iLumin System Written Specification (PDF Doc)
... e. Low Voltage Dimming (0-10V); Meet following requirements: 1) Capable of controlling any 0-10V source. 2) 0-10V analog voltage signal. a) Provide isolated 0-10V output signal conforming to IEC 60929. b) Sink current via IEC 60929. c) Source current. Dimmer: SC-RP and SC-RPB Series a. Up to 24 Low ...
... e. Low Voltage Dimming (0-10V); Meet following requirements: 1) Capable of controlling any 0-10V source. 2) 0-10V analog voltage signal. a) Provide isolated 0-10V output signal conforming to IEC 60929. b) Sink current via IEC 60929. c) Source current. Dimmer: SC-RP and SC-RPB Series a. Up to 24 Low ...
Vanya Ignatova*, Pierre Granjon**, Seddik Bacha
... domain, currents and voltages spectra are obtained by application of Fourier transform. This domain can not give an analytical harmonic solution for the considered system and the relations between harmonics can not be expressed. In the frequency domain, several methods for power network harmonic ana ...
... domain, currents and voltages spectra are obtained by application of Fourier transform. This domain can not give an analytical harmonic solution for the considered system and the relations between harmonics can not be expressed. In the frequency domain, several methods for power network harmonic ana ...
A Compact Low Voltage CMOS Four-Quadrant Analog Multiplier
... two identical voltage controlled square root blocks which operate as non-linear cancellation paths. Injecting the output currents of the input transistors into the square root blocks, a differential output current of the overall circuit will become a multiplication function of two input signals V12 ...
... two identical voltage controlled square root blocks which operate as non-linear cancellation paths. Injecting the output currents of the input transistors into the square root blocks, a differential output current of the overall circuit will become a multiplication function of two input signals V12 ...
G6 - CIRCUIT COMPONENTS [3 exam question
... A. It will increase by 20% for every 10 degrees centigrade B. It will stay the same C. It will change depending on the resistor's temperature ...
... A. It will increase by 20% for every 10 degrees centigrade B. It will stay the same C. It will change depending on the resistor's temperature ...
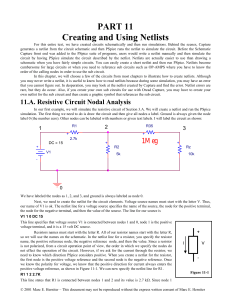
PART 11 Creating and Using Netlists - Rose
... Although the bias point simulation calculates currents and voltages for all elements in the circuit, all currents are not displayed in the output file. To display this information, we need to run a DC simulation at a single point. To do this, we will use the list version of the DC statement: .DC V1 ...
... Although the bias point simulation calculates currents and voltages for all elements in the circuit, all currents are not displayed in the output file. To display this information, we need to run a DC simulation at a single point. To do this, we will use the list version of the DC statement: .DC V1 ...
Unit-8Lecture 51 TESTING OF ISOLATORS AND CIRCUIT
... In this section, the testing of isolators and circuit breakers is covered, giving common characteristics for both. While these characteristics are directly relevant to the testing of circuit breakers, they are not much relevant as far as the testing of isolators are concerned since isolators are not ...
... In this section, the testing of isolators and circuit breakers is covered, giving common characteristics for both. While these characteristics are directly relevant to the testing of circuit breakers, they are not much relevant as far as the testing of isolators are concerned since isolators are not ...
Chapter 13
... External Parallel Load Resistance • Often an external load resistance appears in parallel with a tank circuit • The external resistance effectively appears in parallel with the equivalent parallel resistance (Rp(eq)) of the coil: Rp(tot) = RL||Rp(eq) • The external resistor (RL) will lower the overa ...
... External Parallel Load Resistance • Often an external load resistance appears in parallel with a tank circuit • The external resistance effectively appears in parallel with the equivalent parallel resistance (Rp(eq)) of the coil: Rp(tot) = RL||Rp(eq) • The external resistor (RL) will lower the overa ...
Document
... Superposition theorem states that in a linear bilateral network containing more than one source, the current flowing through the branch is the algebraic sum of the current flowing through that branch when sources are considered one at a time and replacing other sources by ...
... Superposition theorem states that in a linear bilateral network containing more than one source, the current flowing through the branch is the algebraic sum of the current flowing through that branch when sources are considered one at a time and replacing other sources by ...
21111014 Draft 2 PN-3-4963
... When implemented within the guidelines of this Standard, multiple generators and receivers may be attached to a common interconnecting cable. The generators and receivers operate with no errors if the balanced interconnecting cables are connected normally or with the differential signal wires revers ...
... When implemented within the guidelines of this Standard, multiple generators and receivers may be attached to a common interconnecting cable. The generators and receivers operate with no errors if the balanced interconnecting cables are connected normally or with the differential signal wires revers ...
Network analysis (electrical circuits)

A network, in the context of electronics, is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, every component in the network. There are many different techniques for calculating these values. However, for the most part, the applied technique assumes that the components of the network are all linear.The methods described in this article are only applicable to linear network analysis, except where explicitly stated.









![T6D [21]-[49]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002752171_1-e2a0c5332cd6cb9c9bd4bad2a4dbe26d-300x300.png)