Transition Metal Chemistry 2 2011.12.2 Ⅰ Fundamental
... (4) Role of transition metal catalysts in industrial acetic acid synthesis. Acetic acid is one of the most important chemicals and was produced by (destructive distillation of coal. History of acetic acid production revealed importance of transition metal catalysts. (4-1) Hydration of acetylene---M ...
... (4) Role of transition metal catalysts in industrial acetic acid synthesis. Acetic acid is one of the most important chemicals and was produced by (destructive distillation of coal. History of acetic acid production revealed importance of transition metal catalysts. (4-1) Hydration of acetylene---M ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034 PART-A
... 11. Give an example for α, β, γ and δ-elimination reaction. 12. State and explain the Hammond postulate to the bromination of n-propane. 13. How will you determine the reaction mechanism of hydrolysis of an ester using isotoping labeling method? 14. Write and explain the Steven’s rearrangement. 15. ...
... 11. Give an example for α, β, γ and δ-elimination reaction. 12. State and explain the Hammond postulate to the bromination of n-propane. 13. How will you determine the reaction mechanism of hydrolysis of an ester using isotoping labeling method? 14. Write and explain the Steven’s rearrangement. 15. ...
Chem 400 Review Chem 350 JJ.S17
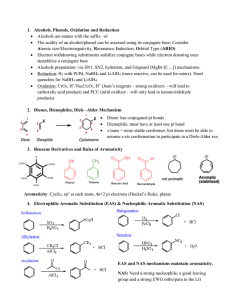
... Atomic size/Electronegativity, Resonance, Induction, Orbital Type (ARIO) Electron withdrawing substituents stabilize conjugate bases while electron donating ones destabilize a conjugate base Alcohols preparation: via SN1, SN2, hydration, and Grignard (MgBr-[C…]) mechanisms Reduction: H2 with P ...
... Atomic size/Electronegativity, Resonance, Induction, Orbital Type (ARIO) Electron withdrawing substituents stabilize conjugate bases while electron donating ones destabilize a conjugate base Alcohols preparation: via SN1, SN2, hydration, and Grignard (MgBr-[C…]) mechanisms Reduction: H2 with P ...
Hein and Arena
... • The boiling points of ethers, thiols, sulfides, and disulfides are much lower than those of alcohols with similar molecular weights, because none of these compounds are able to form hydrogen bonds to like molecules. • Ether molecules are slightly polar as a consequence of the C-O-C linkage, but t ...
... • The boiling points of ethers, thiols, sulfides, and disulfides are much lower than those of alcohols with similar molecular weights, because none of these compounds are able to form hydrogen bonds to like molecules. • Ether molecules are slightly polar as a consequence of the C-O-C linkage, but t ...
슬라이드 1
... Subsequent studies have found improved ligands, including tri-2-furylphsophine and triphenylarsine. Aryl-aryl coupling rates are increased by the presence of ...
... Subsequent studies have found improved ligands, including tri-2-furylphsophine and triphenylarsine. Aryl-aryl coupling rates are increased by the presence of ...
Chem 231 Exam #1 Study Guide
... Be able to write conjugate acid and base pairs Be able to write curved arrow notation for an acid-base reaction Know the relationship of Ka and pKa Be able to predict the outcome of an acid-base reaction Know the bond strength effect and the electronegativity effect for acids and bases Know how enth ...
... Be able to write conjugate acid and base pairs Be able to write curved arrow notation for an acid-base reaction Know the relationship of Ka and pKa Be able to predict the outcome of an acid-base reaction Know the bond strength effect and the electronegativity effect for acids and bases Know how enth ...
CrO3/Al2O3: Rapid oxidation of alcohols to carbonyl compounds in
... Oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols to the corresponding carbonyl compounds has attracted considerable attention during recent years1,2. The use of high oxidation state transition metals3 such as chromium (VI) reagents for alcohol oxidation is well known. Since the chromium residues are envi ...
... Oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols to the corresponding carbonyl compounds has attracted considerable attention during recent years1,2. The use of high oxidation state transition metals3 such as chromium (VI) reagents for alcohol oxidation is well known. Since the chromium residues are envi ...
Experiment 15: Reduction and Oxidation of Organic Compounds
... is the more powerful of the two, capable of reducing aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters and amides, NaBH4 is easier to handle and more selective, reducing only aldehydes and ketones. Sodium borohydride can be utilized under non-anhydrous conditions and in alcoholic solutions, in contrast t ...
... is the more powerful of the two, capable of reducing aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters and amides, NaBH4 is easier to handle and more selective, reducing only aldehydes and ketones. Sodium borohydride can be utilized under non-anhydrous conditions and in alcoholic solutions, in contrast t ...
Problem Set 2
... Peroxyacylnitrate is one of the components of smog. It is a compound of C, H, N, and O. It has the following percent composition by mass: 19.8% C, 2.59% H, 11.6% N, and 66.0% O. a. Determine the simplest formula of the compound. b. What is the molecular formula of the compound if its molar mass is a ...
