Tin-Catalyzed Esterification and Transesterification Reactions: A
... same rate, and the same can be stated about propyl and butyl alcohol, although this last pair has reacted more slowly. However, at longer reaction times, the reactivity of two first alcohols undergoes a higher split. After 12 hours reaction, the conversion reached in esterification of both methyl an ...
... same rate, and the same can be stated about propyl and butyl alcohol, although this last pair has reacted more slowly. However, at longer reaction times, the reactivity of two first alcohols undergoes a higher split. After 12 hours reaction, the conversion reached in esterification of both methyl an ...
HIGHLY SELECTIVE RHODIUM–CATALYZED C–H BORYLATIONS IN
... synthesis of new carbon–carbon bonds has increased the demand for efficient routes to organoboron starting materials. C–H borylation (activation) has provided an interesting approach to alleviate the requirement for prefunctionalized molecules such as aryl halides to obtain these desired organoboron ...
... synthesis of new carbon–carbon bonds has increased the demand for efficient routes to organoboron starting materials. C–H borylation (activation) has provided an interesting approach to alleviate the requirement for prefunctionalized molecules such as aryl halides to obtain these desired organoboron ...
Exam #3
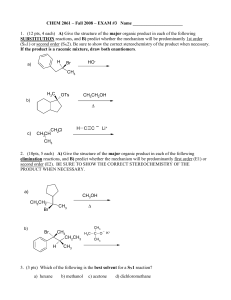
... A) Using mechanistic reasoning, EXPLAIN WHY menthyl chloride gives only 2-menthene as its E2 elimination product. B) Explain why 3-menthene (rather than 2- menthene) is the major product in the E2 elimination of neomenthyl chloride. H H3C ...
... A) Using mechanistic reasoning, EXPLAIN WHY menthyl chloride gives only 2-menthene as its E2 elimination product. B) Explain why 3-menthene (rather than 2- menthene) is the major product in the E2 elimination of neomenthyl chloride. H H3C ...
Hydrogenation, Transfer Hydrogenat- ion and Hydrogen Transfer Reactions
... The word “chirality” is derived from the Greek, χειρ (kheir) which means “hand”. Our hands cannot be superimposed onto each other but are mirror images of each other. Chirality can be traced back to the beginning of the 1900s, when the phrase was first introduced by Lord Kelvin,3 whose original stat ...
... The word “chirality” is derived from the Greek, χειρ (kheir) which means “hand”. Our hands cannot be superimposed onto each other but are mirror images of each other. Chirality can be traced back to the beginning of the 1900s, when the phrase was first introduced by Lord Kelvin,3 whose original stat ...
A Simple and Advantageous Protocol for the Oxidation of Alcohols
... simple filtration. Reactions in several other solvents provided higher yields and shorter reaction times, but required chromatographic purification. The oxidation proceeds well with as few as 1.1 equiv of IBX, but an increased reaction rate is observed with excess oxidant. As a matter of convenience ...
... simple filtration. Reactions in several other solvents provided higher yields and shorter reaction times, but required chromatographic purification. The oxidation proceeds well with as few as 1.1 equiv of IBX, but an increased reaction rate is observed with excess oxidant. As a matter of convenience ...
BSA - Sigma
... glycol phases). Silicones are the most useful phases for TMS derivatives – they combine inertness and stability with excellent separating characteristics for these derivatives. Nonpolar silicone phases include SPB™-1 and SPB-5. Normal hydrocarbons (carbonhydrogen analytes with single bonds) are sepa ...
... glycol phases). Silicones are the most useful phases for TMS derivatives – they combine inertness and stability with excellent separating characteristics for these derivatives. Nonpolar silicone phases include SPB™-1 and SPB-5. Normal hydrocarbons (carbonhydrogen analytes with single bonds) are sepa ...
Synthesis and Structure of Alcohols
... (1) Name the longest carbon chain bearing the –OH group. Drop the last –e from the alkane name and add –ol to obtain the root name. (2) Number the longest chain starting at the end nearest the –OH group, and designate a number for the –OH group. (Hydroxyl has greater priority than carbon-carbon mult ...
... (1) Name the longest carbon chain bearing the –OH group. Drop the last –e from the alkane name and add –ol to obtain the root name. (2) Number the longest chain starting at the end nearest the –OH group, and designate a number for the –OH group. (Hydroxyl has greater priority than carbon-carbon mult ...
ALCOHOLS AND ETHERS
... 3640 cm-l in the spectrum of a 10% solution of ethanol in carbon tetrachloride (Figure 15-2b). However, there is a relatively broad band around 3350 cm-l, which is characteristic of hydrogen-bonded hydroxyl groups. The shift in frequency of about 300 cm-I arises because hydrogen bonding weakens the ...
