression of eukaryotic genes requires transcription factors. – general transcription factors are required for transcription initiation • required for proper binding of RNA polymerase to the DNA – specific transcription factors increase transcription in cert ...
... Eukaryotic Regulation • Controlling the expression of eukaryotic genes requires transcription factors. – general transcription factors are required for transcription initiation • required for proper binding of RNA polymerase to the DNA – specific transcription factors increase transcription in cert ...
Control of Gene Expression
... Eukaryotic Regulation • Controlling the expression of eukaryotic genes requires transcription factors. – general transcription factors are required for transcription initiation • required for proper binding of RNA polymerase to the DNA – specific transcription factors increase transcription in cert ...
... Eukaryotic Regulation • Controlling the expression of eukaryotic genes requires transcription factors. – general transcription factors are required for transcription initiation • required for proper binding of RNA polymerase to the DNA – specific transcription factors increase transcription in cert ...
Lecture 14 Student Powerpoint
... transcription that involved the production of a primary transcript and the processing of this into aspects of how this is processed into an mRNA in Eukaryotes. This lecture focuses on these topics and on how signals are perceived that modulate the expression of eukaryotic genes. The next lecture wil ...
... transcription that involved the production of a primary transcript and the processing of this into aspects of how this is processed into an mRNA in Eukaryotes. This lecture focuses on these topics and on how signals are perceived that modulate the expression of eukaryotic genes. The next lecture wil ...
Control of Gene Expression Control of Gene Expression Regulatory
... • Methylation (the addition of –CH3 to DNA or histone proteins) is associated with the control of gene expression. • Clusters of methylated cytosine nucleotides bind to a protein that prevents activators from binding to DNA. • Methylated histone proteins are associated with inactive regions of chrom ...
... • Methylation (the addition of –CH3 to DNA or histone proteins) is associated with the control of gene expression. • Clusters of methylated cytosine nucleotides bind to a protein that prevents activators from binding to DNA. • Methylated histone proteins are associated with inactive regions of chrom ...
Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation
... Chain of aa called polypeptide Peptide bonds hold aa together 1 or more polypeptide chains can link and fold together to form a 3-dimensional protein • Proteins differ in number and sequence of aa • Protein structure determines their function ...
... Chain of aa called polypeptide Peptide bonds hold aa together 1 or more polypeptide chains can link and fold together to form a 3-dimensional protein • Proteins differ in number and sequence of aa • Protein structure determines their function ...
Chapter 16 - HCC Learning Web
... 1. The RNA polymerase binds at regions called promoters. 2. TATA box is where a transcription factor binds enabling RNA polymerase to recognize the promoter region. B. Elongation of the RNA strand by RNA polymerase II. 1. First function: untwists and opens a short segment of DNA. 2. Links incoming R ...
... 1. The RNA polymerase binds at regions called promoters. 2. TATA box is where a transcription factor binds enabling RNA polymerase to recognize the promoter region. B. Elongation of the RNA strand by RNA polymerase II. 1. First function: untwists and opens a short segment of DNA. 2. Links incoming R ...
Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
... – Function independent of orientation – Function independent of position – upstream, downstream, etc. (different than promotors‐ close to gene and only one orientation) ...
... – Function independent of orientation – Function independent of position – upstream, downstream, etc. (different than promotors‐ close to gene and only one orientation) ...
Gene expression PPT
... sites called promoters on DNA template strand. Transcription factor – Binds to promoter so that RNA polymerase can then bind Initiation – Other transcription factors bind, assembling a transcription initiation complex. – RNA polymerase begins to unwind DNA helix. ...
... sites called promoters on DNA template strand. Transcription factor – Binds to promoter so that RNA polymerase can then bind Initiation – Other transcription factors bind, assembling a transcription initiation complex. – RNA polymerase begins to unwind DNA helix. ...
PERSISTENCE: Mechanisms underlying the “Central Dogma
... E. mature mRNA travels out to the cytoplasm where it makes a single protein ...
... E. mature mRNA travels out to the cytoplasm where it makes a single protein ...