... Peroxyacylnitrate is one of the components of smog. It is a compound of C, H, N, and O. It has the following percent composition by mass: 19.8% C, 2.59% H, 11.6% N, and 66.0% O. a. Determine the simplest formula of the compound. b. What is the molecular formula of the compound if its molar mass is a ...
alcohols-II-12-ques
... RCH2OH + PDC [(C5H5NH+)2 Cr2O72–] A) The alcohol is oxidized to an acid, and the Cr(VI) is reduced. B) The alcohol is oxidized to an aldehyde, and the Cr(VI) is reduced. C) The alcohol is reduced to an aldehyde, and the Cr(III) is oxidized. D) The alcohol is oxidized to a ketone, and the Cr(VI) is ...
... RCH2OH + PDC [(C5H5NH+)2 Cr2O72–] A) The alcohol is oxidized to an acid, and the Cr(VI) is reduced. B) The alcohol is oxidized to an aldehyde, and the Cr(VI) is reduced. C) The alcohol is reduced to an aldehyde, and the Cr(III) is oxidized. D) The alcohol is oxidized to a ketone, and the Cr(VI) is ...
Chemistry: Selected Topics
... The aim of the course is to acquaint the students with the properties and synthesis of some important types of chemical compounds. In the first part of the course, the general concepts of chemical reaction kinetics are presented with emphasis on the relation between reaction rate and reaction mechan ...
... The aim of the course is to acquaint the students with the properties and synthesis of some important types of chemical compounds. In the first part of the course, the general concepts of chemical reaction kinetics are presented with emphasis on the relation between reaction rate and reaction mechan ...
Chem 30CL-Lecture 15..
... • The lone pair on the carbon forms a s-bond with a suitable d-orbital of the metal (i.e., d(x2-y2)) • The metal can form a p-backbond via the p*-orbital of the CO ligand (i.e., d(xy)) • Electron-rich metals i.e., late transition metals in low oxidation states are more likely to donate electrons for ...
... • The lone pair on the carbon forms a s-bond with a suitable d-orbital of the metal (i.e., d(x2-y2)) • The metal can form a p-backbond via the p*-orbital of the CO ligand (i.e., d(xy)) • Electron-rich metals i.e., late transition metals in low oxidation states are more likely to donate electrons for ...
Alkane
... {3。RX undergo elimination easily if heating under reflux with KOH(aq) in addition to substitution . It is better to warm with AgNO3(aq) + ethanol mixture.} ...
... {3。RX undergo elimination easily if heating under reflux with KOH(aq) in addition to substitution . It is better to warm with AgNO3(aq) + ethanol mixture.} ...
Exp`t 70
... Guide. DO NOT ADD DICHLOROMETHANE, but instead analyze the pure liquid as a “neat” sample on the gas chromatograph. (Check the GC compendium in 206 W for GC conditions). In analyzing your results, consider that the carbocation can lose any of 6 primary hydrogen atoms, but only 2 secondary hydrogen a ...
... Guide. DO NOT ADD DICHLOROMETHANE, but instead analyze the pure liquid as a “neat” sample on the gas chromatograph. (Check the GC compendium in 206 W for GC conditions). In analyzing your results, consider that the carbocation can lose any of 6 primary hydrogen atoms, but only 2 secondary hydrogen a ...
New aniline photocage for carboxylic acids
... 2-nitrobenzylalcohols the decaging reaction is slow. Therefore, research for new PPGs is very important topic of current research in organic photochemistry. Wang et al. have recently reported an interesting example of photocage for alcohols, based on m-hydroxyaniline ethers.[5] We decided to further ...
... 2-nitrobenzylalcohols the decaging reaction is slow. Therefore, research for new PPGs is very important topic of current research in organic photochemistry. Wang et al. have recently reported an interesting example of photocage for alcohols, based on m-hydroxyaniline ethers.[5] We decided to further ...
- Wiley Online Library
... (R,R)-16 a and (R,R)-16 b. The authors found the 1,2-reduction to be slower than the hydroacylation; it did in fact not occur at lower temperature (4 8C instead of 40 8C). a-Chiral ketones such as (R)-17 a and (R)-17 c thus became accessible. The groups of Liu and Buchwald even accomplished the addi ...
... (R,R)-16 a and (R,R)-16 b. The authors found the 1,2-reduction to be slower than the hydroacylation; it did in fact not occur at lower temperature (4 8C instead of 40 8C). a-Chiral ketones such as (R)-17 a and (R)-17 c thus became accessible. The groups of Liu and Buchwald even accomplished the addi ...
packet 1, 2325 key
... Benzyl alcohol (MW = 108 g/mol) was reacted under different conditions to generate products A-C. The IRs are shown for products A-C. The value of the molecular ion peak is given along with the intensity ratio (relative to the parent peak) of the M+2 peak. Indicate the ...
... Benzyl alcohol (MW = 108 g/mol) was reacted under different conditions to generate products A-C. The IRs are shown for products A-C. The value of the molecular ion peak is given along with the intensity ratio (relative to the parent peak) of the M+2 peak. Indicate the ...