... 3640 cm-l in the spectrum of a 10% solution of ethanol in carbon tetrachloride (Figure 15-2b). However, there is a relatively broad band around 3350 cm-l, which is characteristic of hydrogen-bonded hydroxyl groups. The shift in frequency of about 300 cm-I arises because hydrogen bonding weakens the ...
10.4 Alcohols - SCIS Teachers
... carboxylic acids in a two-step process. Step 2: aldehyde → carboxylic acid Ex. Ethanal is further reduced to become ethanoic acid ...
... carboxylic acids in a two-step process. Step 2: aldehyde → carboxylic acid Ex. Ethanal is further reduced to become ethanoic acid ...
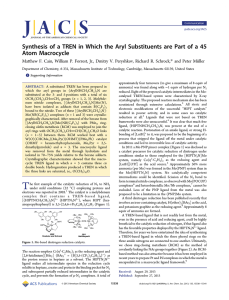
Synthesis of a TREN in Which the Aryl Substituents are... Atom Macrocycle ̈ller *
... reduced. Eight of the proposed catalytic intermediates in the Mocatalyzed TREN-based system were characterized by X-ray crystallography. The proposed reaction mechanism also has been scrutinized through extensive calculations.2 All steric and electronic modifications of the successful “HIPT catalysts ...
... reduced. Eight of the proposed catalytic intermediates in the Mocatalyzed TREN-based system were characterized by X-ray crystallography. The proposed reaction mechanism also has been scrutinized through extensive calculations.2 All steric and electronic modifications of the successful “HIPT catalysts ...
Anionic rearrangement of 2-benzyloxypyridine derivatives and a synthetic approach to aldingenin B
... [1,2]-Anionic rearrangements are important tools for altering the complexity of molecules at hand. In Part I of this dissertation, an anionic rearrangement of 2-benzyloxypyridine is described. Pyridine-directed metallation of the benzylic carbon leads to 1,2-migration of pyridine via a postulated as ...
... [1,2]-Anionic rearrangements are important tools for altering the complexity of molecules at hand. In Part I of this dissertation, an anionic rearrangement of 2-benzyloxypyridine is described. Pyridine-directed metallation of the benzylic carbon leads to 1,2-migration of pyridine via a postulated as ...
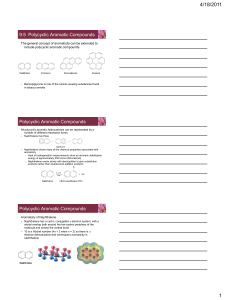
Aromatic Compounds
... Rings: The Friedel-Crafts Reaction Alkylation • The introduction of an alkyl group onto the benzene ring • Called the Friedel-Crafts reaction after its discoverers • Among the most useful electrophilic aromatic substitution ...
... Rings: The Friedel-Crafts Reaction Alkylation • The introduction of an alkyl group onto the benzene ring • Called the Friedel-Crafts reaction after its discoverers • Among the most useful electrophilic aromatic substitution ...
Synthesis of DiamidoPyrrolyl Molybdenum Complexes Relevant to Reduction DOI: 10.1021/ic100856n
... stepwise addition of protons and electrons. ...
... stepwise addition of protons and electrons. ...
Ch. 10 Notes with Answers
... • 3º, 2º, and 1º alkyl halides all work well • Aryl and Vinyl halides as well as alkyl halides work well • RCl, RBr, and RI all work well • For class, we will normally use bromides, due to synthetic accessibility 6. View as carbanions: RMgBr = R Super Strong Bases and Nucleophiles ...
... • 3º, 2º, and 1º alkyl halides all work well • Aryl and Vinyl halides as well as alkyl halides work well • RCl, RBr, and RI all work well • For class, we will normally use bromides, due to synthetic accessibility 6. View as carbanions: RMgBr = R Super Strong Bases and Nucleophiles ...
Amide bond formation and peptide coupling
... thermodynamics as the equilibrium shown in Scheme 1 and lies on the side of hydrolysis rather than synthesis.3 The direct condensation of the salt can be achieved at high temperature (160–180 8C),4 which is usually quite incompatible with the presence of other functionalities (see also Section 2.6.3 ...
... thermodynamics as the equilibrium shown in Scheme 1 and lies on the side of hydrolysis rather than synthesis.3 The direct condensation of the salt can be achieved at high temperature (160–180 8C),4 which is usually quite incompatible with the presence of other functionalities (see also Section 2.6.3 ...
