1-14 Amines Amides
... Again, the nitrogen atom is attached to the number one carbon, so part of the name is 1-aminoethane. Since there are two methyl groups attached to the nitrogen, we add N,N-dimethyl- to the front of the name. Note each methyl group gets its own locator, thus there are two Ns in the name. The IUPAC na ...
... Again, the nitrogen atom is attached to the number one carbon, so part of the name is 1-aminoethane. Since there are two methyl groups attached to the nitrogen, we add N,N-dimethyl- to the front of the name. Note each methyl group gets its own locator, thus there are two Ns in the name. The IUPAC na ...
Are You suprised ?
... For the following reaction 2 NH3(g) ⇌ N2(g) + 3 H2(g) if, Kc = 2.6×10-5 mol2 L-2 at 127oC. Then Kp at the same temperature is: A) 2.8×10-2 atm2 C) 8.2×10-4 atm2 ...
... For the following reaction 2 NH3(g) ⇌ N2(g) + 3 H2(g) if, Kc = 2.6×10-5 mol2 L-2 at 127oC. Then Kp at the same temperature is: A) 2.8×10-2 atm2 C) 8.2×10-4 atm2 ...
phenol - Knockhardy
... • it is a stronger acid than aliphatic alcohols • the aromatic ring helps weaken the O-H bond and stabilises the resulting anion • it dissolves very slightly in water to form a weak acidic solution C6H5OH(aq) ...
... • it is a stronger acid than aliphatic alcohols • the aromatic ring helps weaken the O-H bond and stabilises the resulting anion • it dissolves very slightly in water to form a weak acidic solution C6H5OH(aq) ...
Semester 2 Review
... 63. For the reaction: Heat + H2(g) + I2(g) 2HI(g) A. How will an increase in temperature change the concentration of hydrogen gas? ________ B. How will an increase in pressure affect the system? ___________________ C. Which direction will the addition of iodine gas shift the system? ___________ ...
... 63. For the reaction: Heat + H2(g) + I2(g) 2HI(g) A. How will an increase in temperature change the concentration of hydrogen gas? ________ B. How will an increase in pressure affect the system? ___________________ C. Which direction will the addition of iodine gas shift the system? ___________ ...
Introduction to enzymes
... rates. 2. Kinetics alone will not give a chemical mechanism but combined with chemical and structural data mechanisms can be elucidated. 3. Kinetics help understand the enzymes role in metabolic pathways. 4. Under “proper” conditions rates are proportional to enzyme concentrations and these can be d ...
... rates. 2. Kinetics alone will not give a chemical mechanism but combined with chemical and structural data mechanisms can be elucidated. 3. Kinetics help understand the enzymes role in metabolic pathways. 4. Under “proper” conditions rates are proportional to enzyme concentrations and these can be d ...
The Mole Ratio · the ratio between the molar amounts of any two
... another reactant or product in the reaction ...
... another reactant or product in the reaction ...
chapters 16-17 test re
... 3. _______ A low Ea means that relatively few collisions will have the required energy to produce the activated complex, and the reaction rate is fast. 4. _______ Catalysts are enzymes that aren’t consumed in a chemical reaction, but they raise the reaction rate by lowering the Ea. 5. _______ To cal ...
... 3. _______ A low Ea means that relatively few collisions will have the required energy to produce the activated complex, and the reaction rate is fast. 4. _______ Catalysts are enzymes that aren’t consumed in a chemical reaction, but they raise the reaction rate by lowering the Ea. 5. _______ To cal ...
Dehydration of 2-methylcyclohexanol
... The Experiment An alcohol is dehydrated and an alkene is formed. In today’s experiment, 2methylcyclohexanol is reacted with phosphoric acid, and three different products can result. The overall reaction is shown below. ...
... The Experiment An alcohol is dehydrated and an alkene is formed. In today’s experiment, 2methylcyclohexanol is reacted with phosphoric acid, and three different products can result. The overall reaction is shown below. ...
Question paper - Edexcel
... SECTION A Answer ALL the questions in this section. You should aim to spend no more than 20 minutes on this section. For each question, select one answer from A to D and put a cross in the box . and then mark your new answer with If you change your mind, put a line through the box a cross . 1 Metho ...