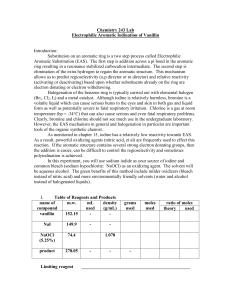
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution of Vanillin
... Aromatic Substitution (EAS). The first step is addition across a pi bond in the aromatic ring resulting in a resonance stabilized carbocation intermediate. The second step is elimination of the extra hydrogen to regain the aromatic structure. This mechanism allows us to predict regioselectivity (o,p ...
... Aromatic Substitution (EAS). The first step is addition across a pi bond in the aromatic ring resulting in a resonance stabilized carbocation intermediate. The second step is elimination of the extra hydrogen to regain the aromatic structure. This mechanism allows us to predict regioselectivity (o,p ...
Table
... AlcoholsEthers+Water Condensation reaction, eliminating H2O ; Dehydration Preparation Primary alcohols aldehydes Controlled oxidation reactions Secondary alcohols ketones Controlled oxidation reactions Pathways to other groups Aldehydes primary alcohols Addition reaction with hydrogen: hydroge ...
... AlcoholsEthers+Water Condensation reaction, eliminating H2O ; Dehydration Preparation Primary alcohols aldehydes Controlled oxidation reactions Secondary alcohols ketones Controlled oxidation reactions Pathways to other groups Aldehydes primary alcohols Addition reaction with hydrogen: hydroge ...
Syn Addition
... Alternatively Asymmetric, terminal, alkyne if you want to have strong regioselectivity then use a borane with stronger selectivity for more open site of ...
... Alternatively Asymmetric, terminal, alkyne if you want to have strong regioselectivity then use a borane with stronger selectivity for more open site of ...
M.Sc. 2015
... (i) chloronium ion can attack the π-electron cloud of benzene to form π-complex. (ii) the π-complex is then converted into σ-complex. (iii) the σ-complex thus formed is a carbonium ion which is stabilized by resonance. (i), (ii) and (iii) are false (i), (ii) and (iii) are true (i), (ii) are true and ...
... (i) chloronium ion can attack the π-electron cloud of benzene to form π-complex. (ii) the π-complex is then converted into σ-complex. (iii) the σ-complex thus formed is a carbonium ion which is stabilized by resonance. (i), (ii) and (iii) are false (i), (ii) and (iii) are true (i), (ii) are true and ...
Slides
... Asymmetric synthesis of L-dopa, drug for treating Parkinson’s disease Syn Addition of Hydrogen: Synthesis of cis- Alkenes è The P-2 catalyst nickel boride results in syn addition of one equivalent of hydrogen to a triple bond è An internal alkyne will yield a cis double bond ...
... Asymmetric synthesis of L-dopa, drug for treating Parkinson’s disease Syn Addition of Hydrogen: Synthesis of cis- Alkenes è The P-2 catalyst nickel boride results in syn addition of one equivalent of hydrogen to a triple bond è An internal alkyne will yield a cis double bond ...
Exam 2 review sheet
... preparation of aldehydes and ketones: (a) oxidation of alcohols; (b) F-C acylation; (c) ozonolysis (review); (d) reduction of esters or acyl chlorides with specialized hydride reagents LiAlH(OtBu)3 or DIBAL-H to form aldehydes five nucleophilic reactions of aldehyde/ketone: relative reactivity of al ...
... preparation of aldehydes and ketones: (a) oxidation of alcohols; (b) F-C acylation; (c) ozonolysis (review); (d) reduction of esters or acyl chlorides with specialized hydride reagents LiAlH(OtBu)3 or DIBAL-H to form aldehydes five nucleophilic reactions of aldehyde/ketone: relative reactivity of al ...
Wolff–Kishner reduction

The Wolff–Kishner reduction is a reaction used in organic chemistry to convert carbonyl functionalities into methylene groups. In the context of complex molecule synthesis, it is most frequently employed to remove a carbonyl group after it has served its synthetic purpose of activating an intermediate in a preceding step. As such, there is no obvious retron for this reaction. Originally reported by Nikolai Kischner in 1911 and Ludwig Wolff in 1912, it has been applied to the total synthesis of scopadulcic acid B, aspidospermidine and dysidiolide.In general, the reaction mechanism first involves the in situ generation of a hydrazone by condensation of hydrazine with the ketone or aldehyde substrate. Sometimes it is however advantageous to use a pre-formed hydrazone as substrate (see modifications). The hydrazone is deprotonated by alkoxide base followed by a concerted, rate-determining step in which a diimide anion is formed. Collapse of this alkyldiimde with loss of N2 leads to formation of an alkylanion which can be protonated by solvent to give the desired product.Because the Wolff–Kishner reduction requires highly basic conditions, it is unsuitable for base-sensitive substrates. However, this method can be superior over the related Clemmensen reduction for acid-sensitive compounds such as pyrroles and for high-molecular weight compounds.