6 Review of Molecular Biology
... Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is the main component of the ribosome. The ribosome makes proteins. The rRNA and about 70 – 80 ribosomal proteins fold up into two complex folded structures. rRNA decodes mRNA into amino acids (at center of small ribosomal subunit) and interacts with the tR ...
... Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is the main component of the ribosome. The ribosome makes proteins. The rRNA and about 70 – 80 ribosomal proteins fold up into two complex folded structures. rRNA decodes mRNA into amino acids (at center of small ribosomal subunit) and interacts with the tR ...
Test 2 answer - UniMAP Portal
... ribosome's P site; GTP supplies the energy required for binding. The larger ribosomal subunit attaches to form a complete initiation complex Elongation The transfer RNA whose anticodon matches the next codon delivers its amino acid to the A site. Another protein called elongation factor escorts the ...
... ribosome's P site; GTP supplies the energy required for binding. The larger ribosomal subunit attaches to form a complete initiation complex Elongation The transfer RNA whose anticodon matches the next codon delivers its amino acid to the A site. Another protein called elongation factor escorts the ...
gida bi̇yoteknoloji̇si̇-2
... recognize the appropriate synthesis sites. These sites are known as promoter. ...
... recognize the appropriate synthesis sites. These sites are known as promoter. ...
Chapter 1 Introduction
... explosive information is being provided at an unprecedented speed. Biochemistry is a window opening to the world of life science. Thus, the knowledge of biochemistry which involves the study of chemical molecules and reactions in living organisms, and the elucidations of the nature of live phenomeno ...
... explosive information is being provided at an unprecedented speed. Biochemistry is a window opening to the world of life science. Thus, the knowledge of biochemistry which involves the study of chemical molecules and reactions in living organisms, and the elucidations of the nature of live phenomeno ...
Advanced Techniques in Molecular Biology
... Histone modifications are proposed to affect chromosome function. The first mechanism suggests modifications may alter the electrostatic charge of the histone resulting in a structural change in histones or their binding to DNA. The second mechanism proposes that these modifications are binding site ...
... Histone modifications are proposed to affect chromosome function. The first mechanism suggests modifications may alter the electrostatic charge of the histone resulting in a structural change in histones or their binding to DNA. The second mechanism proposes that these modifications are binding site ...
DNA vs. RNA - WordPress.com
... RNA Editing Intron = intervening sequence of DNA; does not code for a protein Exon = expressed sequence of DNA; codes for a protein When RNA molecules are formed, both the introns and the exons are copied from the DNA introns are cut out of RNA molecules while they are still in the nucleus ...
... RNA Editing Intron = intervening sequence of DNA; does not code for a protein Exon = expressed sequence of DNA; codes for a protein When RNA molecules are formed, both the introns and the exons are copied from the DNA introns are cut out of RNA molecules while they are still in the nucleus ...
Supplementary table 2: Description of the gene pathways
... transition; DNA damage stimulates the DNAPK/ATM/ATR kinases, which inactivate Cdc2. Presenilin is required for gamma-secretase activity to activate Notch signaling; presenilin also inhibits beta-catenin in the Wnt/Frizzled pathway. PNAS 2002: Cancer related genes involved in cell adhesion and metall ...
... transition; DNA damage stimulates the DNAPK/ATM/ATR kinases, which inactivate Cdc2. Presenilin is required for gamma-secretase activity to activate Notch signaling; presenilin also inhibits beta-catenin in the Wnt/Frizzled pathway. PNAS 2002: Cancer related genes involved in cell adhesion and metall ...
Document
... – RNA polymerases bind to promoters – they cannot recognize promoters on their own – but require help of other proteins (transcription factors) – TFs particularly important in initiation of eukaryotic gene transcription – Promoter specifies which strand Copyright, ©, 2002, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., ...
... – RNA polymerases bind to promoters – they cannot recognize promoters on their own – but require help of other proteins (transcription factors) – TFs particularly important in initiation of eukaryotic gene transcription – Promoter specifies which strand Copyright, ©, 2002, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., ...
Nucleic Acids Placemat
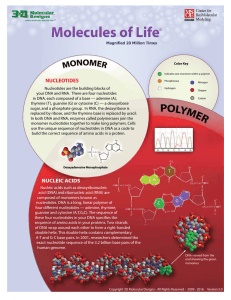
... Nucleic acids such as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are composed of monomers known as nucleotides. DNA is a long, linear polymer of four different nucleotides — adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine (A,T,G,C). The sequence of these four nucleotides in your DNA specifies the ...
... Nucleic acids such as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are composed of monomers known as nucleotides. DNA is a long, linear polymer of four different nucleotides — adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine (A,T,G,C). The sequence of these four nucleotides in your DNA specifies the ...
Name: Cell Biology Test #1: 50 points
... DNA before RNA polymerase II can optimally bind. a) D, A, B b) F, E, H c) 1, 2, 3 12) In eukaryotes, which required promoter sequence is located the closest to the initiation site on the DNA upstream of the gene in question? a) GC box b) TATA box c) CAAT box d) Enhancers/Suppressors 13) When RNA is ...
