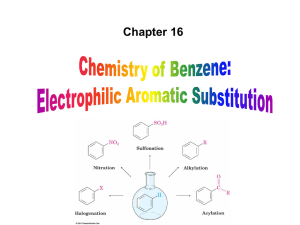
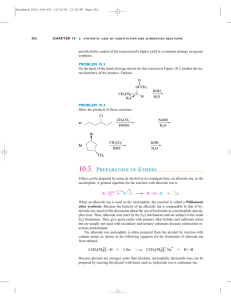
ch16 by dr. Dina
... Dissolving aldehydes (or ketones) in water causes formation of an equilibrium between the carbonyl compound and its hydrate The hydrate is also called a gem-diol (gem i.e. geminal, indicates the presence of two identical substituents on the same carbon) The equilibrum favors a ketone over its hyd ...
... Dissolving aldehydes (or ketones) in water causes formation of an equilibrium between the carbonyl compound and its hydrate The hydrate is also called a gem-diol (gem i.e. geminal, indicates the presence of two identical substituents on the same carbon) The equilibrum favors a ketone over its hyd ...
Practice Problem - HCC Southeast Commons
... Only alkyl halides can be used (F, Cl, Br, I) – Aryl halides and vinylic halides do not react (their carbocations are too high in energy to form) ...
... Only alkyl halides can be used (F, Cl, Br, I) – Aryl halides and vinylic halides do not react (their carbocations are too high in energy to form) ...
Compounds Containing A Single Bond To A
... iodine, and astatine, occupying group VIIA (17) of the periodic table. They are reactive nonmetallic elements that form strongly acidic compounds with hydrogen, from which simple salts can be made. ...
... iodine, and astatine, occupying group VIIA (17) of the periodic table. They are reactive nonmetallic elements that form strongly acidic compounds with hydrogen, from which simple salts can be made. ...
Kinetics of Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol with Dilute Nitric Acid
... amount of NaNO2, in 40 vol % dioxan as a solvent, was first studied in detail by Ogata et al.15 They proposed that the reaction proceeded through some intermediate; however, it was not identified. Many other investigators have also studied the oxidation of benzyl alcohol using nitric acid.17-21 Howe ...
... amount of NaNO2, in 40 vol % dioxan as a solvent, was first studied in detail by Ogata et al.15 They proposed that the reaction proceeded through some intermediate; however, it was not identified. Many other investigators have also studied the oxidation of benzyl alcohol using nitric acid.17-21 Howe ...
Organic Chemistry Chapter 2 - Snow College | It's SNOWing
... same carbon, use the number twice. When two or more substituents are identical, use prefixes When two chains are the same length, use the one with the most substituents on it. If substituents are at equall distances from the ends of the chain, go to the next substituent. Iso and cyclo are included a ...
... same carbon, use the number twice. When two or more substituents are identical, use prefixes When two chains are the same length, use the one with the most substituents on it. If substituents are at equall distances from the ends of the chain, go to the next substituent. Iso and cyclo are included a ...
Chapter 19 Amines
... • To produce a 1 amine, react an aldehyde or ketone with hydroxylamine, then reduce the oxime. • To produce a 2 amine, react an aldehyde or ketone with a 1 amine, then reduce the imine. • To produce a 3 amine, react an aldehyde or ketone with a 2 amine, then reduce the imine salt. ...
... • To produce a 1 amine, react an aldehyde or ketone with hydroxylamine, then reduce the oxime. • To produce a 2 amine, react an aldehyde or ketone with a 1 amine, then reduce the imine. • To produce a 3 amine, react an aldehyde or ketone with a 2 amine, then reduce the imine salt. ...
Unit-5-Lipids
... form esters. Since there are three hydroxyl groups, three fatty acids can react to form three esters. ...
... form esters. Since there are three hydroxyl groups, three fatty acids can react to form three esters. ...
Handout: Naming Organic Compounds Substituents Longest carbon
... with same R groups on N: Treat alkyl groups attached to nitrogen as substituents. For same substituents, use “di” and “tri.” 2°, 3° amines with different R groups on N: Parent amine is the one with largest R group; name other groups as substituents, starting with N-. [Ions derived from a ...
... with same R groups on N: Treat alkyl groups attached to nitrogen as substituents. For same substituents, use “di” and “tri.” 2°, 3° amines with different R groups on N: Parent amine is the one with largest R group; name other groups as substituents, starting with N-. [Ions derived from a ...
Unit-5-LipidsClick copy
... form esters. Since there are three hydroxyl groups, three fatty acids can react to form three esters. ...
... form esters. Since there are three hydroxyl groups, three fatty acids can react to form three esters. ...
Ultrasound Assisted Synthesis of 5,9
... Recent research has shown that several hydrocarbons with a 1,5-dimethyl skeleton are insect pheromones [1]. 5,9-Dimethylpentadecane (1) and 5,9-dimethylhexadecane (2) are known as the major and minor constituents, respectively, of the sex pheromone of Leucoptera coffeella, a pest of coffee trees [2] ...
... Recent research has shown that several hydrocarbons with a 1,5-dimethyl skeleton are insect pheromones [1]. 5,9-Dimethylpentadecane (1) and 5,9-dimethylhexadecane (2) are known as the major and minor constituents, respectively, of the sex pheromone of Leucoptera coffeella, a pest of coffee trees [2] ...
