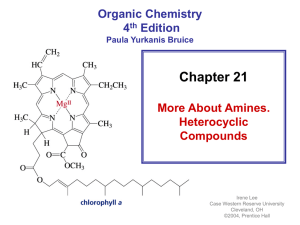
Chapter 12 Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation
... A ketone is formed by the first molar equivalent of Grignard reagent and this immediately reacts with a second equivalent to produce the alcohol The final product contains two identical groups at the alcohol carbon that are both derived from the Grignard reagent ...
... A ketone is formed by the first molar equivalent of Grignard reagent and this immediately reacts with a second equivalent to produce the alcohol The final product contains two identical groups at the alcohol carbon that are both derived from the Grignard reagent ...
Chapter 1-
... A ketone is formed by the first molar equivalent of Grignard reagent and this immediately reacts with a second equivalent to produce the alcohol The final product contains two identical groups at the alcohol carbon that are both derived from the Grignard reagent ...
... A ketone is formed by the first molar equivalent of Grignard reagent and this immediately reacts with a second equivalent to produce the alcohol The final product contains two identical groups at the alcohol carbon that are both derived from the Grignard reagent ...
19.19 Summary
... Esters occur naturally or are prepared from alcohols by Fischer esterification or by acylation with acyl chlorides or acid anhydrides (see Table 19.3). Esters are polar and have higher boiling points than alkanes of comparable size and shape. Esters don’t form hydrogen bonds to other ester molecules ...
... Esters occur naturally or are prepared from alcohols by Fischer esterification or by acylation with acyl chlorides or acid anhydrides (see Table 19.3). Esters are polar and have higher boiling points than alkanes of comparable size and shape. Esters don’t form hydrogen bonds to other ester molecules ...
Topic 3 The chemistry of life
... Topic 2 Molecular Biology Review **Review all the “understanding” statements at the beginning of each section. Key facts ...
... Topic 2 Molecular Biology Review **Review all the “understanding” statements at the beginning of each section. Key facts ...
FINAL EXAM Spring 2012
... A) 2SO3 (g) → 2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) B) Ag+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) → AgCl (s) C) CaO (s) + CO2 (g) → CaCO3 (s) D) N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) → 2NH3 (g) E) H2O (l) → H2O (s) 5) Consider the oxidation of SO2(g) to form SO3(g) in the presence of NO(g): ...
... A) 2SO3 (g) → 2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) B) Ag+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) → AgCl (s) C) CaO (s) + CO2 (g) → CaCO3 (s) D) N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) → 2NH3 (g) E) H2O (l) → H2O (s) 5) Consider the oxidation of SO2(g) to form SO3(g) in the presence of NO(g): ...
Lecture Resource ()
... The leaving group of a protonated amine cannot dissociate to form a carbocation or be replaced by a halide ion ...
... The leaving group of a protonated amine cannot dissociate to form a carbocation or be replaced by a halide ion ...
Seminar_1 1. Classification and nomenclature of organic
... Whilst many of the alkanes present in crude oil are aliphatic, having straight–or branched–chain molecules, some of them form rings – they are alicyclic. These compounds are denoted as cycloalkanes. These cycloalkanes have the general formula CnH2n instead of CnH2n+2 for the chain molecules. Cycloal ...
... Whilst many of the alkanes present in crude oil are aliphatic, having straight–or branched–chain molecules, some of them form rings – they are alicyclic. These compounds are denoted as cycloalkanes. These cycloalkanes have the general formula CnH2n instead of CnH2n+2 for the chain molecules. Cycloal ...
Group 2 - UC Davis Canvas
... a formal charge of +1. The oxygen–oxygen bond order is between 1 and 2. Although many resonance structures can be drawn for SO2, in the most important structure, the formal charge on the S atom is zero and the sulfur–oxygen bonds are double bonds. 109. ∆H fo = 639 kJ mol−1. The formation reaction is ...
... a formal charge of +1. The oxygen–oxygen bond order is between 1 and 2. Although many resonance structures can be drawn for SO2, in the most important structure, the formal charge on the S atom is zero and the sulfur–oxygen bonds are double bonds. 109. ∆H fo = 639 kJ mol−1. The formation reaction is ...
FUNCTIONAL GROUPS ORGANIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING
... • Hydrogen bonding with water? O • Solubility in water? • Boiling point? O ...
... • Hydrogen bonding with water? O • Solubility in water? • Boiling point? O ...
PHYSICAL SCIENCE PAPER 2 QUESTIONS SECTION A
... The most common silver artifacts recovered from shipwrecks are “silver” coins. In the 17th19th centuries, there were many Dutch East Indiaman wrecks around the African coast. The silver coins recovered by treasure hunters have been found to contain between 95% silver to 60% silver. Other major eleme ...
