Catalytic Hydrogenation of Alkenes: Relative Stability of
... The protonated hydroxy forms an alkyloxonium ion providing a good leaving group: water. Loss of water forms a secondary or tertiary carbocation. Deprotonation forms the alkene. Carbocation side reactions (hydrogen shifts, alkyl shifts, etc.) are possible. ...
... The protonated hydroxy forms an alkyloxonium ion providing a good leaving group: water. Loss of water forms a secondary or tertiary carbocation. Deprotonation forms the alkene. Carbocation side reactions (hydrogen shifts, alkyl shifts, etc.) are possible. ...
Chapter 13 - WebAssign
... Draw the Lewis structure of formaldehyde. Draw the resonance form of formaldehyde that accounts for its reactivity c) Use arrows to suggest how the HCl might attack formaldehyde. d) Draw the Lewis structure of the reaction product. a) ...
... Draw the Lewis structure of formaldehyde. Draw the resonance form of formaldehyde that accounts for its reactivity c) Use arrows to suggest how the HCl might attack formaldehyde. d) Draw the Lewis structure of the reaction product. a) ...
W19 Aldehydes ketones I
... physical properties of aldehydes and ketones reaction scheme of aldehydes and ketones nucleophilic addition AN to C=O group: ...
... physical properties of aldehydes and ketones reaction scheme of aldehydes and ketones nucleophilic addition AN to C=O group: ...
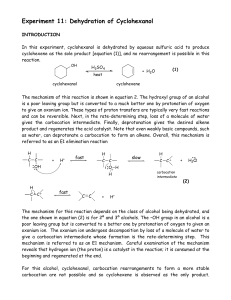
Dehydration of Cyclohexanol
... carbocations derived from certain 2°alcohols may undergo rearrangement to form more stable carbocations. This can result in the formation of rearranged isomeric alkenes. Both 2° and 3° alcohols primarily undergo the E1 reaction under these conditions, whereas for 1° alcohols and methyl alcohol, symm ...
... carbocations derived from certain 2°alcohols may undergo rearrangement to form more stable carbocations. This can result in the formation of rearranged isomeric alkenes. Both 2° and 3° alcohols primarily undergo the E1 reaction under these conditions, whereas for 1° alcohols and methyl alcohol, symm ...
Synthesis of 1
... 1.11) to remove traces of acid, separate, and be careful to save the proper layer. In experiments of this type, it is good practice to save all layers until the product is in hand. • Dry the cloudy 1-bromobutane by adding anhydrous calcium chloride pellets and mixing until the liquid clears and the ...
... 1.11) to remove traces of acid, separate, and be careful to save the proper layer. In experiments of this type, it is good practice to save all layers until the product is in hand. • Dry the cloudy 1-bromobutane by adding anhydrous calcium chloride pellets and mixing until the liquid clears and the ...
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
... Above are two sets of resonance structures. In each set, the right-hand structure reflects the positive polarization of the carbon atom which undergoes attack by nucleophiles. In the protonated structures, both are charged and the right hand structure has an electron deficient carbon atom. In the no ...
... Above are two sets of resonance structures. In each set, the right-hand structure reflects the positive polarization of the carbon atom which undergoes attack by nucleophiles. In the protonated structures, both are charged and the right hand structure has an electron deficient carbon atom. In the no ...
Document
... A reaction in which an ester is formed from an alcohol and a carboxylic acid. Gives an orange brown precipitate with an aldehyde but not a ketone. The introduction of an acyl group, RCO-, into a benzene ring. Named after it’s discoverers. The introduction of an alkyl group into a benzene ring. Named ...
... A reaction in which an ester is formed from an alcohol and a carboxylic acid. Gives an orange brown precipitate with an aldehyde but not a ketone. The introduction of an acyl group, RCO-, into a benzene ring. Named after it’s discoverers. The introduction of an alkyl group into a benzene ring. Named ...
2010-09-16 Alcohols
... The simple way to think of alcohols is that there is a water molecule where the hydrogen at one of the termini is replaced by a carbon chain. The alcohol present in beverages is ethanol, which is the mildest depressant and narcotic poison of all alcohols. Other alcohols magnify this effect and are ...
... The simple way to think of alcohols is that there is a water molecule where the hydrogen at one of the termini is replaced by a carbon chain. The alcohol present in beverages is ethanol, which is the mildest depressant and narcotic poison of all alcohols. Other alcohols magnify this effect and are ...
Reduction of Camphor to Borneol
... showing the expected stereochemistry of the products. Label the products as having been formed from exo approach or endo approach. 2. How might the geometry of the product change (OH in an endo or exo position?) if all the methyl groups of camphor were replaced with H? 3. The reduction mechanism is ...
