Programming Gene Expression
... CAP binds with cAMP to forms a dimer. and then stimulates the transcription of lactose- and arabinose-catabolizing genes as sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. The E. coli genome contains many CAP-binding sites in positions appropriate for interactions with RNA polymerase. Thus, an increase in th ...
... CAP binds with cAMP to forms a dimer. and then stimulates the transcription of lactose- and arabinose-catabolizing genes as sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. The E. coli genome contains many CAP-binding sites in positions appropriate for interactions with RNA polymerase. Thus, an increase in th ...
The Nature of Genes The Nature of Genes
... Gene expression requires the participation of multiple types of RNA: messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the information from DNA that encodes proteins ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is a structural component of the ribosome transfer RNA (tRNA) carries amino acids to the ribosome for translation ...
... Gene expression requires the participation of multiple types of RNA: messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the information from DNA that encodes proteins ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is a structural component of the ribosome transfer RNA (tRNA) carries amino acids to the ribosome for translation ...
Transcription in Prokaryotes
... c. different promoters have similar, but not identical –10 and –35 region sequences d. mutations within these regions alter promoter strength & function e. distance between –10 and –35 regions important f. strength of promoter mostly determined by affinity of RNA pol for promoter DNA sequences g. re ...
... c. different promoters have similar, but not identical –10 and –35 region sequences d. mutations within these regions alter promoter strength & function e. distance between –10 and –35 regions important f. strength of promoter mostly determined by affinity of RNA pol for promoter DNA sequences g. re ...
10/23 Gene expression in Prokaryotes
... transcription is usually on and needs to be turned off, so the transcription is repressible. • Corepressor: a small molecule that binds to the repressor and makes it capable of binding to the operator to turn off transcription ...
... transcription is usually on and needs to be turned off, so the transcription is repressible. • Corepressor: a small molecule that binds to the repressor and makes it capable of binding to the operator to turn off transcription ...
sample
... 8. Alkyltransferase is required for direct reversal of photodimers. 9. A mutation that leads to the overexpression of a normal protein can lead to a dominant oncogenic mutation. 10. The normal activity of the RB protein is to negatively regulate the progression from G1 to S of the cell cycle. ...
... 8. Alkyltransferase is required for direct reversal of photodimers. 9. A mutation that leads to the overexpression of a normal protein can lead to a dominant oncogenic mutation. 10. The normal activity of the RB protein is to negatively regulate the progression from G1 to S of the cell cycle. ...
Table S2. Number of genes with identifiable Arabidopsis orthologs
... Table S2. Number of genes with identifiable Arabidopsis orthologs in the full matrix for each GO Slim category. Each gene may belong to more than one category. ...
... Table S2. Number of genes with identifiable Arabidopsis orthologs in the full matrix for each GO Slim category. Each gene may belong to more than one category. ...
Transcription And Translation
... referred to as the SENSE or TEMPLATE strand. The complimentary DNA strand that is not used is referred to as the NONSENSE strand. Only a very small part of the genome is copied. April 20, 2001 ...
... referred to as the SENSE or TEMPLATE strand. The complimentary DNA strand that is not used is referred to as the NONSENSE strand. Only a very small part of the genome is copied. April 20, 2001 ...
Everything you wanted to know about ENCODE
... Proteins that bind to specific DNA sequences in the promoter region together turn a gene on or off. These proteins are themselves regulated by their own promoters leading to a gene regulatory network with many of the same properties as a neural network. ...
... Proteins that bind to specific DNA sequences in the promoter region together turn a gene on or off. These proteins are themselves regulated by their own promoters leading to a gene regulatory network with many of the same properties as a neural network. ...
RNA, Protein Synthesis, Transcription, and Translation
... • When mRNA is produced. • Part of a DNA nucleotide sequence is copied. • Starts at places called promoter. • Stops when a specific code is given. • Occurs in the nucleus of the cell • Purpose – copy instructions onto mRNA ...
... • When mRNA is produced. • Part of a DNA nucleotide sequence is copied. • Starts at places called promoter. • Stops when a specific code is given. • Occurs in the nucleus of the cell • Purpose – copy instructions onto mRNA ...
The ATM repair pathway inhibits RNA polymerase I transcription in
... •Replacement of damaged/worn-out parts ...
... •Replacement of damaged/worn-out parts ...
Gene Section ATF1 (activating transcription factor 1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... References Yoshimura T, Fujisawa J, Yoshida M. Multiple cDNA clones encoding nuclear proteins that bind to the tax-dependent enhancer of HTLV-1: all contain a leucine zipper structure and basic amino acid domain. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2537-42 ...
... References Yoshimura T, Fujisawa J, Yoshida M. Multiple cDNA clones encoding nuclear proteins that bind to the tax-dependent enhancer of HTLV-1: all contain a leucine zipper structure and basic amino acid domain. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2537-42 ...
File
... 3 One strand of each short doublestranded RNA is degraded; the other strand (miRNA) then associates with a complex of proteins. ...
... 3 One strand of each short doublestranded RNA is degraded; the other strand (miRNA) then associates with a complex of proteins. ...
