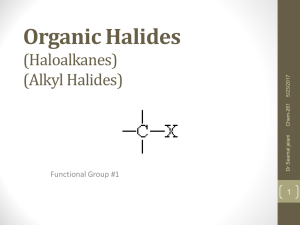H - CashmereChemistry
... Oxidation of Alcohols Primary alcohols can be oxidised to form carboxylic acids. For example when ethanol is oxidised by an acidified solution of potassium dichromate it is converted to ethanoic acid, CH3COOH, a carboxylic acid. The equation for the oxidation of the primary alcohol ethanol is ...
... Oxidation of Alcohols Primary alcohols can be oxidised to form carboxylic acids. For example when ethanol is oxidised by an acidified solution of potassium dichromate it is converted to ethanoic acid, CH3COOH, a carboxylic acid. The equation for the oxidation of the primary alcohol ethanol is ...
Elimination Reactions
... Geometry of E2 Elimination Like the SN2 substitution (which requires backside attack), the E2 elimination reaction has a geometric preference for an anti-coplanar orientation of the H-C-C-X bonds. In some cases, this may result in a stereospecific reaction, where one stereoisomer of the halide resu ...
... Geometry of E2 Elimination Like the SN2 substitution (which requires backside attack), the E2 elimination reaction has a geometric preference for an anti-coplanar orientation of the H-C-C-X bonds. In some cases, this may result in a stereospecific reaction, where one stereoisomer of the halide resu ...
A Straightforward Route to Enantiopure Pyrrolizidines and
... Our next aim was to gain access to trichloromethanesulfonates 11. Such esters seemed to be highly attractive electrophiles in SN2-type reactions possessing the properties mentioned above: the three chlorine atoms should, on the one hand, strongly activate due to their powerful electron-withdrawing a ...
... Our next aim was to gain access to trichloromethanesulfonates 11. Such esters seemed to be highly attractive electrophiles in SN2-type reactions possessing the properties mentioned above: the three chlorine atoms should, on the one hand, strongly activate due to their powerful electron-withdrawing a ...
CHEMISTRY 1000
... We’ve already seen one reaction which organic chemists would consider to be a reduction reaction – the nucleophilic addition of hydrogen to a carbonyl (using NaBH4 or LiAlH4 as the source of nucleophilic hydrogen). This was a chemoselective reaction – in other words, the reducing agent only reduced ...
... We’ve already seen one reaction which organic chemists would consider to be a reduction reaction – the nucleophilic addition of hydrogen to a carbonyl (using NaBH4 or LiAlH4 as the source of nucleophilic hydrogen). This was a chemoselective reaction – in other words, the reducing agent only reduced ...
fference: mechanistic How phenyl makes a di insights into the ruthenium( )-catalysed
... in activity. This result was intriguing, and stimulated us to investigate the reaction in more detail (vide infra). The reaction conditions that were employed initially are already highly effective, and therefore further optimisation would be of little use. Instead, the use of milder conditions and r ...
... in activity. This result was intriguing, and stimulated us to investigate the reaction in more detail (vide infra). The reaction conditions that were employed initially are already highly effective, and therefore further optimisation would be of little use. Instead, the use of milder conditions and r ...
Demonstrate skill in organic chemistry techniques.
... Analyze and examine the structure, properties, and reactions of carboxylic acids. Learning Objectives Draw and name carboxylic acids and dicarboxylic acids; describe trends in acidity and physical properties and explain variations in their acidity. Predict products and propose mechanisms for reactio ...
... Analyze and examine the structure, properties, and reactions of carboxylic acids. Learning Objectives Draw and name carboxylic acids and dicarboxylic acids; describe trends in acidity and physical properties and explain variations in their acidity. Predict products and propose mechanisms for reactio ...
full size
... ¾Aldehydes have one hydrogen atom bonded to the carbonyl group (methanal, the simplest, has two). ¾The group is somewhat more polar than ethers, but like ethers it cannot donate a hydrogen bond to itself. Thus aldehydes are less volatile (higher boiling) than alkanes or ethers but are more volatile ...