... The most common silver artifacts recovered from shipwrecks are “silver” coins. In the 17th19th centuries, there were many Dutch East Indiaman wrecks around the African coast. The silver coins recovered by treasure hunters have been found to contain between 95% silver to 60% silver. Other major eleme ...
packet 1, 2325 key
... Benzyl alcohol (MW = 108 g/mol) was reacted under different conditions to generate products A-C. The IRs are shown for products A-C. The value of the molecular ion peak is given along with the intensity ratio (relative to the parent peak) of the M+2 peak. Indicate the ...
... Benzyl alcohol (MW = 108 g/mol) was reacted under different conditions to generate products A-C. The IRs are shown for products A-C. The value of the molecular ion peak is given along with the intensity ratio (relative to the parent peak) of the M+2 peak. Indicate the ...
This is an author version of the contribution published on: Questa è
... in the synthesis of neryl acetate, showed that the catalytic activity decreased slightly only after EMImMeSO3 and BMImMeSO3 had been used four times. Fairly good yields could still be obtained even in the 5th recycle. This indicates that these ILs were sufficiently stable to be recycled as catalysts ...
... in the synthesis of neryl acetate, showed that the catalytic activity decreased slightly only after EMImMeSO3 and BMImMeSO3 had been used four times. Fairly good yields could still be obtained even in the 5th recycle. This indicates that these ILs were sufficiently stable to be recycled as catalysts ...
Oxidation of Cyclohexanol to Cyclohexanone Notes
... 8. Cyclohexanol and cyclohexanone have different solubilities in water. This allows the product to be isolated without distillation. The roughly 2 mL of cyclohexanol is soluble in the 30 mL of bleach (sodium hypochlorite in water) and acetic acid. When bleach and cyclohexanol are mixed, one homogeno ...
... 8. Cyclohexanol and cyclohexanone have different solubilities in water. This allows the product to be isolated without distillation. The roughly 2 mL of cyclohexanol is soluble in the 30 mL of bleach (sodium hypochlorite in water) and acetic acid. When bleach and cyclohexanol are mixed, one homogeno ...
ALDEHYDES , KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
... 1. From acyl chloride:(Rosenmund’s Reduction) Acid chlorides react with hydrogen in presence of Pd supported on BaSO4, we get aldehydes. This reaction is called Rosenmund’s reduction. R-COCl + H2 Pd/BaSO4 R-CHO + HCl ...
... 1. From acyl chloride:(Rosenmund’s Reduction) Acid chlorides react with hydrogen in presence of Pd supported on BaSO4, we get aldehydes. This reaction is called Rosenmund’s reduction. R-COCl + H2 Pd/BaSO4 R-CHO + HCl ...
MOLES, MASS, and VOLUME OF A GAS
... What is the mass of the product? a) less than 10 g b) between 100 and 120 g c) exactly 120 g d) over 120 g What is true about the Chemical Properties of the product? a) the properties are more like chemical A b) the properties are more like chemical B ...
... What is the mass of the product? a) less than 10 g b) between 100 and 120 g c) exactly 120 g d) over 120 g What is true about the Chemical Properties of the product? a) the properties are more like chemical A b) the properties are more like chemical B ...
"Introduction" Kinetics in Process Chemistry: Case Studies Baran Group Meeting Mike DeMartino
... Excellent approach. Notably, Michael addition occurred at higher temperature than anticipated, and the combination of MOM group with tert-butyl ester provided excellent diastereoselectivity (>98%). Abandoned because later hydrogenation reduced aryl bromide. 2nd generation: Asymmetric enamine reducti ...
... Excellent approach. Notably, Michael addition occurred at higher temperature than anticipated, and the combination of MOM group with tert-butyl ester provided excellent diastereoselectivity (>98%). Abandoned because later hydrogenation reduced aryl bromide. 2nd generation: Asymmetric enamine reducti ...
What are the functions of biomolecules
... what are we made of? how do we work? why we react in a certain way? ...
... what are we made of? how do we work? why we react in a certain way? ...
Full answers
... A 1.0 L solution of 0.020 M lactic acid is added to 1.0 L of 0.020 M sodium hydroxide solution. Write the ionic equation for the reaction that occurs. HC3H5O3(aq) + OH-(aq) ! C3H5O3-(aq) + H2O(l) Is the resulting solution acidic, basic or neutral? Give a reason for your answer. All of the lactic aci ...
