Chapter 21 aldehydes and ketones
... • Electron-donating groups near the carbonyl carbon stabilize the carbonyl group, decreasing the amount of the hydrate at equilibrium. • Electron-withdrawing groups near the carbonyl carbon destabilize the carbonyl group, increasing the amount of hydrate at equilibrium. • This explains why chloral f ...
... • Electron-donating groups near the carbonyl carbon stabilize the carbonyl group, decreasing the amount of the hydrate at equilibrium. • Electron-withdrawing groups near the carbonyl carbon destabilize the carbonyl group, increasing the amount of hydrate at equilibrium. • This explains why chloral f ...
1 - University of Missouri
... utilize your course textbook (pp. 764-766), if you need assistance. Please note that the frequency given below should be exact (one number), not a range. Use the frequency of the center of the band at its strongest point. Then, on the spectrum itself, mark the characteristic bands at their strongest ...
... utilize your course textbook (pp. 764-766), if you need assistance. Please note that the frequency given below should be exact (one number), not a range. Use the frequency of the center of the band at its strongest point. Then, on the spectrum itself, mark the characteristic bands at their strongest ...
Chem 30CL-Lecture 12.. - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... pathway requires two equivalents of the Grignard reagent, which becomes a problem if the precursor is available in limited quantities After the protection of the phenol function with the TMS-group only one equivalent of the Grignard reagent is required. ...
... pathway requires two equivalents of the Grignard reagent, which becomes a problem if the precursor is available in limited quantities After the protection of the phenol function with the TMS-group only one equivalent of the Grignard reagent is required. ...
notes07
... The n-alkyl radical is unstable at higher temperatures (as we shall see later), but at low temperatures, the n-alkyl radical is sufficiently stable such that it can undergo two different reaction paths: one route leads to chain branching and other leads to chain termination. 4.1.2 Termination Route. ...
... The n-alkyl radical is unstable at higher temperatures (as we shall see later), but at low temperatures, the n-alkyl radical is sufficiently stable such that it can undergo two different reaction paths: one route leads to chain branching and other leads to chain termination. 4.1.2 Termination Route. ...
Organocatalysed asymmetric Mannich reactions
... with a dr ranging from 1 : 1 to 4 : 1 (syn : anti). The analogous proline-catalysed addition of protected glycolaldehydes 29 to aromatic imines 30 afforded b-aminoa-oxyaldehydes 25 in good yields (up to 95%) and high enantioselectivity (up to 99% ee). The diastereoselectivity was generally moderate ...
... with a dr ranging from 1 : 1 to 4 : 1 (syn : anti). The analogous proline-catalysed addition of protected glycolaldehydes 29 to aromatic imines 30 afforded b-aminoa-oxyaldehydes 25 in good yields (up to 95%) and high enantioselectivity (up to 99% ee). The diastereoselectivity was generally moderate ...
Organic Chemistry Structures of Organic Compounds
... The overall reaction with Cl2 faster than Br2 If excess halogen, e.g., Cl2, more chlorination ie. CH4 → ...
... The overall reaction with Cl2 faster than Br2 If excess halogen, e.g., Cl2, more chlorination ie. CH4 → ...
16.18 Summary
... There is another oxygen-stabilized cation of m/z 87 capable of being formed by fragmentation of the molecular ion in the mass spectrum of sec-butyl ethyl ether. Suggest a reasonable structure for this ion. ...
... There is another oxygen-stabilized cation of m/z 87 capable of being formed by fragmentation of the molecular ion in the mass spectrum of sec-butyl ethyl ether. Suggest a reasonable structure for this ion. ...
Acylation of aromatic alcohols and phenols over InCl3
... Table 1. Effect of InCl3 loading on the acidity (ammonia chemisorbed at 200°C) and yield in the benzoylation of benzyl alcohol (by benzoyl chloride) over InCl3/Mont. K-10 catalyst at 50°C. InCl3 loading ...
... Table 1. Effect of InCl3 loading on the acidity (ammonia chemisorbed at 200°C) and yield in the benzoylation of benzyl alcohol (by benzoyl chloride) over InCl3/Mont. K-10 catalyst at 50°C. InCl3 loading ...
TOPIC 7. ELIMINATION REACTIONS (chapter 7 and parts of
... SYNTHETIC STRATEGIES: TWO (OR MORE) STEP SYNTHESES ...
... SYNTHETIC STRATEGIES: TWO (OR MORE) STEP SYNTHESES ...
Stockholm University
... 7), are tolerated under the applied reaction conditions. The reactions involving substituted allylacetates provide the branched products with very high regioselectivity. The diastereoselectivity of the reaction is also very high. In many cases a single diastereomer was obtained (Entries 2, 6, 7 and ...