... DNA before RNA polymerase II can optimally bind. a) D, A, B b) F, E, H c) 1, 2, 3 12) In eukaryotes, which required promoter sequence is located the closest to the initiation site on the DNA upstream of the gene in question? a) GC box b) TATA box c) CAAT box d) Enhancers/Suppressors 13) When RNA is ...
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Chapter 28 DNA Replication
... Some genes are transcribed frequently—as often as every 2 seconds. The promoters for these genes are referred to as strong promoters. In contrast, other genes are transcribed less frequently, about once in 10 minutes; the promoters for these genes are weak promoters. How to determine promoter streng ...
... Some genes are transcribed frequently—as often as every 2 seconds. The promoters for these genes are referred to as strong promoters. In contrast, other genes are transcribed less frequently, about once in 10 minutes; the promoters for these genes are weak promoters. How to determine promoter streng ...
Chapter 10 Protein Synthesis
... acids to make protein B.TL occurs in the cytoplasm on Ribosomes C. TL is also called Protein Synthesis ...
... acids to make protein B.TL occurs in the cytoplasm on Ribosomes C. TL is also called Protein Synthesis ...
Sarah Justvig (`13)
... protein of Ewing’s sarcoma, shares with ERG and ETV1 identification as a Class I ETS factor. The three are more than 60% identical and 80% homologous in their amino acid sequences. YK-4-279 has been identified as a small molecule inhibitor of EWS/FLI1 oncoprotein in Ewing’s sarcoma. Given the strong ...
... protein of Ewing’s sarcoma, shares with ERG and ETV1 identification as a Class I ETS factor. The three are more than 60% identical and 80% homologous in their amino acid sequences. YK-4-279 has been identified as a small molecule inhibitor of EWS/FLI1 oncoprotein in Ewing’s sarcoma. Given the strong ...
CHAPTER 5 Gene Expression: Transcription
... The Transcription Process RNA Synthesis • Animation: RNA Biosynthesis • 1. Transcription, or gene expression, is regulated by gene regulatory elements associated with each gene. • 2. DNA unwinds in the region next to the gene, due to RNA polymerase in prokaryotes and other proteins in eukaryotes. I ...
... The Transcription Process RNA Synthesis • Animation: RNA Biosynthesis • 1. Transcription, or gene expression, is regulated by gene regulatory elements associated with each gene. • 2. DNA unwinds in the region next to the gene, due to RNA polymerase in prokaryotes and other proteins in eukaryotes. I ...
Good Luck and Happy Studying!! Intro to Biochemistry
... Be able to list/describe the several function of proteins and well as their ‘tyoe’ and location in the body (example- collagen is a support/structural protein found in the connective tissue of the body) ...
... Be able to list/describe the several function of proteins and well as their ‘tyoe’ and location in the body (example- collagen is a support/structural protein found in the connective tissue of the body) ...
replication
... TWO exact copies of ALL the DNA. The copies will wind back into chromosomes. There are now TWO copies of each chromosome. ...
... TWO exact copies of ALL the DNA. The copies will wind back into chromosomes. There are now TWO copies of each chromosome. ...
How to Study for the Anatomy and Physiology Prerequisite Exam:
... Topics in Biology to Prepare for APE (Anatomy & Physiology Prerequisite Exam) based on Mader’s biology text Chapter 1: Introduction Levels of Organization Prokaryote vs Eukaryote Characteristics Chapter 2: Basic Chemistry Elements most common in living organisms Atomic Structure Bonding: ...
... Topics in Biology to Prepare for APE (Anatomy & Physiology Prerequisite Exam) based on Mader’s biology text Chapter 1: Introduction Levels of Organization Prokaryote vs Eukaryote Characteristics Chapter 2: Basic Chemistry Elements most common in living organisms Atomic Structure Bonding: ...
Gene regulation I Biochemistry 302
... – β operon contains genes encoding RNAP subunits – str operon contain genes encoding translational elongation factors ...
... – β operon contains genes encoding RNAP subunits – str operon contain genes encoding translational elongation factors ...
Operon Info_pGLO pre lab
... Repressible and Inducible Operons: Two Types of Negative Gene Regulation A repressible operon is one that is usually on; binding of a repressor to the operator shuts off transcription The trp operon is a repressible operon An inducible operon is one that is usually off; a molecule called an i ...
... Repressible and Inducible Operons: Two Types of Negative Gene Regulation A repressible operon is one that is usually on; binding of a repressor to the operator shuts off transcription The trp operon is a repressible operon An inducible operon is one that is usually off; a molecule called an i ...
RNA - Mr. Dudley's Website
... acids are called Introns Segments that DO code for amino acids are called Exons ...
... acids are called Introns Segments that DO code for amino acids are called Exons ...
The Importance of DNA and RNA - Emmanuel Biology 12
... for RNA polymerase and other base sequences known as upstream promoter elements (UPEs). UPEs initiate transcription. Genes vary in the number and type of UPEs. A gene with only one UPE will be weakly expressed. A gene with many UPEs is actively transcribed. Other DNA sequences known as enhancers inc ...
... for RNA polymerase and other base sequences known as upstream promoter elements (UPEs). UPEs initiate transcription. Genes vary in the number and type of UPEs. A gene with only one UPE will be weakly expressed. A gene with many UPEs is actively transcribed. Other DNA sequences known as enhancers inc ...