... A 1.0 L solution of 0.020 M lactic acid is added to 1.0 L of 0.020 M sodium hydroxide solution. Write the ionic equation for the reaction that occurs. HC3H5O3(aq) + OH-(aq) ! C3H5O3-(aq) + H2O(l) Is the resulting solution acidic, basic or neutral? Give a reason for your answer. All of the lactic aci ...
DETECTION OF ALCOHOLS, ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
... 6) Detection of ketone bodies and glucose in the urine using a diagnostic strip Principle: The test for ketone bodies is based on the Legal’s reaction principle. The indication zone contains an alkaline buffer mixed with sodium nitroprusside, whitch gives a purple colored product by a reaction with ...
... 6) Detection of ketone bodies and glucose in the urine using a diagnostic strip Principle: The test for ketone bodies is based on the Legal’s reaction principle. The indication zone contains an alkaline buffer mixed with sodium nitroprusside, whitch gives a purple colored product by a reaction with ...
X273/13/02
... 17. Iodide ions are oxidised by acidified nitrite ions according to the equation 2NO2– + 2I– + 4H+ → 2NO + I2 + 2H2O Addition of sodium ethanoate to the reaction mixture slows down the formation of iodine. The most likely explanation for this effect is that ethanoate ions A ...
... 17. Iodide ions are oxidised by acidified nitrite ions according to the equation 2NO2– + 2I– + 4H+ → 2NO + I2 + 2H2O Addition of sodium ethanoate to the reaction mixture slows down the formation of iodine. The most likely explanation for this effect is that ethanoate ions A ...
Class: 11 Subject: Chemistry Topic: Equilibrium No. of
... 13. Which one of the following gaseous equilibrium system has the unit, mol dm -3 for the equilibrium constant? A. H2 + I2 ƒ 2HI B. PCl5 ƒ PCl3 + Cl2 C. PCl3 + Cl2 ƒ PCl5 D. N2 + 3H2 ƒ 2NH3 ...
... 13. Which one of the following gaseous equilibrium system has the unit, mol dm -3 for the equilibrium constant? A. H2 + I2 ƒ 2HI B. PCl5 ƒ PCl3 + Cl2 C. PCl3 + Cl2 ƒ PCl5 D. N2 + 3H2 ƒ 2NH3 ...
Chemical Reactions PPT
... 3. Combustion Also known as _burning_. Always follows the same form: Compound containing C and H (& sometimes O) + O2 CO2 + H2O Note: In a combustion reaction, the compound always burns in oxygen gas and always releases carbon dioxide and water. ...
... 3. Combustion Also known as _burning_. Always follows the same form: Compound containing C and H (& sometimes O) + O2 CO2 + H2O Note: In a combustion reaction, the compound always burns in oxygen gas and always releases carbon dioxide and water. ...
pdfInt 2 Homework Unit 2 1 MB
... Scientists have been experimenting to find ways of reducing carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. One of these ways involves placing concrete balls on the sea bed. They hope that green plants called algae will grow on the balls and this will help to reduce the carbon dioxide level. Give a reason why the ...
... Scientists have been experimenting to find ways of reducing carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. One of these ways involves placing concrete balls on the sea bed. They hope that green plants called algae will grow on the balls and this will help to reduce the carbon dioxide level. Give a reason why the ...
Strychnine total synthesis

Strychnine total synthesis in chemistry describes the total synthesis of the complex biomolecule strychnine. The first reported method by the group of Robert Burns Woodward in 1954 is considered a classic in this research field. At the time it formed the natural conclusion to an elaborate process of molecular structure elucidation that started with the isolation of strychnine from the beans of Strychnos ignatii by Pierre Joseph Pelletier and Joseph Bienaimé Caventou in 1818. Major contributors to the entire effort were Sir Robert Robinson with over 250 publications and Hermann Leuchs with another 125 papers in a time span of 40 years. Robinson was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1947 for his work on alkaloids, strychnine included. The process of chemical identification was completed with publications in 1946 by Robinson and later confirmed by Woodward in 1947. X-ray structures establishing the absolute configuration became available between 1947 and 1951 with publications from J. M. Bijvoet and J.H. Robertson .Woodward published a very brief account on the strychnine synthesis in 1954 (just 3 pages) and a lengthy one (42 pages) in 1963.Many more methods exist and reported by the research groups of Magnus, Overman, Kuehne, Rawal, Bosch, Vollhardt, Mori, Shibasaki, Li, Fukuyama Vanderwal and MacMillan. Synthetic (+)-strychnine is also known. Racemic synthesises were published by Padwa in 2007 and in 2010 by Andrade and by Reissig.In his 1963 publication Woodward quoted Sir Robert Robinson who said for its molecular size it is the most complex substance known.