Green Polymer Chemistry: Enzyme Catalysis for Polymer
... method for the formation of new carbon-carbon and carbon-heteroatom bonds. Michael-type reactions typically involve the use of either strongly basic or acidic conditions, leading to the generation of potentially hazardous waste by-products and/or undesired side products [12]. Bhanage et al. reported ...
... method for the formation of new carbon-carbon and carbon-heteroatom bonds. Michael-type reactions typically involve the use of either strongly basic or acidic conditions, leading to the generation of potentially hazardous waste by-products and/or undesired side products [12]. Bhanage et al. reported ...
Palladium-Catalyzed Synthesis and Transformation of Organoboranes
... Application of palladium catalysis offers a mild and selective method for synthesis and transformation of allylic organometallic compounds.1 Many excellent methods have been published for synthesis of allylic boranes, silanes, stannanes and other compounds, which are reactive synthetic intermediates ...
... Application of palladium catalysis offers a mild and selective method for synthesis and transformation of allylic organometallic compounds.1 Many excellent methods have been published for synthesis of allylic boranes, silanes, stannanes and other compounds, which are reactive synthetic intermediates ...
Document
... 17 Selective Reduction • using the less reactive NaBH4, it is possible to reduce the carbonyl group of an aldehyde or ketone without affecting a carboxyl group O C6 H5 ...
... 17 Selective Reduction • using the less reactive NaBH4, it is possible to reduce the carbonyl group of an aldehyde or ketone without affecting a carboxyl group O C6 H5 ...
Haloalkanes
... The presence of the hydrogen atoms make these compounds less stable than CFCs. They do not reach the stratosphere in such large concentrations. A programme of tests, including toxicity tests, is being carried out on these compounds. ...
... The presence of the hydrogen atoms make these compounds less stable than CFCs. They do not reach the stratosphere in such large concentrations. A programme of tests, including toxicity tests, is being carried out on these compounds. ...
PDF aldehydes and ketones
... Use of ammonium salts gives unsubstituted amino acids. Primary and secondary amines also successfully give substituted amino acids. Likewise, the use of ketones, instead of aldehydes, gives α,α-disubtituted amino acids Mechanism Reaction type: Nucleophilic Addition followed by Nucleophilic Acyl Subs ...
... Use of ammonium salts gives unsubstituted amino acids. Primary and secondary amines also successfully give substituted amino acids. Likewise, the use of ketones, instead of aldehydes, gives α,α-disubtituted amino acids Mechanism Reaction type: Nucleophilic Addition followed by Nucleophilic Acyl Subs ...
Microsoft Word
... that stored in 95% ethanol and 5% aqueous NaOH. The catalyst prepared at the optimum conditions gave the maximum catalytic activity when it was stored in deionised distilled water under H2 atmosphere at room temperature for a period of 140 hr. PART III : HYDROGENATION OF o-NITROPHENOL ON Pd-CARBQN E ...
... that stored in 95% ethanol and 5% aqueous NaOH. The catalyst prepared at the optimum conditions gave the maximum catalytic activity when it was stored in deionised distilled water under H2 atmosphere at room temperature for a period of 140 hr. PART III : HYDROGENATION OF o-NITROPHENOL ON Pd-CARBQN E ...
Alcohols and Phenols
... • Can be more or less acidic than phenol itself • An electron-withdrawing substituent makes a phenol more acidic by delocalizing the negative charge • Phenols with an electron-donating substituent are less acidic because these substituents concentrate the charge ...
... • Can be more or less acidic than phenol itself • An electron-withdrawing substituent makes a phenol more acidic by delocalizing the negative charge • Phenols with an electron-donating substituent are less acidic because these substituents concentrate the charge ...
` United States
... the possibility of using other solvents instead of benzene, tropic mixture, the water formed during the reaction. i. e. in the case of the 3-glycol ketal of ll-keto-pr-ogester 'It has ‘been known for many years that steroidal ketones 20 one-ZO-cyanohydrin preparation (paper presented to ‘be may ‘be ...
... the possibility of using other solvents instead of benzene, tropic mixture, the water formed during the reaction. i. e. in the case of the 3-glycol ketal of ll-keto-pr-ogester 'It has ‘been known for many years that steroidal ketones 20 one-ZO-cyanohydrin preparation (paper presented to ‘be may ‘be ...
Worked out problems
... balanced chemical equation for the reduction of pyruvic acid to lactic acid (Figure 25.17). (Although H atoms do not exist as such in biochemical systems, biochemical reducing agents deliver hydrogen for such reductions.) ...
... balanced chemical equation for the reduction of pyruvic acid to lactic acid (Figure 25.17). (Although H atoms do not exist as such in biochemical systems, biochemical reducing agents deliver hydrogen for such reductions.) ...
Chapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones
... Ketone has more alkyl groups, stabilizing the C=O carbon inductively ...
... Ketone has more alkyl groups, stabilizing the C=O carbon inductively ...
PHENYLKETONURIA
... of amino acids, which bind as the pearls of a necklace, in a special order for each protein, which determines their spatial shape and thereby, their correct function. When proteins degrade, amino acids are released and can be used to form new proteins or other compounds in our body or to generate en ...
... of amino acids, which bind as the pearls of a necklace, in a special order for each protein, which determines their spatial shape and thereby, their correct function. When proteins degrade, amino acids are released and can be used to form new proteins or other compounds in our body or to generate en ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.