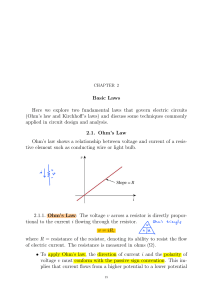
Kirchhoffs_Laws
... where x is the fraction of the total number of turns of the knob. ◦ The resistance between pins 2 and 3 is (1 – x) Rpot, where x is the fraction of the total number of turns of the knob. ◦ There may be a notation on the top surface about the direction that the knob should be turned [Clockwise (CW) o ...
... where x is the fraction of the total number of turns of the knob. ◦ The resistance between pins 2 and 3 is (1 – x) Rpot, where x is the fraction of the total number of turns of the knob. ◦ There may be a notation on the top surface about the direction that the knob should be turned [Clockwise (CW) o ...
Mobile Card Studio Physics Activity – n
... Mobile Card oscilloscope ( 2 channels) and function generator, breadboard, diode, 470 ohm resistor, six wires. 1. Wire the diode and resistor in series on the breadboard. (For consistency, place the diode to the right and the resistor to the left. Place the white line on the diode to the right side ...
... Mobile Card oscilloscope ( 2 channels) and function generator, breadboard, diode, 470 ohm resistor, six wires. 1. Wire the diode and resistor in series on the breadboard. (For consistency, place the diode to the right and the resistor to the left. Place the white line on the diode to the right side ...
Objectives PHY 252 Spring 2011 Practical Lab #1 Ohm’s Law
... V = voltage applied across the circuit and has SI units of volts (V) I = current flowing through the circuit and has SI units of amperes (A) R = resistance of the circuit and has SI units of ohms (Ω) ...
... V = voltage applied across the circuit and has SI units of volts (V) I = current flowing through the circuit and has SI units of amperes (A) R = resistance of the circuit and has SI units of ohms (Ω) ...
Poster - Technology Supplies
... one end of a battery to the other. The electric current can flow but nothing useful happens. The wire just gets hot and the battery goes flat. To do something useful with the electric current, we need to put an electrical component into the circuit, such as a lamp or motor. The bulb will only light ...
... one end of a battery to the other. The electric current can flow but nothing useful happens. The wire just gets hot and the battery goes flat. To do something useful with the electric current, we need to put an electrical component into the circuit, such as a lamp or motor. The bulb will only light ...
AVOP-ELEKTRO-SKA-011
... during the excessive current (so called over current) (usually during overload or short-circuit) automatically disconnects electric circuit and by that protects operating personnel against possible injury caused by an electric current and protected electric device against damage. ...
... during the excessive current (so called over current) (usually during overload or short-circuit) automatically disconnects electric circuit and by that protects operating personnel against possible injury caused by an electric current and protected electric device against damage. ...
Chapter 18 – DC Circuits
... Voltage sources are not perfect, and the voltage will vary with the amount of current that is drawn from the source. A way of modeling this is to think of a voltage source as an ideal voltage source (E) in series with an internal resistor (r). I b ...
... Voltage sources are not perfect, and the voltage will vary with the amount of current that is drawn from the source. A way of modeling this is to think of a voltage source as an ideal voltage source (E) in series with an internal resistor (r). I b ...
Electrical Currents
... That is, the potential difference between the terminals of a cell must equal the sum of the potential differences between the connections to all the loads in series with the cell. ...
... That is, the potential difference between the terminals of a cell must equal the sum of the potential differences between the connections to all the loads in series with the cell. ...
Network analysis (electrical circuits)

A network, in the context of electronics, is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, every component in the network. There are many different techniques for calculating these values. However, for the most part, the applied technique assumes that the components of the network are all linear.The methods described in this article are only applicable to linear network analysis, except where explicitly stated.