... showing the expected stereochemistry of the products. Label the products as having been formed from exo approach or endo approach. 2. How might the geometry of the product change (OH in an endo or exo position?) if all the methyl groups of camphor were replaced with H? 3. The reduction mechanism is ...
Document
... • H2/Transition Metal Catalyst (z.b. CuO•CuCr2O4) • NaBH4 and LiAlH4 are Hydride Transfer Agents • Hydride (H¯) Acts as a Nucleophile • Carbonyls Have Varying Degrees of Ease of Reduction: O ...
... • H2/Transition Metal Catalyst (z.b. CuO•CuCr2O4) • NaBH4 and LiAlH4 are Hydride Transfer Agents • Hydride (H¯) Acts as a Nucleophile • Carbonyls Have Varying Degrees of Ease of Reduction: O ...
Exam 2
... Acidity of the alpha Hydrogens of carbonyls. 18.1 Understand (Ka values) of table 18.1. Know when an acid will be completely deprotonated by hydroxide ion or LDA. Enol Tautomers 18.2. Be able to draw an enol of an aldehyde or ketone. ...
... Acidity of the alpha Hydrogens of carbonyls. 18.1 Understand (Ka values) of table 18.1. Know when an acid will be completely deprotonated by hydroxide ion or LDA. Enol Tautomers 18.2. Be able to draw an enol of an aldehyde or ketone. ...
Тест за III категорија, Општински натпревар по хемија, 14 март
... C. Weakly basic. D. Strongly basic. E. Phenol does not dissolve in water. 25. What is the hybridization of the carbon atom in the aldehyde functional group? A. sp ...
... C. Weakly basic. D. Strongly basic. E. Phenol does not dissolve in water. 25. What is the hybridization of the carbon atom in the aldehyde functional group? A. sp ...
Lecture #
... Chemistry 335 List of topics/study guide. This is a list of topics we will be covering to help you in preparation for exams. Topics from Clayden are indicated clearly by chapter and page numbers where necessary. Topics NOT from Clayden are listed in italics. PLTL topics are in CAPS. This document wi ...
... Chemistry 335 List of topics/study guide. This is a list of topics we will be covering to help you in preparation for exams. Topics from Clayden are indicated clearly by chapter and page numbers where necessary. Topics NOT from Clayden are listed in italics. PLTL topics are in CAPS. This document wi ...
Organic Chemistry III Laboratory
... either side of the carbonyl when it is on the enzyme. As a result, the selectivity of the reaction may be altered. Borohydride reductions of 4-tert-butylcyclohexanone should give the trans diequatorial product as the major product. If the axial face of 4-tert-butylcyclohexanone is not accessible to ...
... either side of the carbonyl when it is on the enzyme. As a result, the selectivity of the reaction may be altered. Borohydride reductions of 4-tert-butylcyclohexanone should give the trans diequatorial product as the major product. If the axial face of 4-tert-butylcyclohexanone is not accessible to ...
info
... i. NaBH4 will reduce an aldehyde, ketone, or acid chloride to the corresponding alcohol. It will not reduce an acid or an ester. ii. LiAlH4 will reduce an aldehyde, ketone, acid, or ester to the corresponding alcohol. iii. LiAlH(OtBu)3 will reduce an acid chloride to an aldehyde. iv. DIBAL will ...
... i. NaBH4 will reduce an aldehyde, ketone, or acid chloride to the corresponding alcohol. It will not reduce an acid or an ester. ii. LiAlH4 will reduce an aldehyde, ketone, acid, or ester to the corresponding alcohol. iii. LiAlH(OtBu)3 will reduce an acid chloride to an aldehyde. iv. DIBAL will ...
Reexamination of Aluminum Hydride as a Stereoselective Reducing
... the reduction of 2-methylcyclohexanone in THF at 0o yields a mixture of cis- and trans-2-methylcyclohexanol in the ratio of 26 : 74. On the contrary, the reduction of bicyclic ketones such as norcamphor and camphor at 0o afforded the thermodynamically less stable alcohols predominantly (Table 1). Th ...
... the reduction of 2-methylcyclohexanone in THF at 0o yields a mixture of cis- and trans-2-methylcyclohexanol in the ratio of 26 : 74. On the contrary, the reduction of bicyclic ketones such as norcamphor and camphor at 0o afforded the thermodynamically less stable alcohols predominantly (Table 1). Th ...
CHEM 2412
... Nomenclature and drawing of alcohols (including hydroxyalkyl groups, diols, triols); Common names of alcohol of 4 carbons or less; Primary, secondary, tertiary alcohols; Physical properties of alcohols; Phenol (very briefly); Absolute alcohol; Denatured alcohol; Acidity of alcohols and phenols; Form ...