... 7), are tolerated under the applied reaction conditions. The reactions involving substituted allylacetates provide the branched products with very high regioselectivity. The diastereoselectivity of the reaction is also very high. In many cases a single diastereomer was obtained (Entries 2, 6, 7 and ...
Chapter 21: Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives
... LG = Cl (acid chloride), R'C(=O)O (acid anhydride), or R'O (ester) ...
... LG = Cl (acid chloride), R'C(=O)O (acid anhydride), or R'O (ester) ...
Homogeneously catalysed hydrogenation of unsaturated fatty acids
... y = x + - a+bx This equation, which represents a hyperbola, allows a simple representation of a complicated chemical reaction and is of practical importance for a systematic study of catalytic processes. It was found that the course of the hydrogenation of unsaturated acids under influence of Cu- an ...
... y = x + - a+bx This equation, which represents a hyperbola, allows a simple representation of a complicated chemical reaction and is of practical importance for a systematic study of catalytic processes. It was found that the course of the hydrogenation of unsaturated acids under influence of Cu- an ...
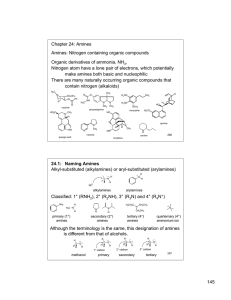
145 Chapter 24: Amines Amines: Nitrogen containing organic
... Table 24.1 (p. 899): pKa values of ammonium ions Alkyl ammonium ions, R3NH+ X-, have pKa values in the range of 10-11 (ammonium ion, H4N+ X-, has a pKa ~ 9.25) The ammonium ions of aryl amines and heterocyclic aromatic amines are considerably less basic than alkyl amines (pKa ~ 5 or less). The nitr ...
... Table 24.1 (p. 899): pKa values of ammonium ions Alkyl ammonium ions, R3NH+ X-, have pKa values in the range of 10-11 (ammonium ion, H4N+ X-, has a pKa ~ 9.25) The ammonium ions of aryl amines and heterocyclic aromatic amines are considerably less basic than alkyl amines (pKa ~ 5 or less). The nitr ...
Chapter 7: Alkene reactions
... The positive charge on the metal attracts electrons and sets a pericyclic reaction in motion; π electrons form σ bonds As the organic functional group gets oxidized, the inorganic reagent gets reduced (by products: MnO2 or OsO3) KMnO4 is cheaper but harsher (can completely oxidize C=C, see nex ...
... The positive charge on the metal attracts electrons and sets a pericyclic reaction in motion; π electrons form σ bonds As the organic functional group gets oxidized, the inorganic reagent gets reduced (by products: MnO2 or OsO3) KMnO4 is cheaper but harsher (can completely oxidize C=C, see nex ...
AddCorrections(KKH) - Spiral
... AgOTf was the first group 11 metal catalyst reported to catalyse the intramolecular addition of carboxylic acids (X = O) and alcohols (X = H2, R2) to C=C bonds.[17] In refluxing DCE, a wide range of substrates underwent excellent conversions to furnish great selectivity for the Markovnikov product. ...
... AgOTf was the first group 11 metal catalyst reported to catalyse the intramolecular addition of carboxylic acids (X = O) and alcohols (X = H2, R2) to C=C bonds.[17] In refluxing DCE, a wide range of substrates underwent excellent conversions to furnish great selectivity for the Markovnikov product. ...
ENGLISH VERSION Exam Organic Chemistry 2
... Acetylcholine acts as a transmitter substance at the transfer of nervous impulses (neurotransmitter) between nerve cells. After the transfer, the substance is quickly degraded to inactive components, a reaction that can take place at neutral pH. Acetylcholine may otherwise be degraded in as well aci ...
... Acetylcholine acts as a transmitter substance at the transfer of nervous impulses (neurotransmitter) between nerve cells. After the transfer, the substance is quickly degraded to inactive components, a reaction that can take place at neutral pH. Acetylcholine may otherwise be degraded in as well aci ...
REACTING MASSES – ACTIVITY SHEET
... ammonia with an excess of sodium chlorate. b) In the reaction, only 280 g of hydrazine was produced. Calculate the percentage yield. c) Calculate the atom economy for this way of making hydrazine. 2) Ibuprofen is a common pain killer used for symptoms such as head aches, tooth ache and period pains. ...
... ammonia with an excess of sodium chlorate. b) In the reaction, only 280 g of hydrazine was produced. Calculate the percentage yield. c) Calculate the atom economy for this way of making hydrazine. 2) Ibuprofen is a common pain killer used for symptoms such as head aches, tooth ache and period pains. ...
