Power Point Notes
... • Enzymes remove -OH from one molecule, H from another, form bond between two molecules • Discarded atoms can join to form water ...
... • Enzymes remove -OH from one molecule, H from another, form bond between two molecules • Discarded atoms can join to form water ...
The term “Chromic Acid” actually refers to a collection of compounds
... contain the chromate ion, CrO42-, and have an intense yellow color. Dichromate salts contain the dichromate ion, Cr2O72−, and have an intense orange color. Potassium dichromate, K2Cr2O7, is a common inorganic chemical reagent, most commonly used as an oxidizing agent in various laboratory and indust ...
... contain the chromate ion, CrO42-, and have an intense yellow color. Dichromate salts contain the dichromate ion, Cr2O72−, and have an intense orange color. Potassium dichromate, K2Cr2O7, is a common inorganic chemical reagent, most commonly used as an oxidizing agent in various laboratory and indust ...
Synthesis of (−)-Epibatidine - David A. Evans
... isomer was determined to be equatorial alcohol 16 by the straightforward conversion of minor isomer 17 to epibatadine (1) by a three-step sequence.22 Although hindered hydride reagents did not produce the desired axial alcohol, relatively smaller reducing agents afforded the equatorial alcohol with ...
... isomer was determined to be equatorial alcohol 16 by the straightforward conversion of minor isomer 17 to epibatadine (1) by a three-step sequence.22 Although hindered hydride reagents did not produce the desired axial alcohol, relatively smaller reducing agents afforded the equatorial alcohol with ...
SCI2199 - Introduction to Organic Chemistry II
... 7. Which of the following could be used to synthesize 2-bromobutane? A) CH3CH2CH=CH2 + Br2(aq) → B) CH3CH2CHOHCH3 + HBr → C) CH3CH2C≡CH + HBr → D) CH3CH2C≡CH + Br2 → E) More than one of these choices. 8. Which of the alcohols listed below would you expect to react most rapidly with ...
... 7. Which of the following could be used to synthesize 2-bromobutane? A) CH3CH2CH=CH2 + Br2(aq) → B) CH3CH2CHOHCH3 + HBr → C) CH3CH2C≡CH + HBr → D) CH3CH2C≡CH + Br2 → E) More than one of these choices. 8. Which of the alcohols listed below would you expect to react most rapidly with ...
Class 15
... 3) Finish with -amine as the suffix (does NOT take priority over -ol, -ene, or -yne) ...
... 3) Finish with -amine as the suffix (does NOT take priority over -ol, -ene, or -yne) ...
Practice Paper - 3
... Five reason for the following (a) Grignard reagents should be prepared under an hydrous condition? (b) Ethanol has higher B. P. in comparison to methoxy methane. OR (a) Explain how does the –OH group attached to a carbon of benzene ring , activate it towards electrophilic substitution? (b) Alcohols ...
... Five reason for the following (a) Grignard reagents should be prepared under an hydrous condition? (b) Ethanol has higher B. P. in comparison to methoxy methane. OR (a) Explain how does the –OH group attached to a carbon of benzene ring , activate it towards electrophilic substitution? (b) Alcohols ...
Alcohol oxidation
... bond. Furthermore, the borane acts as a lewis acid by accepting two electrons in its empty p orbital from an alkene that is electron rich. This process allows boron to have an electron octet. A very interesting characteristic of this process is that it does not require any activation by a catalyst. ...
... bond. Furthermore, the borane acts as a lewis acid by accepting two electrons in its empty p orbital from an alkene that is electron rich. This process allows boron to have an electron octet. A very interesting characteristic of this process is that it does not require any activation by a catalyst. ...
Alkynes
... But typical of synthetic problems side reaction occurs to some extent and must be taken into account. ...
... But typical of synthetic problems side reaction occurs to some extent and must be taken into account. ...
Modules 261 12th edition
... How to test for Chirality: Planes of symmetry Naming Enantiomers: The R, S –System How to Assign (R) and (S) Configurations Properties of Enantiomers: Optical Activity - specific rotation - Plane polarized light - The polarimeter Racemic forms - Racemic forms and Enantiomeric Excess The Synthesis of ...
... How to test for Chirality: Planes of symmetry Naming Enantiomers: The R, S –System How to Assign (R) and (S) Configurations Properties of Enantiomers: Optical Activity - specific rotation - Plane polarized light - The polarimeter Racemic forms - Racemic forms and Enantiomeric Excess The Synthesis of ...
Oxidation of Cyclohexanol
... is a fundamental and widely used reaction. Primary alcohols can be oxidized to aldehydes or carboxylic acids while secondary alcohols oxidize to ketones. Tertiary alcohols are resistant to oxidation. In this experiment common household bleach will be used as a source of sodium hypochlorite, NaOCl (a ...
... is a fundamental and widely used reaction. Primary alcohols can be oxidized to aldehydes or carboxylic acids while secondary alcohols oxidize to ketones. Tertiary alcohols are resistant to oxidation. In this experiment common household bleach will be used as a source of sodium hypochlorite, NaOCl (a ...
unit 17 organic compounds containing oxygen and nitrogen atoms
... Aliphatic aldehydes form a homologous series with the general formula RCHO and ketons with general formula RCOR'. Aldehydes and ketones have the same general formula CnH,"O. Since carbonyl group is present in both aldehydes and ketones, many of their properties are common. But in aldehyde, there is ...
... Aliphatic aldehydes form a homologous series with the general formula RCHO and ketons with general formula RCOR'. Aldehydes and ketones have the same general formula CnH,"O. Since carbonyl group is present in both aldehydes and ketones, many of their properties are common. But in aldehyde, there is ...