Melt Modification of Poly(styrene-co-maleic anhydride)
... esterification to the product side by removing the in situ generated carboxylic acid from the system by a subsequent reaction. For example, 1,3-oxazolines are well known to afford quantitative conversion of carboxylic acids both in melt and in solution processes.16 Because of their high reactivity, ...
... esterification to the product side by removing the in situ generated carboxylic acid from the system by a subsequent reaction. For example, 1,3-oxazolines are well known to afford quantitative conversion of carboxylic acids both in melt and in solution processes.16 Because of their high reactivity, ...
Chapter 24. Amines
... Amines are stronger bases than alcohols, ethers, or water Amines establish an equilibrium with water in which the amine becomes protonated and hydroxide is produced ...
... Amines are stronger bases than alcohols, ethers, or water Amines establish an equilibrium with water in which the amine becomes protonated and hydroxide is produced ...
the suzuki-miyaura reaction and boron reagents – mechanism
... Transmetalate with a variety of metal compounds under exceptionally mild reaction conditions, especially versatile with palladium(II) complexes. ...
... Transmetalate with a variety of metal compounds under exceptionally mild reaction conditions, especially versatile with palladium(II) complexes. ...
Ethers and Epoxides
... How would you prepare the following compounds using a Williamson synthesis? • Methyl propyl ether ...
... How would you prepare the following compounds using a Williamson synthesis? • Methyl propyl ether ...
Visible light photooxidation of nitrate: the dawn of
... pathways in the initial vinyl radical adduct 5 (Scheme 2). While diketone 3 results from a 5-endo cyclization, followed by loss ...
... pathways in the initial vinyl radical adduct 5 (Scheme 2). While diketone 3 results from a 5-endo cyclization, followed by loss ...
research reviews Discovering new arene-catalyzed lithiations
... presence of isopropanol, to yield a secondary amine 45; this reaction involves in situ formation of the corresponding imine followed by its hydrogen-transfer reduction [33]. The second consists of the alkylation of a methyl ketone 46 with a primary alcohol 47 to yield ketone 48 [30,31]; this is an i ...
... presence of isopropanol, to yield a secondary amine 45; this reaction involves in situ formation of the corresponding imine followed by its hydrogen-transfer reduction [33]. The second consists of the alkylation of a methyl ketone 46 with a primary alcohol 47 to yield ketone 48 [30,31]; this is an i ...
Name Reactions in Heterocyclic Chemistry-II
... followed by Wieland (1922), Meerwein (1927), Colonge (1939), and Dilthey (1938). During the usual work-up involving quenching the reaction mixture by adding ice–water, any diacylation products which are water-soluble salts remained undetected and were thrown away, although in some cases they were pr ...
... followed by Wieland (1922), Meerwein (1927), Colonge (1939), and Dilthey (1938). During the usual work-up involving quenching the reaction mixture by adding ice–water, any diacylation products which are water-soluble salts remained undetected and were thrown away, although in some cases they were pr ...
DISTINGUISH TESTS
... Halo alkanes and Halo Arenes find wide applications in industry as well as in day-to-day life. They are used as solvents for relatively non-polar compounds and as starting materials for the synthesis of wide range of organic compounds. Chlorine containing antibiotic, Chloramphenicol, produced by s ...
... Halo alkanes and Halo Arenes find wide applications in industry as well as in day-to-day life. They are used as solvents for relatively non-polar compounds and as starting materials for the synthesis of wide range of organic compounds. Chlorine containing antibiotic, Chloramphenicol, produced by s ...
Wolff–Kishner reduction

The Wolff–Kishner reduction is a reaction used in organic chemistry to convert carbonyl functionalities into methylene groups. In the context of complex molecule synthesis, it is most frequently employed to remove a carbonyl group after it has served its synthetic purpose of activating an intermediate in a preceding step. As such, there is no obvious retron for this reaction. Originally reported by Nikolai Kischner in 1911 and Ludwig Wolff in 1912, it has been applied to the total synthesis of scopadulcic acid B, aspidospermidine and dysidiolide.In general, the reaction mechanism first involves the in situ generation of a hydrazone by condensation of hydrazine with the ketone or aldehyde substrate. Sometimes it is however advantageous to use a pre-formed hydrazone as substrate (see modifications). The hydrazone is deprotonated by alkoxide base followed by a concerted, rate-determining step in which a diimide anion is formed. Collapse of this alkyldiimde with loss of N2 leads to formation of an alkylanion which can be protonated by solvent to give the desired product.Because the Wolff–Kishner reduction requires highly basic conditions, it is unsuitable for base-sensitive substrates. However, this method can be superior over the related Clemmensen reduction for acid-sensitive compounds such as pyrroles and for high-molecular weight compounds.