... SECTION A Answer ALL the questions in this section. You should aim to spend no more than 20 minutes on this section. For each question, select one answer from A to D and put a cross in the box . and then mark your new answer with If you change your mind, put a line through the box a cross . 1 Metho ...
Chemical Reactions and Equations
... 3. Displacement reaction 4. Double displacement reactions 5. Oxidation and Reduction reactions What are ‘Combination Reactions’? When two or more substances (elements or compounds) combine to form a single product, the reactions are called ‘Combination Reactions’. Generally, Combination Reactions ar ...
... 3. Displacement reaction 4. Double displacement reactions 5. Oxidation and Reduction reactions What are ‘Combination Reactions’? When two or more substances (elements or compounds) combine to form a single product, the reactions are called ‘Combination Reactions’. Generally, Combination Reactions ar ...
Chemical Reactions and Equations
... What is a ‘Reaction’? Reaction is a term used for depicting a change or transformation in which a substance decomposes, combines with other substances, or interchanges constituents with other substances. What is a ‘Chemical Reaction’? A chemical change is always accompanied by a chemical reaction. a ...
... What is a ‘Reaction’? Reaction is a term used for depicting a change or transformation in which a substance decomposes, combines with other substances, or interchanges constituents with other substances. What is a ‘Chemical Reaction’? A chemical change is always accompanied by a chemical reaction. a ...
Chem 174-Lecture 15a..
... and also changes the reactivity of the metal center based on X Variations of the cyclopentadiene moiety leads to the formation of catalyst that yield different forms of polypropylene (atatic, isotactic, syndiotactic) ...
... and also changes the reactivity of the metal center based on X Variations of the cyclopentadiene moiety leads to the formation of catalyst that yield different forms of polypropylene (atatic, isotactic, syndiotactic) ...
notes 11/28/16 Monday
... laboratory synthesis, however, dehydrogenation is not practical, and cost is not as large a factor as it would be in industry. Most labs would have chromium trioxide or sodium dichromate available, and the chromic acid oxidation would be simple. PCC and the Swern oxidation would also work, although ...
... laboratory synthesis, however, dehydrogenation is not practical, and cost is not as large a factor as it would be in industry. Most labs would have chromium trioxide or sodium dichromate available, and the chromic acid oxidation would be simple. PCC and the Swern oxidation would also work, although ...
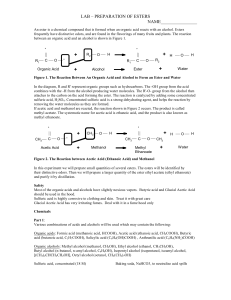
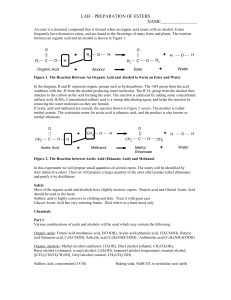
lab – preparation of esters name
... Fill a 400-mL beaker about half full with water. Heat the water to boiling, and then turn off the flame or the hot plate. 2. Prepare the ester. Place 10 drops of one of the organic acids in a dry test tube. If using a solid acid, use a small spatula full, about 0.08 g. Add 10 drops of one of the alc ...
... Fill a 400-mL beaker about half full with water. Heat the water to boiling, and then turn off the flame or the hot plate. 2. Prepare the ester. Place 10 drops of one of the organic acids in a dry test tube. If using a solid acid, use a small spatula full, about 0.08 g. Add 10 drops of one of the alc ...
An ester is a chemical compound that is formed when an organic
... Fill a 400-mL beaker about half full with water. Heat the water to boiling, and then turn off the flame or the hot plate. 2. Prepare the ester. Place 10 drops of one of the organic acids in a dry test tube. If using a solid acid, use a small spatula full, about 0.08 g. Add 10 drops of one of the alc ...
... Fill a 400-mL beaker about half full with water. Heat the water to boiling, and then turn off the flame or the hot plate. 2. Prepare the ester. Place 10 drops of one of the organic acids in a dry test tube. If using a solid acid, use a small spatula full, about 0.08 g. Add 10 drops of one of the alc ...
Slides, Set 12
... Upon cyclization, the carbonyl carbon becomes chiral and is referred to as the anomeric carbon. In the α-form, the anomeric OH (O1) is on the opposite side of the ring from the CH2OH group, and in the β-form, O1 is on the same side. The α- and β-forms are referred to as anomers or anomeric pairs, an ...