... ¾Aldehydes have one hydrogen atom bonded to the carbonyl group (methanal, the simplest, has two). ¾The group is somewhat more polar than ethers, but like ethers it cannot donate a hydrogen bond to itself. Thus aldehydes are less volatile (higher boiling) than alkanes or ethers but are more volatile ...
Nomenclature of Carboxylic Acids 1. Parent alkane + the suffix
... Carboxylic acids can be reduced to primary alcohols with LiAlH4 or with BH3 followed by work-up with aqueous acid. In the reduction with LiAlH4, an intermediate aldehyde is formed, which is rapidly reduced to give the primary alcohol. Reduction by H2 / Pd and by NaBH4 are uneffective! Selective redu ...
... Carboxylic acids can be reduced to primary alcohols with LiAlH4 or with BH3 followed by work-up with aqueous acid. In the reduction with LiAlH4, an intermediate aldehyde is formed, which is rapidly reduced to give the primary alcohol. Reduction by H2 / Pd and by NaBH4 are uneffective! Selective redu ...
H + - uaschemistry
... • For physical evidence, include a comparison of carbon– carbon bond lengths in alkanes, alkenes and benzene, and the number of structural isomers with the formula C6H4X2. • For chemical evidence, include a comparison of the enthalpies of hydrogenation of benzene, cyclohexene, 1,3-cyclohexadiene and ...
... • For physical evidence, include a comparison of carbon– carbon bond lengths in alkanes, alkenes and benzene, and the number of structural isomers with the formula C6H4X2. • For chemical evidence, include a comparison of the enthalpies of hydrogenation of benzene, cyclohexene, 1,3-cyclohexadiene and ...
Alcohols, etc.
... CH3CH2CH2CH2OH, 7 g per 100 mL but HOCH2CH2CH2CH2OH is very soluble! (two OH groups) ...
... CH3CH2CH2CH2OH, 7 g per 100 mL but HOCH2CH2CH2CH2OH is very soluble! (two OH groups) ...
Aldehydes and ketones
... • These names are taken from Latin roots as are the first 5 carboxylic acids • Greek letters are used to indicate the position of substituents with the carbon atom adjacent or bonded to the carbonyl carbon being the a carbon ...
... • These names are taken from Latin roots as are the first 5 carboxylic acids • Greek letters are used to indicate the position of substituents with the carbon atom adjacent or bonded to the carbonyl carbon being the a carbon ...
Unit 15 Organics Day 2 Cyclic Hydrocarbons: If you remove 2
... Unit 15 Organics Day 2 Nomenclature of alcohols: 1. Name the parent compound using the longest continuous carbon chain containing the hydroxyl group. parent name = take off the "e" add "ol" (you can use diol, triol etc if more than one) 2. Number the parent chain to give the lowest possible number ...
... Unit 15 Organics Day 2 Nomenclature of alcohols: 1. Name the parent compound using the longest continuous carbon chain containing the hydroxyl group. parent name = take off the "e" add "ol" (you can use diol, triol etc if more than one) 2. Number the parent chain to give the lowest possible number ...
OCR: Chemistry – Unit 2 – Chains, Energy and
... (f) explain that CFCs: (i) were developed as aerosols, refrigerants, and in air-conditioning and non-toxicity, CFC’s are non flammable and non toxic so were appropriate for uses in fridges etc. (ii) have caused environmental damage to the ozone layer (see also 2.4.1.g); CFC’s break down in the prese ...
... (f) explain that CFCs: (i) were developed as aerosols, refrigerants, and in air-conditioning and non-toxicity, CFC’s are non flammable and non toxic so were appropriate for uses in fridges etc. (ii) have caused environmental damage to the ozone layer (see also 2.4.1.g); CFC’s break down in the prese ...
Chem 3.5 #6 Amines
... Write an equation which shows a reaction that could be used to produce CH3CH2NH2 from CH3CH2Cl. ...
... Write an equation which shows a reaction that could be used to produce CH3CH2NH2 from CH3CH2Cl. ...
Organic Halides (Haloalkanes) (Alkyl Halides)
... Prefixes for halides are inserted into the name of the structure in the exact same fashion as any alkyl group. Remember to write them in alphabetical order ...
... Prefixes for halides are inserted into the name of the structure in the exact same fashion as any alkyl group. Remember to write them in alphabetical order ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.