... Nomenclature and drawing of alcohols (including hydroxyalkyl groups, diols, triols); Common names of alcohol of 4 carbons or less; Primary, secondary, tertiary alcohols; Physical properties of alcohols; Phenol (very briefly); Absolute alcohol; Denatured alcohol; Acidity of alcohols and phenols; Form ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 27. Bromination of an organic compound(A) of formula C6H12 yields C6H12Br2. On reduction of the compound gives 2-methylpentane. On oxidation it yields a mixture of acetic acid and isobutyric acids. Assign the structural formula to the organic compound. Express the above reaction by chemical equation ...
... 27. Bromination of an organic compound(A) of formula C6H12 yields C6H12Br2. On reduction of the compound gives 2-methylpentane. On oxidation it yields a mixture of acetic acid and isobutyric acids. Assign the structural formula to the organic compound. Express the above reaction by chemical equation ...
Chapter 20. Aldehydes and Ketones
... chemical yield would be high, our dedicated student prepared one mole of the Grignard reagent, added two moles of benzaldehyde, and, after working up the reaction, was delighted to obtain a good yield of a crystalline product. Unfortunately, the product that had been formed was benzophenone! On clos ...
... chemical yield would be high, our dedicated student prepared one mole of the Grignard reagent, added two moles of benzaldehyde, and, after working up the reaction, was delighted to obtain a good yield of a crystalline product. Unfortunately, the product that had been formed was benzophenone! On clos ...
TV RajanBabu Chemistry, 730 Autumn 1997
... Generation and use of alkyl lithiums, lithium amides Structures of alkyl lithiums, amides Carbanions stabilized by other functional groups Malontes, acetoacetates, nitrocompounds etc. ...
... Generation and use of alkyl lithiums, lithium amides Structures of alkyl lithiums, amides Carbanions stabilized by other functional groups Malontes, acetoacetates, nitrocompounds etc. ...
Summer Scholar Report
... more easily measured. Unlike methyl lithium solutions whose concentrations are variable and decrease over time, sodium hydride is stable as long as it is desiccated. Use of sodium hydride also obviates the presence of nucleophilic ions whereas methyl lithium solutions contain halide from manufacturi ...
... more easily measured. Unlike methyl lithium solutions whose concentrations are variable and decrease over time, sodium hydride is stable as long as it is desiccated. Use of sodium hydride also obviates the presence of nucleophilic ions whereas methyl lithium solutions contain halide from manufacturi ...
Chapter 7
... Rearrangements • Only the carbocation rearranges, so dehydration of primary alcohols can not have rearrangements since they are E2 and not carbocation is formed! • However, as we will see in Ch 8, the alkene product can react with the acid by using its pi electrons to abstract a proton from an acid ...
... Rearrangements • Only the carbocation rearranges, so dehydration of primary alcohols can not have rearrangements since they are E2 and not carbocation is formed! • However, as we will see in Ch 8, the alkene product can react with the acid by using its pi electrons to abstract a proton from an acid ...
Eliminations
... SN1/SN2/E2/E1 summary/comparison: (1) Primary alkyl halides will prefer SN2 unless a strong hindered base is used in which case E2 will be favored. For example, t-‐butoxide is a sterically hindered base. ...
... SN1/SN2/E2/E1 summary/comparison: (1) Primary alkyl halides will prefer SN2 unless a strong hindered base is used in which case E2 will be favored. For example, t-‐butoxide is a sterically hindered base. ...
Wolff–Kishner reduction

The Wolff–Kishner reduction is a reaction used in organic chemistry to convert carbonyl functionalities into methylene groups. In the context of complex molecule synthesis, it is most frequently employed to remove a carbonyl group after it has served its synthetic purpose of activating an intermediate in a preceding step. As such, there is no obvious retron for this reaction. Originally reported by Nikolai Kischner in 1911 and Ludwig Wolff in 1912, it has been applied to the total synthesis of scopadulcic acid B, aspidospermidine and dysidiolide.In general, the reaction mechanism first involves the in situ generation of a hydrazone by condensation of hydrazine with the ketone or aldehyde substrate. Sometimes it is however advantageous to use a pre-formed hydrazone as substrate (see modifications). The hydrazone is deprotonated by alkoxide base followed by a concerted, rate-determining step in which a diimide anion is formed. Collapse of this alkyldiimde with loss of N2 leads to formation of an alkylanion which can be protonated by solvent to give the desired product.Because the Wolff–Kishner reduction requires highly basic conditions, it is unsuitable for base-sensitive substrates. However, this method can be superior over the related Clemmensen reduction for acid-sensitive compounds such as pyrroles and for high-molecular weight compounds.