... Upon cyclization, the carbonyl carbon becomes chiral and is referred to as the anomeric carbon. In the α-form, the anomeric OH (O1) is on the opposite side of the ring from the CH2OH group, and in the β-form, O1 is on the same side. The α- and β-forms are referred to as anomers or anomeric pairs, an ...
f8560d95306293b
... and reeducing agents. Cleavage takes place under quite vigorous conditions ...
... and reeducing agents. Cleavage takes place under quite vigorous conditions ...
king fahd university of petroleum and minerals chemistry
... the following initial rate data were collected at a constant temperature. Determine the ...
... the following initial rate data were collected at a constant temperature. Determine the ...
Organic Chemistry & Polymers
... flesh) H2N-(CH2)4-NH2 Amines are biologically important for example some illicit drugs like amphetamine & methamphetamine are amines and amino acids & proteins contain amines/amides. Nylon is a polyamide. Carboxylic acid + amine = amide + H2O ...
... flesh) H2N-(CH2)4-NH2 Amines are biologically important for example some illicit drugs like amphetamine & methamphetamine are amines and amino acids & proteins contain amines/amides. Nylon is a polyamide. Carboxylic acid + amine = amide + H2O ...
Chapter 18 – Carbonyl Compounds II (Last Chapter we mostly talk
... chemistry.) (Because they protect functional groups from reacting the groups that are added are called protecting groups. So in the case above, the ketal would be ...
... chemistry.) (Because they protect functional groups from reacting the groups that are added are called protecting groups. So in the case above, the ketal would be ...
Survey on Conditions Catalysis of Chemical Reactions
... C5H5NH(+)CrO3Cl(–), commonly named by the acronym PCC and used in methylene chloride solution. In each case a chromate ester of the alcohol substrate is believed to be an intermediate, which undergoes an E2-like elimination to the carbonyl product. The oxidation state of carbon increases by 2, while ...
... C5H5NH(+)CrO3Cl(–), commonly named by the acronym PCC and used in methylene chloride solution. In each case a chromate ester of the alcohol substrate is believed to be an intermediate, which undergoes an E2-like elimination to the carbonyl product. The oxidation state of carbon increases by 2, while ...
synthpp - Knockhardy
... the reagents required to convert one functional group into another the presence of other functional groups - in case also they react the conditions required - temperature, pressure, catalyst the rate of the reaction the yield - especially important for equilibrium reactions atom economy safety - tox ...
... the reagents required to convert one functional group into another the presence of other functional groups - in case also they react the conditions required - temperature, pressure, catalyst the rate of the reaction the yield - especially important for equilibrium reactions atom economy safety - tox ...
Strychnine total synthesis

Strychnine total synthesis in chemistry describes the total synthesis of the complex biomolecule strychnine. The first reported method by the group of Robert Burns Woodward in 1954 is considered a classic in this research field. At the time it formed the natural conclusion to an elaborate process of molecular structure elucidation that started with the isolation of strychnine from the beans of Strychnos ignatii by Pierre Joseph Pelletier and Joseph Bienaimé Caventou in 1818. Major contributors to the entire effort were Sir Robert Robinson with over 250 publications and Hermann Leuchs with another 125 papers in a time span of 40 years. Robinson was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1947 for his work on alkaloids, strychnine included. The process of chemical identification was completed with publications in 1946 by Robinson and later confirmed by Woodward in 1947. X-ray structures establishing the absolute configuration became available between 1947 and 1951 with publications from J. M. Bijvoet and J.H. Robertson .Woodward published a very brief account on the strychnine synthesis in 1954 (just 3 pages) and a lengthy one (42 pages) in 1963.Many more methods exist and reported by the research groups of Magnus, Overman, Kuehne, Rawal, Bosch, Vollhardt, Mori, Shibasaki, Li, Fukuyama Vanderwal and MacMillan. Synthetic (+)-strychnine is also known. Racemic synthesises were published by Padwa in 2007 and in 2010 by Andrade and by Reissig.In his 1963 publication Woodward quoted Sir Robert Robinson who said for its molecular size it is the most complex substance known.