Lecture 15a - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... organic compounds i.e., Monsanto process (acetic acid), Fischer Tropsch process (gasoline, ethylene glycol, methanol) or Reppe carbonylation (vinyl esters) from simple precursors (CO, CO2, H2, H2O) • Vaska’s complex (IrCl(CO)(PPh3)2) absorbs oxygen reversibly and serves as model for the oxygen absor ...
... organic compounds i.e., Monsanto process (acetic acid), Fischer Tropsch process (gasoline, ethylene glycol, methanol) or Reppe carbonylation (vinyl esters) from simple precursors (CO, CO2, H2, H2O) • Vaska’s complex (IrCl(CO)(PPh3)2) absorbs oxygen reversibly and serves as model for the oxygen absor ...
10.5 Carbonyl Compounds (a) describe: (i) the
... (i) the formation of aldehydes and ketones from primary and secondary alcohols respectively using Cr2O72-/H+ (ii) the reduction of aldehydes and ketones e.g. using NaBH4 (b) describe the mechanism of nucleophilic addition reactions of hydrogen cyanide with aldehydes and ketones (c) describe the use ...
... (i) the formation of aldehydes and ketones from primary and secondary alcohols respectively using Cr2O72-/H+ (ii) the reduction of aldehydes and ketones e.g. using NaBH4 (b) describe the mechanism of nucleophilic addition reactions of hydrogen cyanide with aldehydes and ketones (c) describe the use ...
Expt #7: Synthesis of Esters using Acetic
... heat the reaction mixture briefly to make sure the reaction has gone to completion. You will then follow a severalstep procedure designed to isolate the ester product as a pure substance (free from any leftover starting materials and acetic acid side product). This is a typical, though relatively si ...
... heat the reaction mixture briefly to make sure the reaction has gone to completion. You will then follow a severalstep procedure designed to isolate the ester product as a pure substance (free from any leftover starting materials and acetic acid side product). This is a typical, though relatively si ...
Synthesis of Esters
... alcohol, which you will identify simply by its aroma!! HOW ESTERS ARE MADE: There are several ways to make an ester from an alcohol or a phenol. Reaction (1), mixing a carboxylic acid with an alcohol (or phenol) is not effective - these two react with each other only slowly and, worse, it's an equil ...
... alcohol, which you will identify simply by its aroma!! HOW ESTERS ARE MADE: There are several ways to make an ester from an alcohol or a phenol. Reaction (1), mixing a carboxylic acid with an alcohol (or phenol) is not effective - these two react with each other only slowly and, worse, it's an equil ...
lab – preparation of esters name
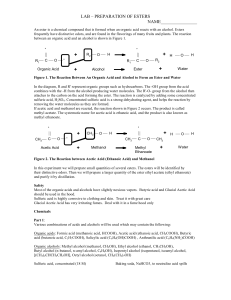
... Figure 1. The Reaction Between An Organic Acid and Alcohol to Form an Ester and Water In the diagram, R and R' represent organic groups such as hydrocarbons. The -OH group from the acid combines with the -H from the alcohol producing water molecules. The R'-O- group from the alcohol then attaches to ...
... Figure 1. The Reaction Between An Organic Acid and Alcohol to Form an Ester and Water In the diagram, R and R' represent organic groups such as hydrocarbons. The -OH group from the acid combines with the -H from the alcohol producing water molecules. The R'-O- group from the alcohol then attaches to ...
An ester is a chemical compound that is formed when an organic
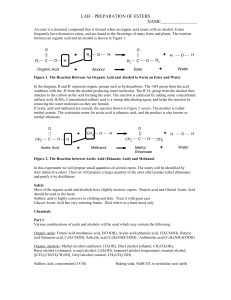
... Figure 1. The Reaction Between An Organic Acid and Alcohol to Form an Ester and Water In the diagram, R and R' represent organic groups such as hydrocarbons. The -OH group from the acid combines with the -H from the alcohol producing water molecules. The R'-O- group from the alcohol then attaches to ...
... Figure 1. The Reaction Between An Organic Acid and Alcohol to Form an Ester and Water In the diagram, R and R' represent organic groups such as hydrocarbons. The -OH group from the acid combines with the -H from the alcohol producing water molecules. The R'-O- group from the alcohol then attaches to ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... the presence of a platinum catalyst and high enough temperature forms nitrogen gas and oxygen gas. ...
... the presence of a platinum catalyst and high enough temperature forms nitrogen gas and oxygen gas. ...
Organic Chemistry – Summary of Reactions and Conditions
... If several products are possible, the double bond tends to form between carbon atoms which have fewest hydrogen atoms attached. Note the difference in reagent and conditions in reaction 1. ...
... If several products are possible, the double bond tends to form between carbon atoms which have fewest hydrogen atoms attached. Note the difference in reagent and conditions in reaction 1. ...
chapter 4 review_package
... 9. Given the following balanced equations, solve the stoichiometric problems (PLO-D5) a. Ammonia combines with oxygen gas in the following reaction: 4 NH3 + 5O2 → 6H2O + 4NO i. How many moles of NH3 are needed to combine with 3.57 moles of O2 gas? ...
... 9. Given the following balanced equations, solve the stoichiometric problems (PLO-D5) a. Ammonia combines with oxygen gas in the following reaction: 4 NH3 + 5O2 → 6H2O + 4NO i. How many moles of NH3 are needed to combine with 3.57 moles of O2 gas? ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.

















![+ [O] - MrFisherChemistry](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008194573_1-9c1e57b3af8f6a74ecb3216d2ce704f3-300x300.png)