8.5 Translation
... 8.5 Translation • Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis. Ribosomes are made of rRNA. • Helps form peptide bonds between amino acids. – Reading frame: where 3 non-overlapping nucleotides are read in order to code for the correct formation of a protein. ...
... 8.5 Translation • Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis. Ribosomes are made of rRNA. • Helps form peptide bonds between amino acids. – Reading frame: where 3 non-overlapping nucleotides are read in order to code for the correct formation of a protein. ...
Lecture 8a - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... • “If chelation between the carbonyl group and one of the substituents of the a-stereocenter facilitated by a metal cation can occur, the substrate will be locked into conformation, where these two substituents are on the same side. This will place the remaining two substituents on different sides o ...
... • “If chelation between the carbonyl group and one of the substituents of the a-stereocenter facilitated by a metal cation can occur, the substrate will be locked into conformation, where these two substituents are on the same side. This will place the remaining two substituents on different sides o ...
Chapter 1 Chemical Bonding and Chemical Structure
... whether they are primary, secondary or tertiary • Fewer than 5 carbons usually = solubility in water ...
... whether they are primary, secondary or tertiary • Fewer than 5 carbons usually = solubility in water ...
File
... c. recall optical activity as the ability of a single optical isomer to rotate the plane of polarization of plane-polarized monochromatic light in molecules containing a single chiral centre and understand the nature of a racemic mixture d. use data on optical activity of reactants and products as e ...
... c. recall optical activity as the ability of a single optical isomer to rotate the plane of polarization of plane-polarized monochromatic light in molecules containing a single chiral centre and understand the nature of a racemic mixture d. use data on optical activity of reactants and products as e ...
Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acids
... Ethyl orthoformate resembles an acetal with an extra alkoxy group, so this mechanism should resemble the hydrolysis of an acetal (Section 18-18). There are three equivalent basic sites: the three oxygen atoms. Protonation of one of these sites allows ethanol to leave, giving a resonance-stabilized c ...
... Ethyl orthoformate resembles an acetal with an extra alkoxy group, so this mechanism should resemble the hydrolysis of an acetal (Section 18-18). There are three equivalent basic sites: the three oxygen atoms. Protonation of one of these sites allows ethanol to leave, giving a resonance-stabilized c ...
Microsoft Word - Open Access Repository of Indian Theses
... Section A: Enantio selective synthesis of N-Boc-(2S,3S)-3-hydroxy-2-phenylpiperidine Functionalized piperidines are useful as biologically active agents. The piperidine ring is a common moiety found in bioactive natural products, drugs, and drug candidates. In recent years, N-Boc-(2S,3S)-3-hydroxy-2 ...
... Section A: Enantio selective synthesis of N-Boc-(2S,3S)-3-hydroxy-2-phenylpiperidine Functionalized piperidines are useful as biologically active agents. The piperidine ring is a common moiety found in bioactive natural products, drugs, and drug candidates. In recent years, N-Boc-(2S,3S)-3-hydroxy-2 ...
Chem263_Nov 25_notes_2010
... Nucleophilic acyl substitution reactions usually take place in two steps: addition of the nucleophile and elimination of a leaving group. Although both steps can affect the overall rate of the reaction, it is generally the first step that is rate-limiting. Therefore any factor that makes the carbony ...
... Nucleophilic acyl substitution reactions usually take place in two steps: addition of the nucleophile and elimination of a leaving group. Although both steps can affect the overall rate of the reaction, it is generally the first step that is rate-limiting. Therefore any factor that makes the carbony ...
Facile Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohols with Sodium Nitrate/p
... present reaction conditions. Electron donating groups such as –CH and –OCH present in the aromatic rings facilitated the oxidations and the reactions are completed within 150 sec (entries 3-4). Even in cases of benzyl alcohols with powerful electron withdrawing groups (entries 5-7) in the aromatic r ...
... present reaction conditions. Electron donating groups such as –CH and –OCH present in the aromatic rings facilitated the oxidations and the reactions are completed within 150 sec (entries 3-4). Even in cases of benzyl alcohols with powerful electron withdrawing groups (entries 5-7) in the aromatic r ...
Sulfur analogs of alcohols, phenols and ethers
... R-CH2-Cl > R-CH2-Br > R-CH2-I alkyl chloride reacts at oxygen atom ...
... R-CH2-Cl > R-CH2-Br > R-CH2-I alkyl chloride reacts at oxygen atom ...
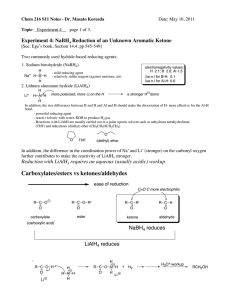
Carboxylates/esters vs ketones/aldehydes
... BH3 becomes B(OC2H5)3 by reacting with ethanol, then, when heated with water, becomes B(OH)3. The mechanism of the NaBH4 reduction in a protic solvent such as ethanol, methanol, and water is known to be quite complex since NaBH4 reacts with the solvent, e.g., NaBH4 + C2H5OH → NaBH3(OC2H5) + H2 Becau ...
