COS126 EXAM 1, SPRING 2004 7
... 6. Combinational Circuits (8 points) The well-known Fibonnacci numbers are 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, ... Let the Boolean variables a, b, and c together represent a 3-bit non-negative binary number (that is, not in 2's-complement representation). Let c be the least significant bit (that is, write the num ...
... 6. Combinational Circuits (8 points) The well-known Fibonnacci numbers are 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, ... Let the Boolean variables a, b, and c together represent a 3-bit non-negative binary number (that is, not in 2's-complement representation). Let c be the least significant bit (that is, write the num ...
Circuit Analysis Vocabulary Teachers Guide
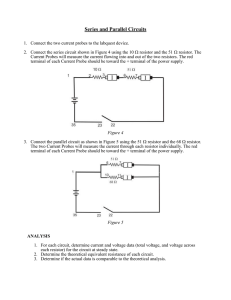
... Nodal analysis – a circuit analysis technique of using Kirchhoff’s Current Law to define the currents at nodes Mesh analysis – a circuit analysis technique of creating virtual mesh currents Superposition Theorem – States that the effects on a circuit of multiple power sources is the linear sum of th ...
... Nodal analysis – a circuit analysis technique of using Kirchhoff’s Current Law to define the currents at nodes Mesh analysis – a circuit analysis technique of creating virtual mesh currents Superposition Theorem – States that the effects on a circuit of multiple power sources is the linear sum of th ...
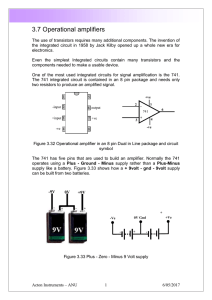
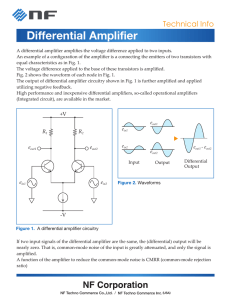
3.7 Operational amplifiers
... If Rin 10K calculate the value of Rf to give a gain of 10 When the circuit is operational monitor the waveforms on the oscilloscope and try different values of Rf to change the gain. With only a single 9 Volt battery a different approach has to be taken to make the device operate as an amplifier. T ...
... If Rin 10K calculate the value of Rf to give a gain of 10 When the circuit is operational monitor the waveforms on the oscilloscope and try different values of Rf to change the gain. With only a single 9 Volt battery a different approach has to be taken to make the device operate as an amplifier. T ...
Chapter 19
... are equal (z12=z21), the network is said to be reciprocal. • This means that if the input and output are switched, the transfer impedances remain the same. • Any two-port network that is composed entirely of resistors, capacitors, and inductors must be reciprocal. ...
... are equal (z12=z21), the network is said to be reciprocal. • This means that if the input and output are switched, the transfer impedances remain the same. • Any two-port network that is composed entirely of resistors, capacitors, and inductors must be reciprocal. ...
Document
... For smaller sine waves the problem will show at different frequencies according to the formula: fM ...
... For smaller sine waves the problem will show at different frequencies according to the formula: fM ...
Final Exam W0809
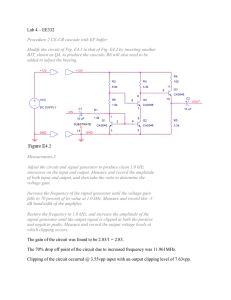
... If the feedback factor β is independent of frequency, find (i) The frequency at which the phase margin of the loop gain function A(s) is zero (i.e., the angle of A(s) is 180 degrees). (ii) The critical value of β at which oscillation will commence. Q.5: The schematic below shows a typical two-st ...
... If the feedback factor β is independent of frequency, find (i) The frequency at which the phase margin of the loop gain function A(s) is zero (i.e., the angle of A(s) is 180 degrees). (ii) The critical value of β at which oscillation will commence. Q.5: The schematic below shows a typical two-st ...
High Voltage CMOS Amplifier Enables High Impedance Sensing
... Introduction Accurately measuring voltages requires minimizing the impact of the instrument connection to the tested circuit. Typical digital voltmeters (DVMs) use 10M resistor networks to keep loading effects to an inconspicuous level, but even this can introduce significant error, particularly in ...
... Introduction Accurately measuring voltages requires minimizing the impact of the instrument connection to the tested circuit. Typical digital voltmeters (DVMs) use 10M resistor networks to keep loading effects to an inconspicuous level, but even this can introduce significant error, particularly in ...
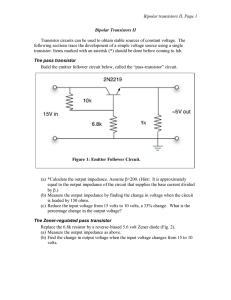
Bipolar transistors II, Page 1 Bipolar Transistors II
... Figure 4: Feedback Voltage Regulator. load conditions are variable. These can give output impedances less than an ohm and high stability against temperature variation. Figure 4 is a common example of a negative-feedback circuit. Transistor Q1 is normally conducting because of the bias current throug ...
... Figure 4: Feedback Voltage Regulator. load conditions are variable. These can give output impedances less than an ohm and high stability against temperature variation. Figure 4 is a common example of a negative-feedback circuit. Transistor Q1 is normally conducting because of the bias current throug ...