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 10 – Alkyl Halides II Chem 2310 I
... ◦ NaNH2 has a conjugate acid pKa of 36, while tert-butoxide has a conjugate acid pKa of 18. This makes it 1018 more basic, which is a whole different level of “strong base.” ◦ Using these much stronger bases, vinyl halides can form alkynes, and aryl halides can form benzynes. Alkynes are stable prod ...
... ◦ NaNH2 has a conjugate acid pKa of 36, while tert-butoxide has a conjugate acid pKa of 18. This makes it 1018 more basic, which is a whole different level of “strong base.” ◦ Using these much stronger bases, vinyl halides can form alkynes, and aryl halides can form benzynes. Alkynes are stable prod ...
Chpt 23Final7e
... The stereochemistry of the product will be determined by the stereochemistry of the starting material; if the product is racemic, the starting material must have been racemic as well. Problem 23.11 How might you bring about this conversion? OH CH3NO2, KOH H2,Pt O ethanol CH2NO2 (Aldol reaction) ...
... The stereochemistry of the product will be determined by the stereochemistry of the starting material; if the product is racemic, the starting material must have been racemic as well. Problem 23.11 How might you bring about this conversion? OH CH3NO2, KOH H2,Pt O ethanol CH2NO2 (Aldol reaction) ...
Aromatic amines The
... A Nitrogen, containing a lone pair is the key atom Resembles Ammonia where one or more H’s Are replaced by alkyl groups The lone pair participates in the reactivity Of amines Amines are a core part of ‘amino acids’ ...
... A Nitrogen, containing a lone pair is the key atom Resembles Ammonia where one or more H’s Are replaced by alkyl groups The lone pair participates in the reactivity Of amines Amines are a core part of ‘amino acids’ ...
$doc.title
... (in principle but not in pracHce) : the lone pair of electrons is the fourth subsHtuent • Most amines that have 3 different subsHtuents on N cannot be resolved because the molecules interconvert by ...
... (in principle but not in pracHce) : the lone pair of electrons is the fourth subsHtuent • Most amines that have 3 different subsHtuents on N cannot be resolved because the molecules interconvert by ...
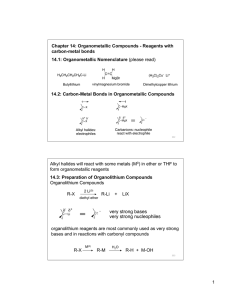
Organometallic Compounds - Reagents
... to a starting compound using known and reliable reactions. “it is a problem solving technique for transforming the structure of a synthetic target molecule (TM) to a sequence of progressively simpler structures along the pathway which ultimately leads to simple or commercially available starting mat ...
... to a starting compound using known and reliable reactions. “it is a problem solving technique for transforming the structure of a synthetic target molecule (TM) to a sequence of progressively simpler structures along the pathway which ultimately leads to simple or commercially available starting mat ...
Derivatization of polar compounds for GC - Sigma
... • This can be done with gentle heating and/or under a stream of dry nitrogen •If there is high humidity in the room, it may be helpful to store syringes, vials, etc. in a dry box •Silyl reagents are used in excess and can tolerate very small amounts of moisture – but still try to keep things dry! •C ...
... • This can be done with gentle heating and/or under a stream of dry nitrogen •If there is high humidity in the room, it may be helpful to store syringes, vials, etc. in a dry box •Silyl reagents are used in excess and can tolerate very small amounts of moisture – but still try to keep things dry! •C ...
Montmorillonite: An efficient, heterogeneous and
... renewed interest has been shown in the use of natural and synthetic smectitic clays as highly selective acid catalysts (e.g., Adams et al., 1978, 1979a, 1979b; Ballantine et al., 1981a, 1981b). Clay catalysts have been shown to contain both Brönsted and Lewis acid sites [4, 5] with the Bronsted site ...
... renewed interest has been shown in the use of natural and synthetic smectitic clays as highly selective acid catalysts (e.g., Adams et al., 1978, 1979a, 1979b; Ballantine et al., 1981a, 1981b). Clay catalysts have been shown to contain both Brönsted and Lewis acid sites [4, 5] with the Bronsted site ...
Hofmann–Löffler reaction

The Hofmann–Löffler reaction (also referred to as Hofmann–Löffler–Freytag reaction, Löffler–Freytag reaction, Löffler–Hofmann reaction, as well as Löffler's method) is an organic reaction in which a cyclic amine 2 (pyrrolidine or, in some cases, piperidine) is generated by thermal or photochemical decomposition of N-halogenated amine 1 in the presence of a strong acid (concentrated sulfuric acid or concentrated CF3CO2H). The Hofmann–Löffler–Freytag reaction proceeds via an intramolecular hydrogen atom transfer to a nitrogen-centered radical and is an example of a remote intramolecular free radical C–H functionalization.