... BH3 becomes B(OC2H5)3 by reacting with ethanol, then, when heated with water, becomes B(OH)3. The mechanism of the NaBH4 reduction in a protic solvent such as ethanol, methanol, and water is known to be quite complex since NaBH4 reacts with the solvent, e.g., NaBH4 + C2H5OH → NaBH3(OC2H5) + H2 Becau ...
OCR_Organic_Chemistry_AS_summary
... • Secondary alcohols may only be oxidised to form ketones. • Tertiary alcohols cannot normally be oxidised ...
... • Secondary alcohols may only be oxidised to form ketones. • Tertiary alcohols cannot normally be oxidised ...
nucleophilic addition
... mixed with another aldehyde that doesn’t have any alphahydrogens and conc. NaOH, all of the formaldehyde is oxidized and all of the other aldehyde is reduced. ...
... mixed with another aldehyde that doesn’t have any alphahydrogens and conc. NaOH, all of the formaldehyde is oxidized and all of the other aldehyde is reduced. ...
Exam 1 - Winona State University
... min. Exams must be turned in immediately upon my call of time up. Grading will be on the basis of a highest possible score of 100 points. I. Multiple Choice – 2 points each, 20 points total II. Nomenclature/Structure – 2 points each, 20 points total III. Synthesis – 5 points each, 15 points total IV ...
... min. Exams must be turned in immediately upon my call of time up. Grading will be on the basis of a highest possible score of 100 points. I. Multiple Choice – 2 points each, 20 points total II. Nomenclature/Structure – 2 points each, 20 points total III. Synthesis – 5 points each, 15 points total IV ...
A study of the mechanism of certain chemical reactions—I: The
... It has been shown, that the rate of reaction betw reen dibenzal-ethylenediamine formic acid is very slow at room temperature, and this could be an argument against the ionic mechanism for the reaction. The reaction of benzylidene-bismpiperidine and formic acid has been investigated under anhydrous c ...
... It has been shown, that the rate of reaction betw reen dibenzal-ethylenediamine formic acid is very slow at room temperature, and this could be an argument against the ionic mechanism for the reaction. The reaction of benzylidene-bismpiperidine and formic acid has been investigated under anhydrous c ...
Expt #10 - Proteins
... If you look closely at the structure of aspartame, you will notice that the terminal acid group is not a carboxylic acid, but rather the methyl ester of carboxylic acid. This type of variation in protein structure is very common throughout all types of amino acids. Therefore, upon hydrolysis, aspart ...
... If you look closely at the structure of aspartame, you will notice that the terminal acid group is not a carboxylic acid, but rather the methyl ester of carboxylic acid. This type of variation in protein structure is very common throughout all types of amino acids. Therefore, upon hydrolysis, aspart ...
File - Dr KHALID SHADID
... atom is relatively open to attack from above or below. The positive charge on the carbonyl carbon atom means that it is especially susceptible to attack by a nucleophile. The negative charge on the carbonyl oxygen atom means that nucleophilic addition is susceptible to acid catalysis. ...
... atom is relatively open to attack from above or below. The positive charge on the carbonyl carbon atom means that it is especially susceptible to attack by a nucleophile. The negative charge on the carbonyl oxygen atom means that nucleophilic addition is susceptible to acid catalysis. ...
Amines
... t Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions l Alkylation of Ammonia with an alkyl halide è Initial aminium salt is treated with base to give the primary amine è The method is limited because multiple alkylations usually occur ...
... t Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions l Alkylation of Ammonia with an alkyl halide è Initial aminium salt is treated with base to give the primary amine è The method is limited because multiple alkylations usually occur ...
MAIN GROUP ORGANOMETALLICS Dr. S. Draper 8 lecture course
... in the low volatility and insolubility of (LiCH3)4 in nonsolvating media. The structure of t butyl lithium is similar but the intermolecular forces are weaker and hence tBuLi is soluble in hydrocarbons and sublimes at 70o C/1 mbar. Coordinating solvents will tend to give monomeric or dimeric species ...
... in the low volatility and insolubility of (LiCH3)4 in nonsolvating media. The structure of t butyl lithium is similar but the intermolecular forces are weaker and hence tBuLi is soluble in hydrocarbons and sublimes at 70o C/1 mbar. Coordinating solvents will tend to give monomeric or dimeric species ...
EXPERIMENT 9 (Organic Chemistry II) Pahlavan/Cherif
... shown in equation (3). Acid anhydride, which is made by the removal of a water molecule from two acetic acid molecules, reacts with alcohols in much the same way as acids to form the ester. Drug manufacturers prepare aspirin from salicylic acid by this method, which is a much better synthetic method ...
... shown in equation (3). Acid anhydride, which is made by the removal of a water molecule from two acetic acid molecules, reacts with alcohols in much the same way as acids to form the ester. Drug manufacturers prepare aspirin from salicylic acid by this method, which is a much better synthetic method ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.