DMACC - Ind Maint - ELEM 575
... Develop an understanding of electromagnetic induction. 20.1 Explain the construction of an AC alternator (generator). 20.2 Discuss the four basic parts of an AC alternator (generator). 20.3 Discuss the operation of an AC alternator (generator). 20.4 Explain instantaneous, peak and effective voltage. ...
... Develop an understanding of electromagnetic induction. 20.1 Explain the construction of an AC alternator (generator). 20.2 Discuss the four basic parts of an AC alternator (generator). 20.3 Discuss the operation of an AC alternator (generator). 20.4 Explain instantaneous, peak and effective voltage. ...
Current Measurements using Shunt
... “Shunt” is the resistor used for the measurements of circuit currents in electric circuits. Actually, shunt was previously taken as the resistor connecting up to the ammeters in parallel to expand the measuring range of electric indicating instruments (indicating meters). *See Diagram1 However, rece ...
... “Shunt” is the resistor used for the measurements of circuit currents in electric circuits. Actually, shunt was previously taken as the resistor connecting up to the ammeters in parallel to expand the measuring range of electric indicating instruments (indicating meters). *See Diagram1 However, rece ...
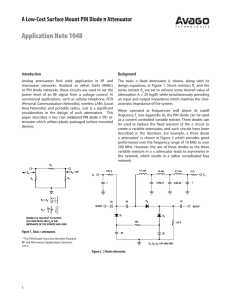
Application Note 1048 A Low-Cost Surface Mount PIN Diode π Attenuator Introduction Background
... isolation of the network is set by the capacitive reactance of the series diode(s), the use of two diodes in place of one will increase the maximum attenuation or double the upper frequency limit for a given value of attenuation. Second, the twin diodes which occupy the position of the series resist ...
... isolation of the network is set by the capacitive reactance of the series diode(s), the use of two diodes in place of one will increase the maximum attenuation or double the upper frequency limit for a given value of attenuation. Second, the twin diodes which occupy the position of the series resist ...
Analysis of electrical equivalent circuit of metal–insulator–semiconductor structure based on admittance measurements
... values of the equivalent circuit parameters are presented in Fig. 4 and the theoretical dependences calculated for these data are shown as full lines in Fig. 2. From the data presented in Fig. 4, one can see that the frequency behaviour of the investigated structures is very well reproduced by the p ...
... values of the equivalent circuit parameters are presented in Fig. 4 and the theoretical dependences calculated for these data are shown as full lines in Fig. 2. From the data presented in Fig. 4, one can see that the frequency behaviour of the investigated structures is very well reproduced by the p ...
Chapter 3
... node voltages V1, V2,… Vn-1 to the remaining n-1nodes . The voltages are referenced with respect to the reference node. Apply KCL to each of the n-1 independent nodes. Use Ohm’s law to express the branch currents in terms of node voltages. Solve the resulting simultaneous equations to obtain the unk ...
... node voltages V1, V2,… Vn-1 to the remaining n-1nodes . The voltages are referenced with respect to the reference node. Apply KCL to each of the n-1 independent nodes. Use Ohm’s law to express the branch currents in terms of node voltages. Solve the resulting simultaneous equations to obtain the unk ...
DN302 - Ultraprecise Instrumentation Amplifier Makes Robust Thermocouple Interface
... LTC2053 offers exceptionally low 10μV maximum input offset along with 116dB typical CMRR and PSRR, a result of a combination of switched capacitor and zero-drift op amp technologies. It is optimized for low voltage supplies from 2.7V to 11V single ended or up to ±5.5V with split supplies. The LTC205 ...
... LTC2053 offers exceptionally low 10μV maximum input offset along with 116dB typical CMRR and PSRR, a result of a combination of switched capacitor and zero-drift op amp technologies. It is optimized for low voltage supplies from 2.7V to 11V single ended or up to ±5.5V with split supplies. The LTC205 ...
Modeling of six-pulse rectifier operating under
... System differential equations are derived for each converter conduction state (i.e. based on the effective circuit as determined by which diodes are conducting) and then solved to obtain system currents, voltages, power flows, etc. On detecting a change in diode conduction states, a new set of diffe ...
... System differential equations are derived for each converter conduction state (i.e. based on the effective circuit as determined by which diodes are conducting) and then solved to obtain system currents, voltages, power flows, etc. On detecting a change in diode conduction states, a new set of diffe ...
v C
... Impedances of Series or Parallel Collections of Circuit Elements Impedances of individual passive circuit elements: zR R ...
... Impedances of Series or Parallel Collections of Circuit Elements Impedances of individual passive circuit elements: zR R ...
Smart troubleshooting pinpoints rectifier failures
... voltage,” says Gengler. “In most cases, the result is an open, but it may also be a short.* A shorted diode in a bridge rectifier circuit would more than likely burn open because of sufficiently high current that would exist during one half of the input cycle. (See Figure 4.) The amount of current i ...
... voltage,” says Gengler. “In most cases, the result is an open, but it may also be a short.* A shorted diode in a bridge rectifier circuit would more than likely burn open because of sufficiently high current that would exist during one half of the input cycle. (See Figure 4.) The amount of current i ...
Source Transformations, Lecture Set 8
... A portion of a circuit where we have a voltage source in series with a resistance is equivalent to current source in parallel with a resistance. The resistances for these two equivalents are equal. These two cases are equivalent as long as the resistances are equal and if the voltage source and curr ...
... A portion of a circuit where we have a voltage source in series with a resistance is equivalent to current source in parallel with a resistance. The resistances for these two equivalents are equal. These two cases are equivalent as long as the resistances are equal and if the voltage source and curr ...
Series and Parallel Circuits
... resistor examples, because it’s harder to measure capacitance directly with a multimeter. Let’s first talk about what happens when a capacitor charges up from zero volts. When current starts to go in one of the leads, an equal amount of current comes out the other. And if there’s no resistance in se ...
... resistor examples, because it’s harder to measure capacitance directly with a multimeter. Let’s first talk about what happens when a capacitor charges up from zero volts. When current starts to go in one of the leads, an equal amount of current comes out the other. And if there’s no resistance in se ...
Network analysis (electrical circuits)

A network, in the context of electronics, is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, every component in the network. There are many different techniques for calculating these values. However, for the most part, the applied technique assumes that the components of the network are all linear.The methods described in this article are only applicable to linear network analysis, except where explicitly stated.