Regulation of Gene Expression
... binds with a specific nucleotide sequence in the DNA. A specific combination of transcription factors is necessary to activate a gene. Transcription factors are regulated by signals produced from other molecules. For example, hormones activate transcription factors and thus enable transcription. Hor ...
... binds with a specific nucleotide sequence in the DNA. A specific combination of transcription factors is necessary to activate a gene. Transcription factors are regulated by signals produced from other molecules. For example, hormones activate transcription factors and thus enable transcription. Hor ...
Transcription - Effingham County Schools
... make a copy of it for your own use, put the reference material back on the shelf so that others can use it too. Can you imagine if DNA was physically lost? That’s why chromosomes never leave the ...
... make a copy of it for your own use, put the reference material back on the shelf so that others can use it too. Can you imagine if DNA was physically lost? That’s why chromosomes never leave the ...
Lesson 2
... Mutations occur at the DNA level, and then carried over to the mRNA during transcription. ...
... Mutations occur at the DNA level, and then carried over to the mRNA during transcription. ...
Regulation of gene expression: Prokaryotic
... – 1 g/ml -amanitin inhibits – makes mRNA and snRNA (small nuclear RNA) ...
... – 1 g/ml -amanitin inhibits – makes mRNA and snRNA (small nuclear RNA) ...
Document
... 1. DNA-chromatin structure. This includes gene amplification—increase in copy number; gene rearrangement— as in immunoglobulin genes; DNA methylation—attachment of methyl groups, which inhibits transcription; locus control regions—sites that control chromatin conformation. 2. Transcription. This inc ...
... 1. DNA-chromatin structure. This includes gene amplification—increase in copy number; gene rearrangement— as in immunoglobulin genes; DNA methylation—attachment of methyl groups, which inhibits transcription; locus control regions—sites that control chromatin conformation. 2. Transcription. This inc ...
C1. The common points of control are as follows: 1. DNA
... 1. DNA-chromatin structure. This includes gene amplification—increase in copy number; gene rearrangement— as in immunoglobulin genes; DNA methylation—attachment of methyl groups, which inhibits transcription; locus control regions—sites that control chromatin conformation. 2. Transcription. This inc ...
... 1. DNA-chromatin structure. This includes gene amplification—increase in copy number; gene rearrangement— as in immunoglobulin genes; DNA methylation—attachment of methyl groups, which inhibits transcription; locus control regions—sites that control chromatin conformation. 2. Transcription. This inc ...
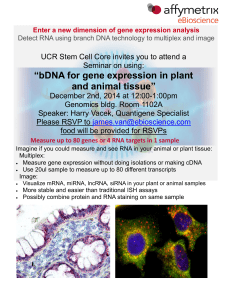
“bDNA for gene expression in plant and animal tissue”
... “bDNA for gene expression in plant and animal tissue” December 2nd, 2014 at 12:00-1:00pm Genomics bldg. Room 1102A Speaker: Harry Vacek, Quantigene Specialist Please RSVP to [email protected] food will be provided for RSVPs Measure up to 80 genes or 4 RNA targets in 1 sample Imagine if you c ...
... “bDNA for gene expression in plant and animal tissue” December 2nd, 2014 at 12:00-1:00pm Genomics bldg. Room 1102A Speaker: Harry Vacek, Quantigene Specialist Please RSVP to [email protected] food will be provided for RSVPs Measure up to 80 genes or 4 RNA targets in 1 sample Imagine if you c ...
Advanced Biology\Stem Cells, histones, etc
... While the genome is quite stable, the epigenome is not. Transcription factors, miRs, etc. can affect it as can protein activation. Our protein synthesis/use can be controlled via phosphorylation. Using a kinase, such as tyrosine kinase, an inactive protein can become activated by adding a phosphate ...
... While the genome is quite stable, the epigenome is not. Transcription factors, miRs, etc. can affect it as can protein activation. Our protein synthesis/use can be controlled via phosphorylation. Using a kinase, such as tyrosine kinase, an inactive protein can become activated by adding a phosphate ...
lec3
... 2. Accessory transcription activator proteins a) Can bind to specific DNA sequences and help RNA polymerase initiate transcription via protein-protein interactions or by altering the structure of the DNA. b) Transcription of some promoters requires an accessory transcriptional activator; at other pr ...
... 2. Accessory transcription activator proteins a) Can bind to specific DNA sequences and help RNA polymerase initiate transcription via protein-protein interactions or by altering the structure of the DNA. b) Transcription of some promoters requires an accessory transcriptional activator; at other pr ...
Proteins
... • Genes comprise only about 2% of the human genome. • The rest consists of non-coding regions – chromosomal structural integrity, – cell division (e.g. centromere) – regulatory regions: regulating when, where, and in what quantity proteins are made . ...
... • Genes comprise only about 2% of the human genome. • The rest consists of non-coding regions – chromosomal structural integrity, – cell division (e.g. centromere) – regulatory regions: regulating when, where, and in what quantity proteins are made . ...